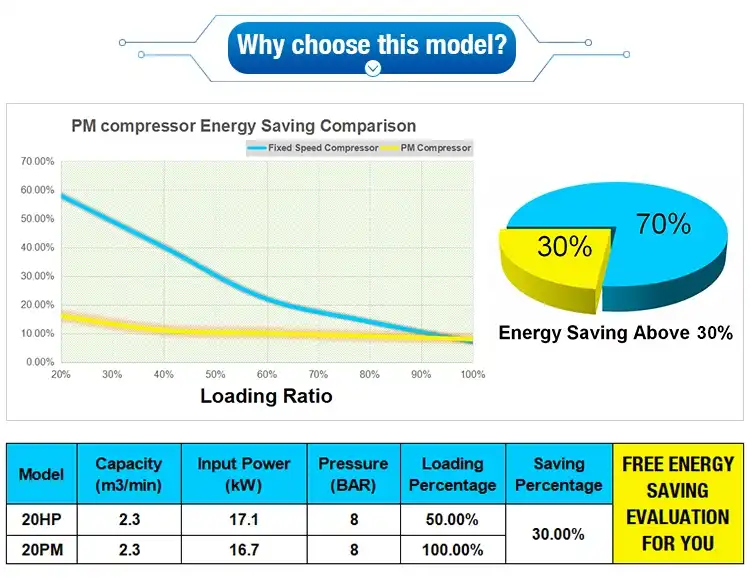
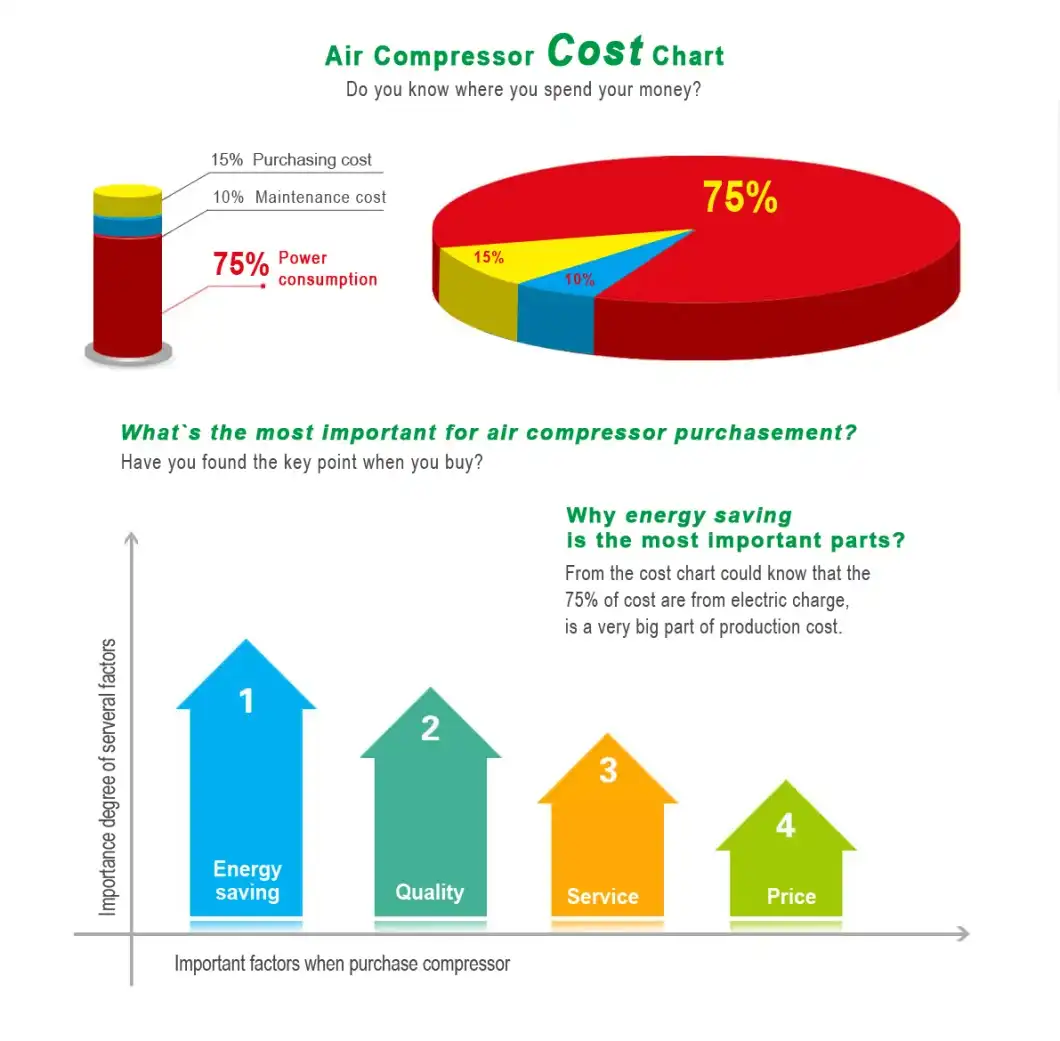
Product Description
Company Profile
ZheZheJiang nshine Industrial Technology Co., Ltd., as a professional overseas sales team and sales service team, is committed to providing customers with piston compressor and diaphragm compressor solutions. The company adheres to the concept of one-stop service and provides customers with a complete set of air compressor equipment solutions.
Product Description
Our products mainly include 2 series: piston compressors and diaphragm compressors, covering more than 30 types of products. These products are widely used in fields such as hydrogen energy, semiconductors, chemicals, petrochemicals, and natural gas transportation. We have over 3000 industrial enterprise users, covering all aspects of the hydrogen energy industry chain, including hydrogen production, filling, and hydrogen refueling station compressors, and providing a complete set of gas compression equipment solutions. As an efficient, energy-saving, environmentally friendly, and reliable compressor type, diaphragm compressors have also achieved great success and have been widely used in various fields.
Product Description:
Piston compressors are a type of positive displacement compressor that are commonly used in the chemical industry for a variety of applications. These compressors work by using a piston and cylinder to compress gas or air, which creates pressure and allows it to be transported through pipelines or used in other processes.
Diaphragm compressor :according to the needs of the user, choose the right type of compressor to meet the needs of the user. The diaphragm of the metal diaphragm compressor completely separates the gas from the hydraulic oil system to ensure the purity of the gas and no pollution to the gas. At the same time, advanced manufacturing technology and accurate membrane cavity design technology are adopted to ensure the service life of the diaphragm compressor diaphragm. No pollution: the metal diaphragm group completely separates the process gas from the hydraulic oil and lubricating oil parts to ensure the gas purity.
In the chemical industry, piston compressors are used for a variety of functions, including:
Gas compression – Piston compressors are used to compress natural gas, hydrogen, and other gases used in chemical processes. product-list-1.html product-list-1.html
Pneumatic conveying – Piston compressors are used to transport materials in a powdered or granular form through pipelines.
Refrigeration – Piston compressors are used in refrigeration systems to compress refrigerant gases, which are then used to cool industrial processes and equipment.
Process air compression – Piston compressors are used to compress air for use in chemical processes, such as in pneumatic equipment and air-powered tools.
Piston compressors are popular in the chemical industry because they are reliable, efficient, and can handle specific types of gases and air with ease. Additionally, they require minimal maintenance and can operate at high pressures, making them suitable for many applications
When choosing a piston compressor for use in the chemical industry, it is important to consider factors such as:
Type of gas or air being compressed – Different types of gases and air require different types of compression.
Required flow rate and pressure – The capacity and pressure capabilities of the compressor must meet the requirements of the application.
Environmental conditions – Factors such as temperature, humidity, and altitude can affect the performance of the compressor.
Maintenance requirements – The frequency and complexity of maintenance and servicing should be considered when selecting a compressor.
Overall, piston compressors are an important tool in the chemical industry, providing reliable and efficient compression for a variety of applications. Choosing the right compressor for the specific application is critical to ensuring optimal performance and efficiency.
Piston compressor model:
1. Single-stage piston compressor
Single-stage piston compressor is the simplest compressor, mainly composed of cylinder, piston, crankshaft, connecting rod, valve and other components. It has the advantages of simple structure, easy maintenance and low price, so it is widely used in low-pressure air compression, nitrogen and oxygen production and other occasions. Parameters such as air output volume, air outlet pressure, and rotational speed need to be considered when selecting models.
Common models include: W-1.8/5, W-3.6/5, W-4/5, W-6/5, etc.
2. Two-stage piston compressor
A two-stage piston compressor consists of 2 compressors. The first-stage compressor compresses the gas to a higher intermediate pressure, and then is cooled by the cooler and sent to the second-stage compressor to compress it again to the final pressure. Compared with single-stage piston compressors, two-stage piston compressors have higher outlet pressure, higher efficiency, and wider application range.
Common models include: W-1/3-2/3, W-2.5/5-2.5/5, W-3/6-3.6/6, etc.
3. High-pressure piston compressor
High-pressure piston compressors are mainly used to compress high-pressure gases, such as natural gas, hydrogen, helium, etc. It has a complex structure and needs to be equipped with auxiliary equipment such as gas coolers, gas inlet filters, pressure controllers, etc. It also has the advantages of high outlet pressure, low energy consumption, and smooth operation.
Common models include: W-3/20, W-6/30, W-9/30, etc.
Introduction to the meaning of the model number of diaphragm compressor:
For example: 1G3V-300/4-15 AND GV3-310/22-62
1G3V-300/4-15 each represents as follows:
“1” means double first-class product;
“G” indicates diaphragm compressor;
“3” indicates the 3rd series of the product manufacturer’s diaphragm compressor series, and does not indicate piston force; the larger the number, the greater the piston force.
“V” means V-shaped structure.
“3V” means there are main and auxiliary connecting rods, and the crankcase is split.
“300” indicates the amount of gas the compressor handles per hour under standard conditions;
“4” means the inlet pressure is 4kg/cm2 (ie 0.4MPa);
“15” means the exhaust pressure is 15kg/cm2 (ie 1.5MPa).
GV3-310/22-62 each represents as follows:
“G” indicates diaphragm compressor;
“V” means V-shaped structure.
“3” indicates the 3rd series of the product manufacturer’s diaphragm compressor series, and does not indicate piston force; the larger the number, the greater the piston force.
“V3” is another series, indicating a side-by-side structure of connecting rods and a one-piece crankcase.
Basic information:Piston compressor model parameters:
| Piston compressor model parameters | |||||||||
| Piston force | 800 | 500 | 320 | 250 | 160 | 100 | 65 | 45 | 30 |
| Types of compressed gas | Hydrogen, nitrogen, natural gas, ethylene, propylene, coal gas, hydrogen chloride, hydrogen fluoride, carbon dioxide, methyl chloride, carbon monoxide, acetylene ammonia, hydrogen monochloride, difluoromethane, tetrafluoroethylene, pentafluoroethylene, hexafluoroethylene, etc. | ||||||||
| discharge pressureMPa(G) | <=25 | <=30 | |||||||
| Compression levels | 1-4levels | 2-6levels | 1-3levels | ||||||
| Number of columns | 2–4 | 2–6 | 1–4 | ||||||
| Layout form/Type/Model | M/D | M/D | M/D | M/D | M/D | M/D/P | M/D/P | M/D/P | L/P |
| route(mm) | 280-360 | 240-320 | 180-240 | 200 | |||||
| Rotating speed(rpm) | 300-375 | 333-450 | 375-585 | 420-485 | |||||
| Maximum motor power(KW) | 5600 | 3600 | 3300 | 2700 | 1250 | 800 | 560 | 250 | 75 |
| skid mounted | non-skid mounted | skid mounted/non -skid mounted | |||||||
| Digital Analog Computing | yes | ||||||||
| systolic algorithm | yes | ||||||||
| test | According to the quality standard, chemical analysis, mechanical performance, flaw detection, hydrostatic test, airtight test and other inspections are carried out for each component | ||||||||
| Factory inspection | According to the quality standard, carry out no-load mechanical operation test | ||||||||
| Customer acceptance | Actual working conditions, 72-hour assessment and acceptance | ||||||||
| Application | Hydrogen energy, silicon, fluorine chemical industry, petrochemical industry, metallurgy, medicine, aerospace, nuclear power | ||||||||
Basic information:Diaphragm compressor model parameters
| Piston force | 250 | 160 | 110 | 80 | 60 | 45 | 35 | 45 | 10 |
| Types of compressed gas | Hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, helium, xenon, hydrogen chloride, hydrogen sulfide, nitrogen trifluoride, silicon tetrafluoride, silane | ||||||||
| Discharge pressureMPa(G) | <=100 | ||||||||
| Compression levels | 1-3levels | ||||||||
| Layout form/Type/Model | M/D | D/L | D/L/Z | V/Z | L/Z | L/Z | |||
| Route(mm) | 210 | 210/1/0 | 180 | 180 | 150 | 130 | 130 | 105 | 70 |
| Rotating speed(rpm) | 260 | 360-420 | |||||||
| Maximum motor power(KW) | 355 | 250 | 200 | 160 | 110 | 55 | 30 | 22 | 18.5 |
| Skid mounted | skid mounted | ||||||||
| Digital Analog Computing | yes | ||||||||
| Systolic algorithm | According to demand | ||||||||
| Test | According to the quality standard, chemical analysis, mechanical performance, flaw detection, hydrostatic test, airtight test and other inspections are carried out for each component | ||||||||
| Factory inspection | Carry out nitrogen or air full-load mechanical operation test according to quality requirements | ||||||||
| Customer acceptance | Actual working conditions, 72-hour assessment and acceptance | ||||||||
| Application | Hydrogen energy, silicon, fluorine chemical industry, petrochemical industry, metallurgy, medicine, aerospace, nuclear power | ||||||||
Detailed Photos
After Sales Service
We have an independent service operation and maintenance team, providing customers with various support and services, including technical support, debugging services, spare parts supply, renovation and upgrading, and major maintenance. We always adhere to the principle of customer-centrism, ensuring the safe and stable operation of customer equipment. Our service team is committed to providing reliable support for customers’ operations 24/7.
/* March 10, 2571 17:59:20 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | 12 Month |
|---|---|
| Warranty: | 12 Month |
| Lubrication Style: | Lubricated |
.shipping-cost-tm .tm-status-off{background: none;padding:0;color: #1470cc}
|
Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
about shipping cost and estimated delivery time. |
|---|
| Payment Method: |
|
|---|---|
|
Initial Payment Full Payment |
| Currency: | US$ |
|---|
| Return&refunds: | You can apply for a refund up to 30 days after receipt of the products. |
|---|
.webp)
Can Gas Air Compressors Be Used for Well Drilling?
Gas air compressors can be used for well drilling, and they are commonly employed in drilling operations. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Air Drilling Method:
Gas air compressors are often utilized in the air drilling method, also known as pneumatic drilling. In this drilling technique, compressed air is used to create a high-velocity airflow that carries the drill cuttings to the surface. The high-pressure air also aids in cooling the drill bit and providing additional force for efficient drilling.
2. Benefits of Gas Air Compressors:
Gas air compressors offer several advantages for well drilling:
- Portability: Gas air compressors can be easily transported to remote drilling sites, allowing for flexibility in well location.
- Power: Gas air compressors provide high-pressure air output, which is essential for effective drilling in various geological formations.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Gas air compressors can be more cost-effective compared to other drilling methods, as they eliminate the need for drilling mud and associated disposal costs.
- Environmental Considerations: Air drilling with gas compressors produces minimal waste and does not require the use of potentially harmful drilling fluids, making it an environmentally friendly option.
3. Compressor Selection:
When selecting a gas air compressor for well drilling, several factors should be considered:
- Pressure and Flow Requirements: Evaluate the pressure and flow requirements of the drilling operation to ensure that the gas air compressor can deliver the necessary air output.
- Compressor Size and Power: Choose a compressor with adequate size and power output to match the drilling demands. Factors such as borehole depth, drill bit type, and drilling speed will influence the compressor’s power requirements.
- Portability: Consider the portability features of the gas air compressor, such as its weight, dimensions, and mobility options, to facilitate transportation to drilling sites.
4. Safety Considerations:
It is essential to follow safety guidelines when using gas air compressors for well drilling. These may include proper ventilation to prevent the accumulation of exhaust fumes, adherence to equipment operating limits, and the use of personal protective equipment (PPE) for drilling personnel.
5. Other Considerations:
While gas air compressors are commonly used for well drilling, it is worth noting that the suitability of a gas air compressor for a specific drilling project depends on various factors such as geological conditions, well depth, and drilling objectives. It is recommended to consult with drilling experts and professionals to determine the most suitable drilling method and equipment for a particular project.
In summary, gas air compressors can be effectively used for well drilling, particularly in the air drilling method. They offer portability, power, cost-effectiveness, and environmental advantages. Proper selection, considering pressure and flow requirements, as well as safety precautions, is crucial to ensure successful and safe drilling operations.
.webp)
What Are the Key Components of a Gas Air Compressor Control Panel?
A gas air compressor control panel typically consists of several key components. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Power Switch:
The power switch allows the operator to turn the compressor on or off. It is usually a toggle switch or a push-button switch located on the control panel.
2. Pressure Gauges:
Pressure gauges display the compressed air pressure at different stages of the compression process. Commonly, there are two pressure gauges: one to measure the incoming air pressure (suction pressure) and another to measure the outgoing compressed air pressure (discharge pressure).
3. Control Knobs or Buttons:
Control knobs or buttons are used to adjust and set various parameters of the compressor operation. These controls may include pressure settings, on/off timers, automatic start/stop functions, and other operational parameters specific to the compressor model.
4. Emergency Stop Button:
An emergency stop button is a critical safety feature that immediately shuts down the compressor in case of an emergency. Pressing the emergency stop button cuts off power to the compressor and stops its operation.
5. Motor Start/Stop Buttons:
Motor start and stop buttons allow the operator to manually start or stop the compressor motor. These buttons are used when manual control of the motor is required, such as during maintenance or troubleshooting.
6. Control Indicators:
Control indicators include various lights or LEDs that provide visual feedback about the compressor’s status and operation. These indicators may include power indicators, motor running indicators, pressure indicators, and fault indicators to signal any malfunctions or abnormal conditions.
7. Control Panel Display:
Some gas air compressors feature a control panel display that provides real-time information and feedback on the compressor’s performance. The display may show parameters such as operating pressure, temperature, maintenance alerts, fault codes, and other relevant information.
8. Start/Stop Control Circuit:
The start/stop control circuit is responsible for initiating and controlling the motor start and stop sequences. It typically includes relays, contactors, and other electrical components that enable the control panel to safely start and stop the compressor motor.
9. Safety and Protection Devices:
Gas air compressor control panels may incorporate safety and protection devices to safeguard the compressor and prevent potential damage or hazardous situations. These devices can include overload relays, thermal protection, pressure relief valves, and other safety features.
10. Control Panel Enclosure:
The control panel enclosure houses and protects the electrical components and wiring of the control panel. It provides insulation, protection from dust and moisture, and ensures the safety of the operator.
In summary, a gas air compressor control panel typically includes a power switch, pressure gauges, control knobs or buttons, emergency stop button, motor start/stop buttons, control indicators, control panel display (if applicable), start/stop control circuit, safety and protection devices, and a control panel enclosure. These components work together to monitor and control the compressor’s operation, ensure safety, and provide essential information to the operator.
.webp)
Are There Different Types of Gas Air Compressors Available?
Yes, there are different types of gas air compressors available, each designed to suit specific applications and requirements. These different types vary in terms of design, power source, configuration, and intended use. Here’s a detailed explanation of the various types of gas air compressors:
1. Reciprocating Gas Air Compressors:
Reciprocating gas air compressors, also known as piston compressors, use a reciprocating motion of one or more pistons to compress the air. These compressors are commonly used for small to medium-scale applications and are available in both single-stage and two-stage configurations. Single-stage compressors compress the air in a single stroke, while two-stage compressors use an additional cylinder for further compression, resulting in higher pressures.
2. Rotary Screw Gas Air Compressors:
Rotary screw gas air compressors utilize two interlocking helical screws to compress the air. These compressors are known for their continuous and efficient operation, making them suitable for demanding industrial applications. They are often used in industries such as manufacturing, construction, and automotive where a constant supply of compressed air is required.
3. Rotary Vane Gas Air Compressors:
Rotary vane gas air compressors use a rotor with sliding vanes to compress the air. As the rotor rotates, the vanes slide in and out, creating compression chambers that compress the air. These compressors are compact, reliable, and often used for smaller-scale applications or in situations where space is limited.
4. Centrifugal Gas Air Compressors:
Centrifugal gas air compressors operate by accelerating the air using a high-speed impeller. The accelerated air is then redirected into a diffuser, which converts the velocity energy into pressure energy. These compressors are commonly used for large-scale applications requiring high volumes of compressed air, such as in power plants, refineries, or chemical processing industries.
5. Oil-Free Gas Air Compressors:
Oil-free gas air compressors are designed to provide clean, oil-free compressed air. They feature special sealing mechanisms and materials to prevent oil contamination in the compressed air. These compressors are commonly used in industries where oil-free air is essential, such as food and beverage processing, pharmaceuticals, electronics manufacturing, and painting applications.
6. Portable Gas Air Compressors:
Portable gas air compressors are specifically designed for mobility and ease of transportation. These compressors often feature wheels, handles, or trailers for convenient movement. They are commonly used in construction sites, remote job locations, outdoor events, or other situations where compressed air is needed at different locations.
7. High-Pressure Gas Air Compressors:
High-pressure gas air compressors are designed to generate compressed air at elevated pressures. These compressors are used in applications that require air pressure higher than the standard range, such as in diving operations, breathing air systems, or specialized industrial processes.
8. Biogas Air Compressors:
Biogas air compressors are specifically designed to compress biogas, which is generated from the decomposition of organic matter. These compressors are used in biogas production facilities, landfills, wastewater treatment plants, or agricultural operations where biogas is produced and utilized as an energy source.
These are just a few examples of the different types of gas air compressors available. Each type has its own advantages and is suitable for specific applications based on factors such as required airflow, pressure, mobility, oil-free operation, and environmental considerations. It’s important to choose the appropriate type of gas air compressor based on the specific needs of the application to ensure optimal performance and efficiency.


editor by CX 2024-02-21
China Good quality Customized Multipurpose Displacement Reciprocating Diaphragm Piston Booster Gas Compressor with high quality
Product Description
Company Profile
ZheZheJiang nshine Industrial Technology Co., Ltd., as a professional overseas sales team and sales service team, is committed to providing customers with piston compressor and diaphragm compressor solutions. The company adheres to the concept of one-stop service and provides customers with a complete set of air compressor equipment solutions.
Product Description
Our products mainly include 2 series: piston compressors and diaphragm compressors, covering more than 30 types of products. These products are widely used in fields such as hydrogen energy, semiconductors, chemicals, petrochemicals, and natural gas transportation. We have over 3000 industrial enterprise users, covering all aspects of the hydrogen energy industry chain, including hydrogen production, filling, and hydrogen refueling station compressors, and providing a complete set of gas compression equipment solutions. As an efficient, energy-saving, environmentally friendly, and reliable compressor type, diaphragm compressors have also achieved great success and have been widely used in various fields.
Product Description:
Piston compressors are a type of positive displacement compressor that are commonly used in the chemical industry for a variety of applications. These compressors work by using a piston and cylinder to compress gas or air, which creates pressure and allows it to be transported through pipelines or used in other processes.
Diaphragm compressor :according to the needs of the user, choose the right type of compressor to meet the needs of the user. The diaphragm of the metal diaphragm compressor completely separates the gas from the hydraulic oil system to ensure the purity of the gas and no pollution to the gas. At the same time, advanced manufacturing technology and accurate membrane cavity design technology are adopted to ensure the service life of the diaphragm compressor diaphragm. No pollution: the metal diaphragm group completely separates the process gas from the hydraulic oil and lubricating oil parts to ensure the gas purity.
In the chemical industry, piston compressors are used for a variety of functions, including:
Gas compression – Piston compressors are used to compress natural gas, hydrogen, and other gases used in chemical processes. product-list-1.html product-list-1.html
Pneumatic conveying – Piston compressors are used to transport materials in a powdered or granular form through pipelines.
Refrigeration – Piston compressors are used in refrigeration systems to compress refrigerant gases, which are then used to cool industrial processes and equipment.
Process air compression – Piston compressors are used to compress air for use in chemical processes, such as in pneumatic equipment and air-powered tools.
Piston compressors are popular in the chemical industry because they are reliable, efficient, and can handle specific types of gases and air with ease. Additionally, they require minimal maintenance and can operate at high pressures, making them suitable for many applications
When choosing a piston compressor for use in the chemical industry, it is important to consider factors such as:
Type of gas or air being compressed – Different types of gases and air require different types of compression.
Required flow rate and pressure – The capacity and pressure capabilities of the compressor must meet the requirements of the application.
Environmental conditions – Factors such as temperature, humidity, and altitude can affect the performance of the compressor.
Maintenance requirements – The frequency and complexity of maintenance and servicing should be considered when selecting a compressor.
Overall, piston compressors are an important tool in the chemical industry, providing reliable and efficient compression for a variety of applications. Choosing the right compressor for the specific application is critical to ensuring optimal performance and efficiency.
Piston compressor model:
1. Single-stage piston compressor
Single-stage piston compressor is the simplest compressor, mainly composed of cylinder, piston, crankshaft, connecting rod, valve and other components. It has the advantages of simple structure, easy maintenance and low price, so it is widely used in low-pressure air compression, nitrogen and oxygen production and other occasions. Parameters such as air output volume, air outlet pressure, and rotational speed need to be considered when selecting models.
Common models include: W-1.8/5, W-3.6/5, W-4/5, W-6/5, etc.
2. Two-stage piston compressor
A two-stage piston compressor consists of 2 compressors. The first-stage compressor compresses the gas to a higher intermediate pressure, and then is cooled by the cooler and sent to the second-stage compressor to compress it again to the final pressure. Compared with single-stage piston compressors, two-stage piston compressors have higher outlet pressure, higher efficiency, and wider application range.
Common models include: W-1/3-2/3, W-2.5/5-2.5/5, W-3/6-3.6/6, etc.
3. High-pressure piston compressor
High-pressure piston compressors are mainly used to compress high-pressure gases, such as natural gas, hydrogen, helium, etc. It has a complex structure and needs to be equipped with auxiliary equipment such as gas coolers, gas inlet filters, pressure controllers, etc. It also has the advantages of high outlet pressure, low energy consumption, and smooth operation.
Common models include: W-3/20, W-6/30, W-9/30, etc.
Introduction to the meaning of the model number of diaphragm compressor:
For example: 1G3V-300/4-15 AND GV3-310/22-62
1G3V-300/4-15 each represents as follows:
“1” means double first-class product;
“G” indicates diaphragm compressor;
“3” indicates the 3rd series of the product manufacturer’s diaphragm compressor series, and does not indicate piston force; the larger the number, the greater the piston force.
“V” means V-shaped structure.
“3V” means there are main and auxiliary connecting rods, and the crankcase is split.
“300” indicates the amount of gas the compressor handles per hour under standard conditions;
“4” means the inlet pressure is 4kg/cm2 (ie 0.4MPa);
“15” means the exhaust pressure is 15kg/cm2 (ie 1.5MPa).
GV3-310/22-62 each represents as follows:
“G” indicates diaphragm compressor;
“V” means V-shaped structure.
“3” indicates the 3rd series of the product manufacturer’s diaphragm compressor series, and does not indicate piston force; the larger the number, the greater the piston force.
“V3” is another series, indicating a side-by-side structure of connecting rods and a one-piece crankcase.
Basic information:Piston compressor model parameters:
| Piston compressor model parameters | |||||||||
| Piston force | 800 | 500 | 320 | 250 | 160 | 100 | 65 | 45 | 30 |
| Types of compressed gas | Hydrogen, nitrogen, natural gas, ethylene, propylene, coal gas, hydrogen chloride, hydrogen fluoride, carbon dioxide, methyl chloride, carbon monoxide, acetylene ammonia, hydrogen monochloride, difluoromethane, tetrafluoroethylene, pentafluoroethylene, hexafluoroethylene, etc. | ||||||||
| discharge pressureMPa(G) | <=25 | <=30 | |||||||
| Compression levels | 1-4levels | 2-6levels | 1-3levels | ||||||
| Number of columns | 2–4 | 2–6 | 1–4 | ||||||
| Layout form/Type/Model | M/D | M/D | M/D | M/D | M/D | M/D/P | M/D/P | M/D/P | L/P |
| route(mm) | 280-360 | 240-320 | 180-240 | 200 | |||||
| Rotating speed(rpm) | 300-375 | 333-450 | 375-585 | 420-485 | |||||
| Maximum motor power(KW) | 5600 | 3600 | 3300 | 2700 | 1250 | 800 | 560 | 250 | 75 |
| skid mounted | non-skid mounted | skid mounted/non -skid mounted | |||||||
| Digital Analog Computing | yes | ||||||||
| systolic algorithm | yes | ||||||||
| test | According to the quality standard, chemical analysis, mechanical performance, flaw detection, hydrostatic test, airtight test and other inspections are carried out for each component | ||||||||
| Factory inspection | According to the quality standard, carry out no-load mechanical operation test | ||||||||
| Customer acceptance | Actual working conditions, 72-hour assessment and acceptance | ||||||||
| Application | Hydrogen energy, silicon, fluorine chemical industry, petrochemical industry, metallurgy, medicine, aerospace, nuclear power | ||||||||
Basic information:Diaphragm compressor model parameters
| Piston force | 250 | 160 | 110 | 80 | 60 | 45 | 35 | 45 | 10 |
| Types of compressed gas | Hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, helium, xenon, hydrogen chloride, hydrogen sulfide, nitrogen trifluoride, silicon tetrafluoride, silane | ||||||||
| Discharge pressureMPa(G) | <=100 | ||||||||
| Compression levels | 1-3levels | ||||||||
| Layout form/Type/Model | M/D | D/L | D/L/Z | V/Z | L/Z | L/Z | |||
| Route(mm) | 210 | 210/1/0 | 180 | 180 | 150 | 130 | 130 | 105 | 70 |
| Rotating speed(rpm) | 260 | 360-420 | |||||||
| Maximum motor power(KW) | 355 | 250 | 200 | 160 | 110 | 55 | 30 | 22 | 18.5 |
| Skid mounted | skid mounted | ||||||||
| Digital Analog Computing | yes | ||||||||
| Systolic algorithm | According to demand | ||||||||
| Test | According to the quality standard, chemical analysis, mechanical performance, flaw detection, hydrostatic test, airtight test and other inspections are carried out for each component | ||||||||
| Factory inspection | Carry out nitrogen or air full-load mechanical operation test according to quality requirements | ||||||||
| Customer acceptance | Actual working conditions, 72-hour assessment and acceptance | ||||||||
| Application | Hydrogen energy, silicon, fluorine chemical industry, petrochemical industry, metallurgy, medicine, aerospace, nuclear power | ||||||||
Detailed Photos
After Sales Service
We have an independent service operation and maintenance team, providing customers with various support and services, including technical support, debugging services, spare parts supply, renovation and upgrading, and major maintenance. We always adhere to the principle of customer-centrism, ensuring the safe and stable operation of customer equipment. Our service team is committed to providing reliable support for customers’ operations 24/7.
/* March 10, 2571 17:59:20 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | 12 Month |
|---|---|
| Warranty: | 12 Month |
| Lubrication Style: | Lubricated |
.shipping-cost-tm .tm-status-off{background: none;padding:0;color: #1470cc}
|
Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
about shipping cost and estimated delivery time. |
|---|
| Payment Method: |
|
|---|---|
|
Initial Payment Full Payment |
| Currency: | US$ |
|---|
| Return&refunds: | You can apply for a refund up to 30 days after receipt of the products. |
|---|
.webp)
Can Gas Air Compressors Be Used in Cold Weather Conditions?
Gas air compressors are generally designed to operate in a wide range of environmental conditions, including cold weather. However, there are certain considerations and precautions to keep in mind when using gas air compressors in cold weather conditions. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Cold Start-Up:
In cold weather, starting a gas air compressor can be more challenging due to the low temperatures affecting the engine’s performance. It is important to follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for cold start procedures, which may include preheating the engine, using a cold weather starting aid, or ensuring the proper fuel mixture. These measures help facilitate smooth start-up and prevent potential damage to the engine.
2. Fuel Type:
Consider the type of fuel used in the gas air compressor. Some fuels, such as gasoline, can be more susceptible to cold weather issues like vapor lock or fuel line freezing. In extremely cold conditions, it may be necessary to use a fuel additive or switch to a fuel type that is better suited for cold weather operation, such as winter-grade gasoline or propane.
3. Lubrication:
Cold temperatures can affect the viscosity of the oil used in the compressor’s engine. It is important to use the recommended oil grade suitable for cold weather conditions. Thicker oil can become sluggish and impede proper lubrication, while oil that is too thin may not provide adequate protection. Consult the manufacturer’s guidelines for the appropriate oil viscosity range for cold weather operation.
4. Moisture Management:
In cold weather, moisture can condense more readily in the compressed air system. It is crucial to properly drain the moisture from the compressor tank and ensure the air lines are free from any accumulated moisture. Failure to manage moisture can lead to corrosion, freezing of air lines, and decreased performance.
5. Protection from Freezing:
In extremely cold conditions, it is important to protect the gas air compressor from freezing. This may involve using insulated covers or enclosures, providing heat sources in the compressor area, or storing the compressor in a temperature-controlled environment when not in use. Taking measures to prevent freezing helps maintain proper operation and prevents potential damage to the compressor components.
6. Monitoring Performance:
Regularly monitor the performance of the gas air compressor in cold weather conditions. Pay attention to any changes in operation, such as reduced air pressure, increased noise, or difficulties in starting. Promptly address any issues and consult the manufacturer or a qualified technician if necessary.
By considering these factors and taking appropriate precautions, gas air compressors can be effectively used in cold weather conditions. However, it is important to consult the specific guidelines provided by the manufacturer for your compressor model, as they may have additional recommendations or specifications for cold weather operation.
.webp)
Can Gas Air Compressors Be Used for Natural Gas Compression?
Gas air compressors are not typically used for natural gas compression. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Different Compressed Gases:
Gas air compressors are specifically designed to compress atmospheric air. They are not typically designed or suitable for compressing natural gas. Natural gas, which is primarily composed of methane, requires specialized compressors designed to handle the unique properties and characteristics of the gas.
2. Safety Considerations:
Natural gas compression involves handling a flammable and potentially hazardous substance. Compressing natural gas requires specialized equipment that meets stringent safety standards to prevent leaks, minimize the risk of ignition or explosion, and ensure the safe handling of the gas. Gas air compressors may not have the necessary safety features or materials to handle natural gas safely.
3. Equipment Compatibility:
Natural gas compression systems typically include components such as gas compressors, gas coolers, separators, and control systems that are specifically designed and engineered for the compression and handling of natural gas. These components are built to withstand the specific demands and conditions associated with natural gas compression, including the high pressures and potential presence of impurities.
4. Efficiency and Performance:
Compressing natural gas requires specialized compressors that can handle the high-pressure ratios and volumetric flow rates associated with the gas. Gas air compressors are generally not designed to achieve the same compression ratios and performance levels required for natural gas compression. Using gas air compressors for natural gas compression would likely result in inefficient operation and suboptimal performance.
5. Regulatory Compliance:
Compressing natural gas is subject to various regulations and standards to ensure safety, environmental protection, and compliance with industry guidelines. These regulations often dictate specific requirements for equipment, materials, and operating procedures in natural gas compression systems. Gas air compressors may not meet these regulatory requirements for natural gas compression.
6. Industry Standards and Practices:
The natural gas industry has well-established standards and best practices for equipment selection, installation, and operation in gas compression systems. These standards are based on the specific requirements and characteristics of natural gas. Gas air compressors do not align with these industry standards and practices, which are essential for safe and efficient natural gas compression.
In summary, gas air compressors are not suitable for natural gas compression. Natural gas compression requires specialized equipment designed to handle the unique properties and safety considerations associated with the gas. Compressors specifically engineered for natural gas compression offer the necessary performance, safety features, and regulatory compliance required for efficient and reliable operation in natural gas compression systems.
.webp)
What Fuels Are Commonly Used in Gas Air Compressors?
Gas air compressors can be powered by various fuels depending on the specific model and design. The choice of fuel depends on factors such as availability, cost, convenience, and environmental considerations. Here’s a detailed explanation of the fuels commonly used in gas air compressors:
1. Gasoline:
Gasoline is a widely used fuel in gas air compressors, particularly in portable models. Gasoline-powered compressors are popular due to the widespread availability of gasoline and the convenience of refueling. Gasoline engines are generally easy to start, and gasoline is relatively affordable in many regions. However, gasoline-powered compressors may emit more exhaust emissions compared to some other fuel options.
2. Diesel:
Diesel fuel is another common choice for gas air compressors, especially in larger industrial models. Diesel engines are known for their efficiency and durability, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications. Diesel fuel is often more cost-effective than gasoline, and diesel-powered compressors typically offer better fuel efficiency and longer runtime. Diesel compressors are commonly used in construction sites, mining operations, and other industrial settings.
3. Natural Gas:
Natural gas is a clean-burning fuel option for gas air compressors. It is a popular choice in areas where natural gas infrastructure is readily available. Natural gas compressors are often used in natural gas processing plants, pipeline operations, and other applications where natural gas is abundant. Natural gas-powered compressors offer lower emissions compared to gasoline or diesel, making them environmentally friendly.
4. Propane:
Propane, also known as liquefied petroleum gas (LPG), is commonly used as a fuel in gas air compressors. Propane-powered compressors are popular in construction, agriculture, and other industries where propane is used for various applications. Propane is stored in portable tanks, making it convenient for use in portable compressors. Propane-powered compressors are known for their clean combustion, low emissions, and easy availability.
5. Biogas:
In specific applications, gas air compressors can be fueled by biogas, which is produced from the decomposition of organic matter such as agricultural waste, food waste, or wastewater. Biogas compressors are used in biogas production facilities, landfills, and other settings where biogas is generated and utilized as a renewable energy source. The use of biogas as a fuel in compressors contributes to sustainability and reduces dependence on fossil fuels.
It’s important to note that the availability and suitability of these fuel options may vary depending on the region, infrastructure, and specific application requirements. When selecting a gas air compressor, it’s crucial to consider the compatibility of the compressor with the available fuel sources and to follow the manufacturer’s guidelines regarding fuel selection, storage, and safety precautions.


editor by CX 2024-02-19
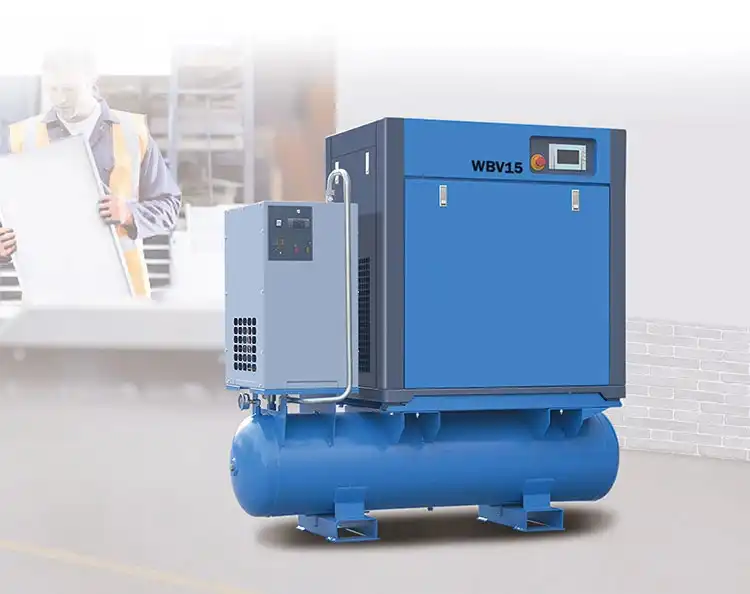
China Standard 30/40 Bar Booster Reciprocating Air Gas Piston Compressor for Industrial air compressor lowes
Product Description
Product Description
Detailed Photos
Product Parameters
| Model | KA 1030 |
| Capacity | 1.0m3/min |
| Power | 11Kw |
| Speed | 630r.p.m |
| Pressure | 3MPa |
| Weight | 450kg |
| Dimensions | 1500*800*1000mm |
Certifications
Packaging & Shipping
Company Profile
ZheJiang Kingair Industrial Co., Ltd., is the core technology solution provider for compressed gas system solutions, with mature operation experience and excellent brand reputation in the 3 major areas : product system, core technology and solutions.
The company has strong comprehensive strength, the factory is located in Xihu (West Lake) Dis., ZheJiang , covers an area of 30000 square meters, has a strong equipment production capacity. In the course of 20 years of operation and development, we have always adhered to the enterprise spirit of “professionalism, innovation, energy saving and service”, deeply implemented the strategic policy of environmental protection and low carbon, and realized the construction of high intelligent and efficient air pressure system industry chain.
Kingair focuses on R&D, production and trade, and produces air compressor products with stable overall performance, advanced control system, superior, gas environment, reasonable design, higher efficiency and longer service life.
Each product of the company has passed the IS09000 quality management system certification, European CE, ISO certification, etc., and has established a complete set of mature foreign trade operation system. The products are popular in more than 80 countries and regions in Asia, Europe,Africa and America.
FAQ
Q1. Is KINGAIR trading company or manufacturer ?
A: We are professional manufacturer of screw air compressor, more than 20 years experience.
Q2. How long is KINGAIR delivery time ?
A: KINGAIR standard delivery time is 15 working days after confirmed order.For the other non-standard requirements will be discussed case by case.
Q3. How about your after-sales service?
A: 1. Provide customers with installation and commissioning online instructions.
2. Well-trained engineers available to overseas service.
3. CHINAMFG agents and after service available arrange our engineers to help you training and installation.
Q4. What is the available voltage KINGAIR compressor?
A:KINGAIR available voltage include 380v/50hz/3p,400v/50hz/3p,415v/50hz/3p,220v/60hz/3p,440v/60hz/3p,And
KIGNAIR also supplies the required voltage.
Q5. Do you have any certificate ?
A: Yes, according to customer’s market need, we can offer CE certificate, ISO certificate, etc.
Q6. Do you offer OEM service ?
A: Yes, both OEM & ODM service can be accepted.
Q7. Can KINGAIR machines be run in high temperature environment?What is working temperature range?
A: Yes, KINGAIR machines would run in high temperature environment countries.Such as India, UAE,South Africa, Saudi Arabia, Iraq, Pakistan,etc.
/* March 10, 2571 17:59:20 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | Online Technology Support |
|---|---|
| Warranty: | 1 Year |
| Lubrication Style: | Lubricated |
| Cooling System: | Air Cooling |
| Cylinder Arrangement: | Balanced Opposed Arrangement |
| Cylinder Position: | Vertical |
| Samples: |
US$ 2115/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|
.webp)
How Do You Troubleshoot Common Issues with Gas Air Compressors?
Troubleshooting common issues with gas air compressors involves identifying and addressing potential problems that may arise during operation. Here’s a detailed explanation of the troubleshooting process:
1. Start with Safety Precautions:
Prior to troubleshooting, ensure that the gas air compressor is turned off and disconnected from the power source. Follow proper safety procedures, such as wearing appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), to avoid accidents or injuries.
2. Check Power Supply and Connections:
Verify that the compressor is receiving power and that all electrical connections are secure. Inspect the power cord, plug, and any switches or controls to ensure they are functioning properly. If the compressor is equipped with a battery, check its charge level and connections.
3. Check Fuel Supply:
For gas air compressors that use gasoline or propane, ensure that there is an adequate fuel supply. Check the fuel tank level and verify that the fuel shut-off valve is open. If the compressor has been sitting idle for an extended period, old or stale fuel may cause starting issues. Consider draining and replacing the fuel if necessary.
4. Inspect Air Filters:
Dirty or clogged air filters can restrict airflow and affect the compressor’s performance. Check the intake air filters and clean or replace them as needed. Clogged filters can be cleaned with compressed air or washed with mild detergent and water, depending on the type of filter.
5. Check Oil Level and Quality:
If the gas air compressor has an engine with an oil reservoir, verify the oil level using the dipstick or oil level indicator. Insufficient oil can lead to engine damage or poor performance. Additionally, check the oil quality to ensure it is clean and within the recommended viscosity range. If needed, change the oil following the manufacturer’s guidelines.
6. Inspect Spark Plug:
If the gas air compressor uses a spark plug ignition system, inspect the spark plug for signs of damage or fouling. Clean or replace the spark plug if necessary, following the manufacturer’s recommendations for gap setting and torque.
7. Check Belts and Pulleys:
Inspect the belts and pulleys that drive the compressor pump. Loose or worn belts can cause slippage and affect the compressor’s performance. Tighten or replace any damaged belts, and ensure that the pulleys are properly aligned.
8. Listen for Unusual Noises:
During operation, listen for any unusual or excessive noises, such as grinding, rattling, or squealing sounds. Unusual noises could indicate mechanical issues, loose components, or improper lubrication. If identified, consult the compressor’s manual or contact a qualified technician for further inspection and repair.
9. Consult the Owner’s Manual:
If troubleshooting steps do not resolve the issue, refer to the compressor’s owner’s manual for specific troubleshooting guidance. The manual may provide additional troubleshooting steps, diagnostic charts, or recommended maintenance procedures.
10. Seek Professional Assistance:
If the issue persists or if you are unsure about performing further troubleshooting steps, it is recommended to seek assistance from a qualified technician or contact the manufacturer’s customer support for guidance.
Remember to always prioritize safety and follow proper maintenance practices to prevent issues and ensure the reliable performance of the gas air compressor.
.webp)
Can Gas Air Compressors Be Used for Natural Gas Compression?
Gas air compressors are not typically used for natural gas compression. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Different Compressed Gases:
Gas air compressors are specifically designed to compress atmospheric air. They are not typically designed or suitable for compressing natural gas. Natural gas, which is primarily composed of methane, requires specialized compressors designed to handle the unique properties and characteristics of the gas.
2. Safety Considerations:
Natural gas compression involves handling a flammable and potentially hazardous substance. Compressing natural gas requires specialized equipment that meets stringent safety standards to prevent leaks, minimize the risk of ignition or explosion, and ensure the safe handling of the gas. Gas air compressors may not have the necessary safety features or materials to handle natural gas safely.
3. Equipment Compatibility:
Natural gas compression systems typically include components such as gas compressors, gas coolers, separators, and control systems that are specifically designed and engineered for the compression and handling of natural gas. These components are built to withstand the specific demands and conditions associated with natural gas compression, including the high pressures and potential presence of impurities.
4. Efficiency and Performance:
Compressing natural gas requires specialized compressors that can handle the high-pressure ratios and volumetric flow rates associated with the gas. Gas air compressors are generally not designed to achieve the same compression ratios and performance levels required for natural gas compression. Using gas air compressors for natural gas compression would likely result in inefficient operation and suboptimal performance.
5. Regulatory Compliance:
Compressing natural gas is subject to various regulations and standards to ensure safety, environmental protection, and compliance with industry guidelines. These regulations often dictate specific requirements for equipment, materials, and operating procedures in natural gas compression systems. Gas air compressors may not meet these regulatory requirements for natural gas compression.
6. Industry Standards and Practices:
The natural gas industry has well-established standards and best practices for equipment selection, installation, and operation in gas compression systems. These standards are based on the specific requirements and characteristics of natural gas. Gas air compressors do not align with these industry standards and practices, which are essential for safe and efficient natural gas compression.
In summary, gas air compressors are not suitable for natural gas compression. Natural gas compression requires specialized equipment designed to handle the unique properties and safety considerations associated with the gas. Compressors specifically engineered for natural gas compression offer the necessary performance, safety features, and regulatory compliance required for efficient and reliable operation in natural gas compression systems.
.webp)
Are There Different Types of Gas Air Compressors Available?
Yes, there are different types of gas air compressors available, each designed to suit specific applications and requirements. These different types vary in terms of design, power source, configuration, and intended use. Here’s a detailed explanation of the various types of gas air compressors:
1. Reciprocating Gas Air Compressors:
Reciprocating gas air compressors, also known as piston compressors, use a reciprocating motion of one or more pistons to compress the air. These compressors are commonly used for small to medium-scale applications and are available in both single-stage and two-stage configurations. Single-stage compressors compress the air in a single stroke, while two-stage compressors use an additional cylinder for further compression, resulting in higher pressures.
2. Rotary Screw Gas Air Compressors:
Rotary screw gas air compressors utilize two interlocking helical screws to compress the air. These compressors are known for their continuous and efficient operation, making them suitable for demanding industrial applications. They are often used in industries such as manufacturing, construction, and automotive where a constant supply of compressed air is required.
3. Rotary Vane Gas Air Compressors:
Rotary vane gas air compressors use a rotor with sliding vanes to compress the air. As the rotor rotates, the vanes slide in and out, creating compression chambers that compress the air. These compressors are compact, reliable, and often used for smaller-scale applications or in situations where space is limited.
4. Centrifugal Gas Air Compressors:
Centrifugal gas air compressors operate by accelerating the air using a high-speed impeller. The accelerated air is then redirected into a diffuser, which converts the velocity energy into pressure energy. These compressors are commonly used for large-scale applications requiring high volumes of compressed air, such as in power plants, refineries, or chemical processing industries.
5. Oil-Free Gas Air Compressors:
Oil-free gas air compressors are designed to provide clean, oil-free compressed air. They feature special sealing mechanisms and materials to prevent oil contamination in the compressed air. These compressors are commonly used in industries where oil-free air is essential, such as food and beverage processing, pharmaceuticals, electronics manufacturing, and painting applications.
6. Portable Gas Air Compressors:
Portable gas air compressors are specifically designed for mobility and ease of transportation. These compressors often feature wheels, handles, or trailers for convenient movement. They are commonly used in construction sites, remote job locations, outdoor events, or other situations where compressed air is needed at different locations.
7. High-Pressure Gas Air Compressors:
High-pressure gas air compressors are designed to generate compressed air at elevated pressures. These compressors are used in applications that require air pressure higher than the standard range, such as in diving operations, breathing air systems, or specialized industrial processes.
8. Biogas Air Compressors:
Biogas air compressors are specifically designed to compress biogas, which is generated from the decomposition of organic matter. These compressors are used in biogas production facilities, landfills, wastewater treatment plants, or agricultural operations where biogas is produced and utilized as an energy source.
These are just a few examples of the different types of gas air compressors available. Each type has its own advantages and is suitable for specific applications based on factors such as required airflow, pressure, mobility, oil-free operation, and environmental considerations. It’s important to choose the appropriate type of gas air compressor based on the specific needs of the application to ensure optimal performance and efficiency.


editor by CX 2024-01-31
China Standard Industrial Medical Compressor Zw-0.7/10-35 Natural Gas Compressor Reciprocating Piston Air Natural Gas Compressor air compressor oil
Product Description
Product Description
Reciprocating Micro-oil/ oil-free Piston Compressor
( Blue Font To View Hyperlink)
Our company specialize in making various kinds of compressors, such as:Diaphragm compressor,Piston compressor, Air compressors,Nitrogen generator,Oxygen generator ,Gas cylinder,etc. All products can be customized according to your parameters and other requirements.
This series of oil-free compressor is one of the first products produced by our factory in China. The product has the characteristics of low speed, high component strength, stable operation, long service life and convenient maintenance. This series compressor is in the form of unit. It integrates compressor, gas-liquid separator, filter, 2 position four-way valve, safety valve, check valve, explosion-proof motor and chassis. The utility model has the advantages of small volume, light weight, low noise, good sealing performance, easy installation, simple operation, etc.
Main components
1. Motion system: crankshaft, piston connecting rod assembly, coupling, etc.
2. Air distribution system: valve plate, valve spring, etc.
3. Sealing system: piston ring, oil seal, gasket, packing, etc.
4. Body system: crankcase, cylinder block, cylinder liner, cover plate, etc.
5. Lubrication system: lubricating oil pump, oil filter, pressure regulating valve, etc.;
6. Safety and energy regulation systems: safety valves, energy regulation devices, etc.
Working principle of piston compressor
When the crankshaft of the piston compressor rotates, the piston will reciprocate through the transmission of the connecting rod, and the working volume formed by the inner wall of the cylinder, the cylinder head and the top surface of the piston will periodically change. When the piston of a piston compressor starts to move from the cylinder head, the working volume in the cylinder gradually increases. At this time, the gas flows along the intake pipe and pushes the intake valve to enter the cylinder until the working volume reaches the maximum. , The intake valve is closed; when the piston of the piston compressor moves in the reverse direction, the working volume in the cylinder is reduced, and the gas pressure is increased. When the pressure in the cylinder reaches and is slightly higher than the exhaust pressure, the exhaust valve opens and the gas is discharged from the cylinder , Until the piston moves to the limit position, the exhaust valve is closed. When the piston of the piston compressor moves in the reverse direction again, the above process repeats. In short, the crankshaft of a piston compressor rotates once, the piston reciprocates once, and the process of air intake, compression, and exhaust is realized in the cylinder, which completes a work cycle.
Advantages of piston compressor
1. The applicable pressure range of the piston compressor is wide, and the required pressure can be reached regardless of the flow rate;
2. The piston compressor has high thermal efficiency and low unit power consumption;
3. Strong adaptability, that is, a wide exhaust range, and is not affected by the pressure level, and can adapt to a wider pressure range and cooling capacity requirements;
4. Piston compressors have low requirements for materials, and use common steel materials, which is easier to process and lower in cost;
5. The piston compressor is relatively mature in technology, and has accumulated rich experience in production and use;
6. The device system of the piston compressor is relatively simple.
Note: In the unloading process, the compressor pressurizes the gas from the storage tank and then presses it into the tank car through the gas-phase pipeline, and presses the liquid from the tank car to the storage tank through the gas-phase differential pressure to complete the unloading process. When the gas phase is pressurized, the temperature of the gas phase will rise. At this time, forced cooling is not necessary, because if the gas phase is compressed and then cooled, it is easy to liquefy, and it is difficult to establish the pressure difference of the gas phase, which is not conducive to the replacement of the gas phase and the liquid phase. In short, it will cause the prolongation of the unloading process. If it is necessary to recover the residual gas, the cooler can be selected to forcibly cool the gas phase during the recovery operation, so as to recover the residual gas as soon as possible.The loading process is opposite to the unloading process.
Chemical Process Compressor Description
Chemical process compressors refer to process reciprocating piston compressors used to compress various single or mixed media gases in petroleum and chemical processes, as well as chemical exhaust gas recycling systems. Its main function is to transport the medium gas in the reaction device and provide the required pressure to the reaction device.
Features 1. Designed for specific process flow. 2. The whole machine is skid-mounted and advanced in structure. 3. The compressor types are: Z type, D type, M type. 4. The middle body of the slideway and the cylinder can be designed in different structural forms according to the process requirements.
Reference Technical parameters and specifications
| Model | Volume flow(Nm3/h) | Suction pressure(Mpa) | Exhaust pressure (Mpa) | Motor power(kw) | Dimension (mm) | |
| 1 | ZW-0.4/ 2-250 | 60 | 0.2 | 25 | 18.5 | 2800*2200*1600 |
| 2 | ZW-0.81/ (1~3)-25 | 120 | 0.1~0.3 | 2.5 | 22 | 1000*580*870 |
| 3 | DW-5.8/0.5-5 | 400~500 | 0.05 | 0.5 | 37 | 2000*1600*1200 |
| 4 | DW-10/2 | 510 | Atmospheric pressure | 0.2 | 37 | 2000*1600*1200 |
| 5 | DW-6.0/5 | 300 | Atmospheric pressure | 0.5 | 37 | 2000*1600*1200 |
| 6 | DW-0.21/(20~30)-250 | 270 | 2~3 | 25 | 45 | 3200*2200*1600 |
| 7 | ZW-0.16/60-250 | 480 | 6 | 25 | 45 | 3000*2200*1600 |
| 8 | ZW-0.46 /(5~10)-250 | 200 | 0.5~1.0 | 25 | 45 | 3000*2200*1600 |
| 9 | DW-1.34/2-250 | 208 | 0.2 | 25 | 55 | 3400*2200*1600 |
| 10 | DW-0.6/24-85 | 720 | 2.4 | 8.5 | 55 | 2200*1600*1200 |
| 11 | ZW-2.9/14.2-20 | 220 | 1.42 | 2 | 55 | 2200*1600*1200 |
| 12 | VW-2.0/(2~4)-25 | 410 | 0.2~0.4 | 2.5 | 55 | 3400*2200*1600 |
| 13 | DW-0.85/(3~4)-250 | 180 | 0.3~0.4 | 25 | 55 | 2400*1800*1500 |
| 14 | DW-25-(0.2~0.3)-1.5 | 1620 | 0.02~0.03 | 0.15 | 75 | 2400*1800*1500 |
| 15 | VW-8.0/0.3-25 | 540 | 0.03 | 2.5 | 90 | 2400*1800*1500 |
| 16 | DW-6.8/0.05-40 | 200~400 | 0.005 | 4 | 90 | 2400*1800*1500 |
/* March 10, 2571 17:59:20 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | 18 Months |
|---|---|
| Warranty: | 18 Months |
| Lubrication Style: | Lubricated |
| Cooling System: | Water Cooling |
| Cylinder Arrangement: | Balanced Opposed Arrangement |
| Cylinder Position: | Angular |
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|
.webp)
How Do Gas Air Compressors Compare to Diesel Air Compressors?
When comparing gas air compressors to diesel air compressors, there are several factors to consider, including fuel efficiency, power output, cost, maintenance requirements, and environmental impact. Here’s a detailed explanation of how these two types of air compressors compare:
1. Fuel Efficiency:
Diesel air compressors are generally more fuel-efficient compared to gas air compressors. Diesel engines have higher energy density and better overall efficiency than gasoline engines. This means that diesel compressors can produce more work output per unit of fuel consumed, resulting in lower fuel costs and longer runtimes between refueling.
2. Power Output:
Diesel air compressors typically provide higher power output compared to gas air compressors. Diesel engines are known for their robustness and ability to generate higher torque, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications that require a larger volume of compressed air or higher operating pressures.
3. Cost:
In terms of upfront cost, gas air compressors are generally more affordable compared to diesel air compressors. Gasoline engines and components are typically less expensive than their diesel counterparts. However, it’s important to consider long-term costs, including fuel expenses and maintenance, which can vary depending on factors such as fuel prices and usage patterns.
4. Maintenance Requirements:
Diesel air compressors often require more regular maintenance compared to gas air compressors. This is because diesel engines have additional components such as fuel filters, water separators, and injector systems that need periodic servicing. Gas air compressors, on the other hand, may have simpler maintenance requirements, resulting in reduced maintenance costs and time.
5. Environmental Impact:
When it comes to environmental impact, diesel air compressors produce higher emissions compared to gas air compressors. Diesel engines emit more particulate matter, nitrogen oxides (NOx), and carbon dioxide (CO2) compared to gasoline engines. Gas air compressors, especially those powered by propane, tend to have lower emissions and are considered more environmentally friendly.
6. Portability and Mobility:
Gas air compressors are generally more portable and easier to move compared to diesel air compressors. Gasoline engines are typically lighter and more compact, making gas air compressors suitable for applications where mobility is essential, such as construction sites or remote locations.
It’s important to note that the specific requirements of the application and the availability of fuel sources also play a significant role in choosing between gas air compressors and diesel air compressors. Each type has its own advantages and considerations, and the choice should be based on factors such as the intended usage, operating conditions, budget, and environmental considerations.
In conclusion, gas air compressors are often more affordable, portable, and suitable for lighter applications, while diesel air compressors offer higher power output, fuel efficiency, and durability for heavy-duty operations. Consider the specific needs and factors mentioned above to determine the most appropriate choice for your particular application.
.webp)
Can Gas Air Compressors Be Used for Natural Gas Compression?
Gas air compressors are not typically used for natural gas compression. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Different Compressed Gases:
Gas air compressors are specifically designed to compress atmospheric air. They are not typically designed or suitable for compressing natural gas. Natural gas, which is primarily composed of methane, requires specialized compressors designed to handle the unique properties and characteristics of the gas.
2. Safety Considerations:
Natural gas compression involves handling a flammable and potentially hazardous substance. Compressing natural gas requires specialized equipment that meets stringent safety standards to prevent leaks, minimize the risk of ignition or explosion, and ensure the safe handling of the gas. Gas air compressors may not have the necessary safety features or materials to handle natural gas safely.
3. Equipment Compatibility:
Natural gas compression systems typically include components such as gas compressors, gas coolers, separators, and control systems that are specifically designed and engineered for the compression and handling of natural gas. These components are built to withstand the specific demands and conditions associated with natural gas compression, including the high pressures and potential presence of impurities.
4. Efficiency and Performance:
Compressing natural gas requires specialized compressors that can handle the high-pressure ratios and volumetric flow rates associated with the gas. Gas air compressors are generally not designed to achieve the same compression ratios and performance levels required for natural gas compression. Using gas air compressors for natural gas compression would likely result in inefficient operation and suboptimal performance.
5. Regulatory Compliance:
Compressing natural gas is subject to various regulations and standards to ensure safety, environmental protection, and compliance with industry guidelines. These regulations often dictate specific requirements for equipment, materials, and operating procedures in natural gas compression systems. Gas air compressors may not meet these regulatory requirements for natural gas compression.
6. Industry Standards and Practices:
The natural gas industry has well-established standards and best practices for equipment selection, installation, and operation in gas compression systems. These standards are based on the specific requirements and characteristics of natural gas. Gas air compressors do not align with these industry standards and practices, which are essential for safe and efficient natural gas compression.
In summary, gas air compressors are not suitable for natural gas compression. Natural gas compression requires specialized equipment designed to handle the unique properties and safety considerations associated with the gas. Compressors specifically engineered for natural gas compression offer the necessary performance, safety features, and regulatory compliance required for efficient and reliable operation in natural gas compression systems.
.webp)
How Do You Choose the Right Size Gas Air Compressor for Your Needs?
Choosing the right size gas air compressor is crucial to ensure optimal performance and efficiency for your specific needs. Selecting a compressor that is too small may result in insufficient airflow or pressure, while choosing one that is too large can lead to unnecessary energy consumption and higher costs. Here’s a detailed explanation of the factors to consider when choosing the right size gas air compressor:
1. Required Airflow:
Determine the airflow requirements of your applications. Consider the tools, equipment, or processes that will be powered by the compressor and their respective airflow demands. The required airflow is typically measured in cubic feet per minute (CFM). Determine the total CFM required, taking into account any simultaneous or intermittent tool usage.
2. Operating Pressure:
Identify the operating pressure required for your applications. Different tools and systems have specific pressure requirements, measured in pounds per square inch (PSI). Ensure that the compressor you choose can deliver the required pressure consistently.
3. Duty Cycle:
Consider the duty cycle, which refers to the amount of time the compressor will be in operation within a given period. Some applications may require continuous operation, while others involve intermittent or occasional use. Take into account the duty cycle to ensure that the compressor can handle the expected workload without overheating or experiencing excessive wear.
4. Tank Size:
The tank size of a gas air compressor determines its ability to store compressed air and provide a steady supply. A larger tank can help accommodate fluctuations in demand and reduce the frequency of the compressor cycling on and off. Consider the required storage capacity based on the specific applications and the desired balance between continuous operation and storage capacity.
5. Power Source:
Gas air compressors can be powered by different fuels, such as gasoline, diesel, natural gas, or propane. Consider the availability and cost of the fuel options in your location, as well as the specific requirements of your applications. Choose a compressor that is compatible with a power source that suits your needs.
6. Portability:
Determine if portability is a requirement for your applications. If you need to move the compressor to different job sites or locations, consider a portable model with features like wheels, handles, or a compact design that facilitates easy transportation.
7. Noise Level:
If noise is a concern in your working environment, consider the noise level of the compressor. Gas air compressors can vary in their noise output, and certain models may have noise-reducing features or insulation to minimize sound emissions.
8. Manufacturer Recommendations:
Consult the manufacturer’s recommendations and guidelines for selecting the appropriate compressor size for your specific needs. Manufacturers often provide guidelines based on the anticipated applications, airflow requirements, and other factors to help you make an informed decision.
By considering these factors and carefully assessing your specific requirements, you can choose the right size gas air compressor that meets your airflow, pressure, duty cycle, and other operational needs. It’s advisable to consult with industry professionals or compressor experts for guidance, especially for complex or specialized applications.


editor by CX 2024-01-18
China wholesaler Air-Cooled 250bar (25MPa) Reciprocating Piston Natural Gas Compressor for CNG Refueling Station air compressor lowes
Product Description
Company Profile
The company’s main products include desulfurization, dehydrocarbons, separation, compression, filling, storage and transportation equipment for natural gas extraction in oil and gas fields; complete sets of wellhead gas recovery equipment; complete sets of vented natural gas recovery equipment; complete sets of coalbed methane, shale gas and biogas development and utilization equipment Equipment; CNG filling station complete equipment; LNG complete equipment; BOG compressor; large-displacement screw-piston compound compressor; membrane nitrogen and adsorption nitrogen production complete equipment; in addition, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, argon, carbon monoxide gas, carbon dioxide gas, coal gas, hydrogen sulfide gas, propylene gas, ethylene gas, methyl chloride gas, trifluoropropane gas, liquefied petroleum gas and other special gases, low-temperature gases and air compressors. Among them, the W and V series non-lubricated compressors produced by introducing advanced foreign technology have reached the international advanced level.
Product Description
The company currently has 10 series of leading products and hundreds of specifications. Its volumetric flow rate: 0.05~200m3/min. Pressure range: low pressure type 0~1.6MPa, medium pressure
Type 1.6~8.0MPa, high pressure type 8.0~50.0MPa. Lubrication methods are divided into 3 types: oil, oil-free and completely oil-free. The structural types include Z, W, V, D, M and H types. There are 3 cooling methods: air cooling, water cooling, and mixed cooling. In addition to providing users with customized products, we can also carry out personalized design and manufacturing according to user needs.
CNG STHangZhouRD STATION COMPRESSOR
CNG standard stations are built where natural gas pipelines pass through.
Gas is taken directly from the natural gas pipeline. Natural gas undergoes desulfurization, pressure regulation, metering, and
Filtration, dehydration and other processes enter the compressor unit, and then compress, cool and purify
Then the pressure is increased to 25Mpa, and finally the high-pressure trailer is supplied to the high-pressure trailer through the air filling column.
Fill up the gas, and also fill up the car through the gas vending machine. Our company can provide overall
Solutions and turnkey projects.
Equipment composition: air inlet filter pressure regulating metering device, desulfurization tower, low-pressure dehydration device, piston compressor, sequence control panel, gas storage bottle group, adding
Gas machines, gas filling columns, CNG trailers, gas alarm devices and other equipment.
Covered area: about 2000~4000m²
Optimal transportation radius: 150km
Suitable scale: ≥40000Nm²/d
Equipment installation time: about 30 days.
| NO. | TYPE | Intake pressure MPa |
CAPACITY Nm3/h |
MOTOR KW |
COOLING | WEIGHT(TONS) | SIZE mm |
|||||
| 1 | W-5.6/0.5-250 | 0.05 | 500 | 160 | WATER COOLING | 9 | 5000×2300×2200 | |||||
| 2 | W-3.6/1-250 | 0.1 | 435 | 110 | WATER/MIX COOLING | 6 | 2400×2220×2150 | |||||
| 3 | W-4.75/1-250 | 0.1 | 570 | 132 | WATER/MIX COOLING | 6 | 2400×2220×2150 | |||||
| 4 | W-7.5/1-250 | 0.1 | 900 | 270 | WATER/MIX COOLING | 17 | 8500×2260×2200 | |||||
| 5 | W-4.5/1.4-250 | 0.14 | 650 | 160 | WATER/MIX COOLING | 7 | 3820×2270×2150 | |||||
| 6 | W-4.7/2-250 | 0.2 | 850 | 185 | WATER/MIX COOLING | 7 | 3820×2270×2150 | |||||
| 7 | WF-3.6/(1.5~2.5)-250 0.15~0.25 | 0.15~0.25 | 540~750 | 160 | AIR COOLING | 14 | 6200×2190×2080 | |||||
| 8 | W-3.6/(1.5~3)-250 | 0.15~0.3 | 540~860 | 185 | WATER/MIX COOLING | 7 | 4000×2270×2150 | |||||
| 9 | V-3.2/(3-5)-250 | 0.3~0.5 | 760-1150 | 220 | AIR COOLING | 14 | 6300×2525×2500 | |||||
| 10 | VF-3.2/(3~5)-250 | 0.3~0.5 | 770~1150 | 220 | WATER/MIX COOLING | 14 | 6300×2500×2500 | |||||
| 11 | W-1.5/8-250 | 0.8 | 810 | 132 | WATER/MIX COOLING | 8 | 4000×2300×2000 | |||||
| 12 | VF-2/(10~16)-250 | 1.0~1.6 | 1320~2000 | 280 | AIR COOLING | 10 | 5600×2500×2300 | |||||
| 13 | D-5/(2~4)-250 | 0.2~0.4 | 900~1500 | 315 | WATER/AIR/MIX COOLING | 23 | 5000×3500×2500 | |||||
| 14 | D-4.2/(3~6)-250 | 0.3~0.6 | 1000-1760 | 280 | WATER/AIR/MIX COOLING | 23 | 5000×3500×2500 | |||||
| 15 | D-3.6/(4~7)-250 | 0.4~0.7 | 1050~1730 | 315 | WATER/AIR/MIX COOLING | 23 | 5000×3500×2500 | |||||
| 16 | D-2.6/(7~12)-250 | 0.7~1.2 | 1250~2000 | 280 | WATER/AIR/MIX COOLING | 20 | 5000×3500×2500 | |||||
| 17 | VF-0.76/(7~13)-250 | 0.7~1.3 | 365~640 | 100 | WATER/AIR/MIX COOLING | 8 | 6000×2200×2230 | |||||
CNG MOTHER STATION COMPRESSOR
The CNG mother station is built in a place where natural gas pipelines pass through.
Take the gas directly from the gas pipeline. Natural gas undergoes desulfurization, pressure regulation, metering, filtration,
Dehydration and other processes enter the compressor unit, and then are compressed, cooled and purified to make it
The pressure is increased to 25Mpa, and finally the high-pressure trailer is filled with air through the air filling column.
Sometimes, cars can also be refueled through gas vending machines. Our company provides turnkey projects.
Equipment composition: air inlet filter pressure regulating metering device, desulfurization tower, low pressure desulfurization tower
Water device, piston compressor, sequence control panel, gas storage bottle group, gas filling
machine, gas filling column, CNG trailer, gas alarm device and other equipment.
Covered area: about 2000~4000m²
Optimal transportation radius: 150km
Suitable scale: ≥40000Nm²/d
Equipment installation time: about 30 days.
| NO. | TYPE | Intake pressure MPa |
CAPACITY Nm3/h |
MOTOR KW |
COOLING | WEIGHT(TONS) | SIZE mm |
||||
| 1 | D-5/(2-4)-250 | 0.2~0.4 | 900~1500 | 315 | WATER/AIR/MIX COOLING | 23 | 5000×3500×2500 | ||||
| 2 | VF-3.2/(3~5)-250 | 0.3~0.5 | 770~1150 | 220 | AIR COOLING | 14 | 6300×2500×2500 | ||||
| 3 | D-4.2/(3-6)-250 | 03~0.6 | 1000-1760 | 280 | WATER/AIR/MIX COOLING | 23 | 5000×3500×2500 | ||||
| 4 | D-3.6/(4~7)-250 | 0.4~0.7 | 1050~1730 | 315 | WATER/AIR/MIX COOLING | 23 | 5000×3500×2500 | ||||
| 5 | D-2.6/(7~12)-250 | 0.7~1.2 | 1250~2000 | 280 | WATER/MIX COOLING | 20 | 5000×3500×2500 | ||||
| 6 | VF-0.76/(7~13)-250 | 0.7~0.3 | 365~640 | 100 | MIX COOLING | 8 | 6000×2200×2230 | ||||
| 7 | D-2.8/(8-12)-250 | 0.8~1.2 | 1350-2150 | 280 | WATER/AIR/MIX COOLING | 23 | 5000×3500×2500 | ||||
| 8 | V-2/(9-14)-250 | 0.9~1.4 | 1200-1800 | 280 | WATER/AIR/MIX COOLING | 12 | 6500×2525×2300 | ||||
| 9 | VFD-2/14-210 | 1.4 | 1800 | 280 | AIR COOLING | 15 | 10000×4000×3000 | ||||
| 10 | D-2.5/(12-14)-250 | 1.2~1.4 | 1950-2250 | 18 | WATER/AIR/MIX COOLING | 23 | 5000×3500×2500 | ||||
| 11 | VF-2/(10~16)-250 | 1.0~1.6 | 1320~2000 | 280 | AIR COOLING | 10 | 5600×2500×2300 | ||||
| 12 | D-2.8/(10~16)-250 | 1.0~1.6 | 1800-2850 | 355 | WATER/AIR/MIX COOLING | 23 | 5000×3500×2500 | ||||
| 13 | V-1.43/(16~20)-250 | 1.6~2.0 | 1460~1800 | 220 | WATER/AIR/MIX COOLING | 11 | 6000×2500×2250 | ||||
| 14 | D-2.4/(16-20)-250 | 1.6~2.0 | 2450-3000 | 355 | WATER/AIR/MIX COOLING | 23 | 5000×3500×2500 | ||||
| 15 | D-2.4/(16-23)-210 | 1.6~2.3 | 2450-3450 | 355 | WATER/AIR/MIX COOLING | 23 | 5000×3500×2500 | ||||
| 16 | V-1.8/(18-23)-210 | 1.8~2.3 | 2000-2590 | 280 | WATER/AIR/MIX COOLING | 12 | 6500×2525×2200 | ||||
| 17 | D-1.45/(20-35)-250 | 2.0~3.5 | 1830-3100 | 280 | WATER/AIR/MIX COOLING | 23 | 5000×3500×2500 | ||||
| 18 | V-0.8/(19~35)-250 | 1.9~3.5 | 960~1720 | 160 | WATER/AIR/MIX COOLING | 13 | 6500×2525×2200 | ||||
| 19 | VF-1/(25~40)-250 | 2.5~4.0 | 1560~2700 | 220 | AIR COOLING | 13.5 | 4250×2525×2100 | ||||
| 20 | D-1.45/(40~60)-250 | 4.0~6.0 | 3600~5300 | 315 | WATER/AIR/MIX COOLING | 23 | 5000×3500×2100 | ||||
| 21 | D-1.3/(50-70)-250 | 5.0~7.0 | 3970~5530 | 315 | WATER/AIR/MIX COOLING | 23 | 5000×3500×2100 | ||||
| 22 | D-1.3/(60-70)-250 | 6.0~7.0 | 4758~5530 | 315 | WATER/AIR/MIX COOLING | 23 | 5000×3500×2100 | ||||
| 23 | D-1.2/(40-80)-250 | 4.0~8.0 | 4758~5530 | 315 | WATER/AIR/MIX COOLING | 23 | 5000×3500×2100 | ||||
| 24 | D-3.5/(7-10)-250 | 0.7~1 | 1680~2240 | 550 | AIR COOLING | 28 | 6600×4300×2500 | ||||
CNG SUBSTATION COMPRESSOR
CNG substations are built in places where no natural gas pipelines pass through.
The CNG trailer transfers the gas from the mother station to the station and unloads the gas through the gas unloading column.
Gas machines refill cars.
Equipment composition: gas unloading column, sub-station compressor, sequence control panel, storage
Gas cylinder sets, gas dispensers, gas alarm devices, CNG trailers and other equipment.
Covered area: about 1000~1500m²
Way of working:
After natural balance, the direct intake air is compressed and supercharged, and the average working capacity is
More than 1000 square meters
Compressor exhaust volume changes range as trailer pressure drops:
1800-400Nm²/h
| NO. | TYPE | Intake pressure MPa |
CAPACITY Nm3/h |
MOTOR KW |
COOLING | WEIGHT(TONS) | SIZE mm |
||||
| 1 | VF-0.32/(30~200)-250 | 3~20 | 1500 | 75 | AIR | 5.5 | 5538×2134×1680 | ||||
| 2 | VFD-0.32/(30~200)-250 | 3~20 | 1500 | 75 | AIR | 9.65 | 5538×2438×2438 | ||||
| 3 | DFD-0.32/(30-200)-250 | 3~20 | 1500 | 75 | AIR | 8.5 | 4400×2610×2591 | ||||
| 4 | VFD-0.32/(20~200)-250 | 2~20 | 1500 | 75 | AIR | 9.65 | 5538×2438×2438 | ||||
| 5 | VF-0.26/(30-200)-250 | 3~20 | 1000 | 55 | AIR | 5.5 | 5538×2350×2000 | ||||
| 6 | VFD-0.26/(30-200)-250 | 3~20 | 1000 | 55 | AIR | 9.5 | 5538×2350×2438 | ||||
| 7 | ZFD-0.1/(30~200)-250 | 3~20 | 650 | 37 | AIR | 8.5 | 7000×2700×2700 | ||||
| 8 | ZFD-0.24/(30-200)-250 | 3~20 | 1400 | 37×2 | AIR | 8.5 | 7000×2700×2700 | ||||
| 9 | KR-1500/(20-200)-250 | 2~20 | 1500 | 30×2 | AIR | 10 | 5500×2500×2950 | ||||
| 10 | KR-2000/(20-200)-250 | 2~20 | 2000 | 37×2 | AIR | 10 | 5500×2500×2950 | ||||
| 11 | DFD-3[0.28]/(2-4)[25-200]-250 | 0.2~0.4
2.5~20 |
540-900 (STANARD STATION AND SUBSTATION) 1300 |
160
75 |
AIR | 12.5 | 4050×3450×2100 | ||||
Detailed Photos
After Sales Service
In addition to the high-quality performance of our products, we also attach great importance to providing customers with comprehensive services. We have an independent service operation and maintenance team, providing customers with various support and services, including technical support, debugging services, spare parts supply, renovation and upgrading, and major maintenance. We always adhere to the principle of customer-centrism, ensuring the safe and stable operation of customer equipment. Our service team is committed to providing reliable support for customers’ operations 24/7.
Training plan
Technical training is divided into 2 parts: company training and on-site training.
1)Company training
Before the unit is delivered, that is during the unit assembly period, users will be provided with a one-week on-site training by the company. Provide local accommodation and transportation facilities, and provide free venues, teaching materials, equipment, tools, etc. required for training. The company training content is as follows:
The working principle, structure and technical performance of the unit.
Unit assembly and adjustment, unit testing.
Operation of the unit, remote/local operation, manual/automatic operation, daily operation and management, familiar with the structure of each system of the unit.
Routine maintenance and upkeep of the unit, and precautions for operation and maintenance.
Analysis and troubleshooting of common faults, and emergency handling methods.
2) On-site training
During the installation and trial operation of the unit, on-site training will be conducted to teach the principles, structure, operation, maintenance, troubleshooting of common faults and other knowledge of the unit, so as to further become familiar with the various systems of the unit, so that the purchaser can independently and correctly operate the unit. Operation, maintenance and management.
Packaging & Shipping
/* March 10, 2571 17:59:20 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | 12 Month |
|---|---|
| Warranty: | 12 Month |
| Lubrication Style: | Lubricated |
.shipping-cost-tm .tm-status-off{background: none;padding:0;color: #1470cc}
|
Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
about shipping cost and estimated delivery time. |
|---|
| Payment Method: |
|
|---|---|
|
Initial Payment Full Payment |
| Currency: | US$ |
|---|
| Return&refunds: | You can apply for a refund up to 30 days after receipt of the products. |
|---|
.webp)
What Is the Fuel Efficiency of Gas Air Compressors?
The fuel efficiency of gas air compressors can vary depending on several factors, including the compressor’s design, engine size, load capacity, and usage patterns. Gas air compressors typically use internal combustion engines powered by gasoline or propane to generate the mechanical energy required for compressing air. Here’s a detailed explanation of the factors that can influence the fuel efficiency of gas air compressors:
1. Engine Design and Size:
The design and size of the engine in a gas air compressor can impact its fuel efficiency. Engines with advanced technologies such as fuel injection and electronic controls tend to offer better fuel efficiency compared to older carbureted engines. Additionally, larger engines may consume more fuel to produce the required power, resulting in lower fuel efficiency compared to smaller engines for the same workload.
2. Load Capacity and Usage Patterns:
The load capacity and usage patterns of the gas air compressor play a significant role in fuel efficiency. Compressors operating at or near their maximum load capacity for extended periods may consume more fuel compared to compressors operating at lower loads. Additionally, compressors used intermittently or for lighter tasks may have better fuel efficiency due to reduced demand on the engine.
3. Maintenance and Tuning:
Proper maintenance and tuning of the gas air compressor’s engine can improve fuel efficiency. Regular maintenance tasks such as oil changes, air filter cleaning/replacement, spark plug inspection, and tuning the engine to the manufacturer’s specifications can help ensure optimal engine performance and fuel efficiency.
4. Operating Conditions:
The operating conditions, including ambient temperature, altitude, and humidity, can affect the fuel efficiency of gas air compressors. Extreme temperatures or high altitudes may require the engine to work harder, resulting in increased fuel consumption. Additionally, operating in humid conditions can affect the combustion process and potentially impact fuel efficiency.
5. Fuel Type:
The type of fuel used in the gas air compressor can influence its fuel efficiency. Gasoline and propane are common fuel choices for gas air compressors. The energy content and combustion characteristics of each fuel can affect the amount of fuel consumed per unit of work done. It is important to consider the specific fuel requirements and recommendations of the compressor manufacturer for optimal fuel efficiency.
6. Operator Skills and Practices:
The skills and practices of the operator can also impact fuel efficiency. Proper operation techniques, such as avoiding excessive idling, maintaining consistent engine speeds, and minimizing unnecessary load cycles, can contribute to improved fuel efficiency.
It is important to note that specific fuel efficiency ratings for gas air compressors can vary widely depending on the aforementioned factors. Manufacturers may provide estimated fuel consumption rates or fuel efficiency data for their specific compressor models, which can serve as a reference point when comparing different models or making purchasing decisions.
Ultimately, to maximize fuel efficiency, it is recommended to select a gas air compressor that suits the intended application, perform regular maintenance, follow the manufacturer’s guidelines, and operate the compressor efficiently based on the workload and conditions.
.webp)
What Is the Role of Air Receivers in Gas Air Compressor Systems?
Air receivers play a crucial role in gas air compressor systems by serving as storage tanks for compressed air. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Storage and Stabilization:
The primary function of an air receiver is to store compressed air generated by the gas air compressor. As the compressor produces compressed air, the air receiver collects and stores it. This storage capacity helps meet fluctuating demand in compressed air usage, providing a buffer between the compressor and the system’s air consumption.
By storing compressed air, the air receiver helps stabilize the supply to the system, reducing pressure fluctuations and ensuring a consistent and reliable flow of compressed air. This is particularly important in applications where the demand for compressed air may vary or experience peaks and valleys.
2. Pressure Regulation:
Another role of the air receiver is to assist in pressure regulation within the gas air compressor system. As compressed air enters the receiver, the pressure inside increases. When the pressure reaches a predetermined upper limit, typically set by a pressure switch or regulator, the compressor stops supplying air, and the excess air is stored in the receiver.
Conversely, when the pressure in the system drops below a certain lower limit, the pressure switch or regulator signals the compressor to start, replenishing the compressed air in the receiver and maintaining the desired pressure level. This cycling of the compressor based on pressure levels helps regulate and control the overall system pressure.
3. Condensate Separation:
During the compression process, moisture or condensate can form in the compressed air due to the cooling effect. The air receiver acts as a reservoir that allows the condensate to settle at the bottom, away from the outlet. The receiver often includes a drain valve at the bottom to facilitate the removal of accumulated condensate, preventing it from reaching downstream equipment and causing potential damage or performance issues.
4. Energy Efficiency:
Air receivers contribute to energy efficiency in gas air compressor systems. They help optimize the operation of the compressor by reducing the occurrence of short-cycling, which refers to frequent on-off cycling of the compressor due to rapid pressure changes. Short-cycling can cause excessive wear on the compressor and reduce its overall efficiency.
The presence of an air receiver allows the compressor to operate in longer and more efficient cycles. The compressor runs until the receiver reaches the upper pressure limit, ensuring a more stable and energy-efficient operation.
5. Air Quality Improvement:
Depending on the design, air receivers can also aid in improving air quality in the compressed air system. They provide a space for the compressed air to cool down, allowing moisture and some contaminants to condense and separate from the air. This can be further enhanced with the use of additional filtration and drying equipment installed downstream of the receiver.
In summary, air receivers play a vital role in gas air compressor systems by providing storage capacity, stabilizing compressed air supply, regulating system pressure, separating condensate, improving energy efficiency, and contributing to air quality control. They are an integral component in ensuring the reliable and efficient operation of compressed air systems across various industries and applications.
.webp)
What Are the Advantages of Using a Gas Air Compressor Over an Electric One?
Using a gas air compressor offers several advantages over an electric air compressor. Gas-powered compressors provide unique benefits in terms of mobility, versatility, power, and convenience. Here’s a detailed explanation of the advantages of using a gas air compressor:
1. Portability and Mobility:
Gas air compressors are typically more portable and mobile compared to electric compressors. They often feature handles, wheels, or trailers, allowing for easy transportation to different locations. This portability is especially advantageous in situations where compressed air is needed at remote job sites, outdoor events, or areas without access to electricity. Gas air compressors can be easily moved and positioned where they are required.
2. Independence from Electricity:
One of the primary advantages of gas air compressors is their independence from electricity. They are powered by gas engines, which means they do not rely on a direct connection to the electrical grid. This makes them suitable for use in areas where electrical power is limited, unreliable, or unavailable. Gas air compressors offer a reliable source of compressed air even in remote locations or during power outages.
3. Versatility in Fuel Options:
Gas air compressors provide versatility in terms of fuel options. They can be powered by various types of combustible gases, including gasoline, diesel, natural gas, or propane. This flexibility allows users to choose the most readily available or cost-effective fuel source based on their specific requirements. It also makes gas compressors adaptable to different environments and fuel availability in various regions.
4. Higher Power Output:
Gas air compressors typically offer higher power output compared to electric compressors. Gas engines can generate more horsepower, allowing gas compressors to deliver greater air pressure and volume. This higher power output is beneficial when operating pneumatic tools or equipment that require a significant amount of compressed air, such as jackhammers, sandblasters, or heavy-duty impact wrenches.
5. Continuous Operation:
Gas air compressors can provide continuous operation without the need for frequent breaks or cooldown periods. Electric compressors may overheat with prolonged use, requiring intermittent rest periods to cool down. Gas compressors, on the other hand, can operate continuously for longer durations without the risk of overheating. This continuous operation capability is particularly advantageous in demanding applications or situations that require extended periods of compressed air usage.
6. Quick Startup and Response:
Gas air compressors offer quick startup and response times. They can be started instantly by simply pulling a cord or pressing a button, whereas electric compressors may require time to power up and reach optimal operating conditions. Gas compressors provide immediate access to compressed air, allowing for efficient and prompt task completion.
7. Durability and Resistance to Voltage Fluctuations:
Gas air compressors are generally more durable and resistant to voltage fluctuations compared to electric compressors. Electric compressors can be affected by voltage drops or surges, which may impact their performance or cause damage. Gas compressors, however, are less susceptible to voltage-related issues, making them reliable in environments where voltage fluctuations are common.
8. Lower Energy Costs:
Gas air compressors can offer lower energy costs compared to electric compressors, depending on the price of the fuel being used. Gasoline or diesel fuel, for example, may be more cost-effective than electricity in certain regions or applications. This cost advantage can result in significant savings over time, especially for high-demand compressed air operations.
Overall, the advantages of using a gas air compressor over an electric one include portability, independence from electricity, fuel versatility, higher power output, continuous operation capability, quick startup and response times, durability, resistance to voltage fluctuations, and potentially lower energy costs. These advantages make gas air compressors a preferred choice in various industries, remote locations, and applications where mobility, power, and reliability are crucial.


editor by CX 2024-01-15
China best Oil-Less Air Cooled Reciprocating Piston Type Nitrogen Oxygen CNG LPG Hydrogen Gas Compressors for Fuel Filling Stations air compressor for sale
Product Description
Piston compressor is a kind of piston reciprocating motion to make gas pressurization and gas delivery compressor mainly consists of working chamber, transmission parts, body and auxiliary parts. The working chamber is directly used to compress the gas, the piston is driven by the piston rod in the cylinder for reciprocating motion, the volume of the working chamber on both sides of the piston changes in turn, the volume decreases on 1 side of the gas due to the pressure increase through the valve discharge, the volume increases on 1 side due to the reduction of air pressure through the valve to absorb the gas.
We have various of gas compressor, such as Hydrogen compressor, Nitrogen compressor, Natrual gas compressor, Biogas compressor, Ammonia compressor, LPG compressor, CNG compressor, Mix gas compressor and so on.
Advantages of Gas Compressor:
1. High quality material, Stable & Reliable operation
2. Low Maintenance cost & Low noise
3. Easy to install on site and connect with the user’s pipeline system to operate
4. Alarm automatic shutdown to protection machine function
5. High pressure and flow
Lubrication includes : Oil lubrication and oil free lubrication;
Cooling method includes: Water cooling and air cooling.
Installation type includes: Stationary,Mobile and Skid Mounting.
Type includes: V-type, W-type,D-type,Z-type
Product description
Hydrogen compressor
Application
This series of compressors are mainly used for (methanol, natural gas, coal gas) cracking hydrogen production, water electrolysis hydrogen production, hydrogen filling bottle, benzene hydrogenation, tar hydrogenation, catalytic cracking and other hydrogen booster compressors.
Product features:
1. The product has the characteristics of low noise, small vibration, compact structure, stable operation, safety and reliability, and high automation level. It can also be configured with a digital remote display and control system according to customer requirements.
2. It has the function of alarm and shutdown of low compressor oil pressure, low water pressure, high temperature, low intake pressure and high exhaust pressure, which makes the compressor run more reliable.
Structure introduction: The unit consists of compressor host, motor, coupling, flywheel, piping system, cooling system, electrical equipment, and auxiliary equipment.
Technical parameters and specifications
| No | Model | Gas flow (Nm3/h) |
Inlet pressure (Mpa) |
Outlet pressure (Mpa) |
Gas | Power (kw) |
Dimensions (mm) |
| 1 | ZW-0.5/15 | 24 | Atmospheric pressure | 1.5 | Hydrogen | 7.5 | 1600*1300*1250 |
| 2 | ZW-0.16/30-50 | 240 | 3 | 5 | Hydrogen | 11 | 1850*1300*1200 |
| 3 | ZW-0.45/22-26 | 480 | 2.2 | 2.6 | Hydrogen | 11 | 1850*1300*1200 |
| 4 | ZW-0.36 /10-26 | 200 | 1 | 2.6 | Hydrogen | 18.5 | 2000*1350*1300 |
| 5 | ZW-1.2/30 | 60 | Atmospheric pressure | 3 | Hydrogen | 18.5 | 2000*1350*1300 |
| 6 | ZW-1.0/1.0-15 | 100 | 0.1 | 1.5 | Hydrogen | 18.5 | 2000*1350*1300 |
| 7 | ZW-0.28/8-50 | 120 | 0.8 | 5 | Hydrogen | 18.5 | 2100*1350*1150 |
| 8 | ZW-0.3/10-40 | 150 | 1 | 4 | Hydrogen | 22 | 1900*1200*1420 |
| 9 | ZW-0.65/8-22 | 300 | 0.8 | 2.2 | Hydrogen | 22 | 1900*1200*1420 |
| 10 | ZW-0.65/8-25 | 300 | 0.8 | 25 | Hydrogen | 22 | 1900*1200*1420 |
| 11 | ZW-0.4/(9-10)-35 | 180 | 0.9-1 | 3.5 | Hydrogen | 22 | 1900*1200*1420 |
| 12 | ZW-0.8/(9-10)-25 | 400 | 0.9-1 | 2.5 | Hydrogen | 30 | 1900*1200*1420 |
| 13 | DW-2.5/0.5-17 | 200 | 0.05 | 1.7 | Hydrogen | 30 | 2200*2100*1250 |
| 14 | ZW-0.4/(22-25)-60 | 350 | 2.2-2.5 | 6 | Hydrogen | 30 | 2000*1600*1200 |
| 15 | DW-1.35/21-26 | 1500 | 2.1 | 2.6 | Hydrogen | 30 | 2000*1600*1200 |
| 16 | ZW-0.5/(25-31)-43.5 | 720 | 2.5-3.1 | 4.35 | Hydrogen | 30 | 2200*2100*1250 |
| 17 | DW-3.4/0.5-17 | 260 | 0.05 | 1.7 | Hydrogen | 37 | 2200*2100*1250 |
| 18 | DW-1.0/7-25 | 400 | 0.7 | 2.5 | Hydrogen | 37 | 2200*2100*1250 |
| 19 | DW-5.0/8-10 | 2280 | 0.8 | 1 | Hydrogen | 37 | 2200*2100*1250 |
| 20 | DW-1.7/5-15 | 510 | 0.5 | 1.5 | Hydrogen | 37 | 2200*2100*1250 |
| 21 | DW-5.0/-7 | 260 | Atmospheric pressure | 0.7 | Hydrogen | 37 | 2200*2100*1250 |
| 22 | DW-3.8/1-7 | 360 | 0.1 | 0.7 | Hydrogen | 37 | 2200*2100*1250 |
| 23 | DW-6.5/8 | 330 | Atmospheric pressure | 0.8 | Hydrogen | 45 | 2500*2100*1400 |
| 24 | DW-5.0/8-10 | 2280 | 0.8 | 1 | Hydrogen | 45 | 2500*2100*1400 |
| 25 | DW-8.4/6 | 500 | Atmospheric pressure | 0.6 | Hydrogen | 55 | 2500*2100*1400 |
| 26 | DW-0.7/(20-23)-60 | 840 | 2-2.3 | 6 | Hydrogen | 55 | 2500*2100*1400 |
| 27 | DW-1.8/47-57 | 4380 | 4.7 | 5.7 | Hydrogen | 75 | 2500*2100*1400 |
| 28 | VW-5.8/0.7-15 | 510 | 0.07 | 1.5 | Hydrogen | 75 | 2500*2100*1400 |
| 29 | DW-10/7 | 510 | Atmospheric pressure | 0.7 | Hydrogen | 75 | 2500*2100*1400 |
| 30 | VW-4.9/2-20 | 750 | 0.2 | 2 | Hydrogen | 90 | 2800*2100*1400 |
| 31 | DW-1.8/15-40 | 1500 | 1.5 | 4 | Hydrogen | 90 | 2800*2100*1400 |
| 32 | DW-5/25-30 | 7000 | 2.5 | 3 | Hydrogen | 90 | 2800*2100*1400 |
| 33 | DW-0.9/20-80 | 1000 | 2 | 8 | Hydrogen | 90 | 2800*2100*1400 |
| 34 | DW-25/3.5-4.5 | 5700 | 0.35 | 0.45 | Hydrogen | 90 | 2800*2100*1400 |
| 35 | DW-1.5/(8-12)-50 | 800 | 0.8-1.2 | 5 | Hydrogen | 90 | 2800*2100*1400 |
| 36 | DW-15/7 | 780 | Atmospheric pressure | 0.7 | Hydrogen | 90 | 2800*2100*1400 |
| 37 | DW-5.5/2-20 | 840 | 0.2 | 2 | Hydrogen | 110 | 3400*2200*1300 |
| 38 | DW-11/0.5-13 | 840 | 0.05 | 1.3 | Hydrogen | 110 | 3400*2200*1300 |
| 39 | DW-14.5/0.04-20 | 780 | 0.004 | 2 | Hydrogen | 132 | 4300*2900*1700 |
| 40 | DW-2.5/10-40 | 1400 | 1 | 4 | Hydrogen | 132 | 4200*2900*1700 |
| 41 | DW-16/0.8-8 | 2460 | 0.08 | 0.8 | Hydrogen | 160 | 4800*3100*1800 |
| 42 | DW-1.3/20-150 | 1400 | 2 | 15 | Hydrogen | 185 | 5000*3100*1800 |
| 43 | DW-16/2-20 | 1500 | 0.2 | 2 | Hydrogen | 28 | 6500*3600*1800 |
Customized is accepted , Pls provide the following information to us ,then we will do the technical proposal and best price to you.
1.Flow rate: _______Nm3/h
2.Gas Media : ______ Hydrogen or Natural Gas or Oxygen or other gas
3.Inlet pressure: ___bar(g)
4.Inlet temperature:_____ºC
5.Outlet pressure:____bar(g)
6.Outlet temperature:____ºC
7.Installation location: _____indoor or outdoor
8.Location ambient temperature: ____ºC
9.Power supply: _V/ _Hz/ _3Ph
10.Cooling method for gas: air cooling or water cooing
Picture display
Applications
Company strength display
HangZhou CZPT Gas Equipment Co., Ltd. is a manufacturer engaged in the research and development, design and production of gas compressors. The company has its own production technology, processing equipment and assembly technology, and has many years of experience in the production of various flammable and explosive special gas compressors.
Huayan compressor products cover almost all gas media, up to 6th-stage compression and 3000kw power. Products can be customized according to customer requirements to better meet customer needs. The products are mainly used in gas compressors in the petroleum industry, chemical and natural gas compressors, industrial compressors, compressors for waste gas treatment and biogas utilization, and compressors for special gases.
After Sales Service
1.Quick response within 2 to 8 hours, with a reaction rate exceeding 98%;
2. 24-hour telephone service, please feel free to contact us;
3. The whole machine is guaranteed for 1 year (excluding pipelines and human factors);
4. Provide consulting service for the service life of the whole machine, and provide 24-hour technical support via email;
5. On-site installation and commissioning by our experienced technicians;
Exhibition Display
Certificate display
Packaging and Shipping
FAQ
1.How to get a prompt quotation of gas compressor ?
1)Flow Rate/Capacity : ___ Nm3/h
2)Suction/ Inlet Pressure : ____ Bar
3)Discharge/Outlet Pressure :____ Bar
4)Gas Medium :_____
5)Voltage and Frequency : ____ V/PH/HZ
2.How long is delivery time ?
Delivery time is around the 30-90 days .
3.What about the voltage of products? Can they be customized?
Yes, the voltage can be customized according to your inquire.
4.Can you accept OEM orders?
Yes, OEM orders is highly welcome.
5.Will you provide some spare parts of the machines?
Yes, we will .
| After-sales Service: | Proive After-Sales Service |
|---|---|
| Warranty: | 18monthes |
| Lubrication Style: | Lubricated |
| Cooling System: | Water Cooling |
| Cylinder Arrangement: | Balanced Opposed Arrangement |
| Cylinder Position: | Angular |
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|

How to Choose the Right Air Compressor
An air compressor uses pressurized air to power a variety of tools. They are most commonly used to power nailers and impact wrenches. Other popular uses for air compressors include paint sprayers and impact wrenches. While all air compressors have the same basic construction, their specialty differs. Ultimately, their differences come down to the amount of air they can push. Read on for information on each type of air compressor. These tools are great for many different purposes, and choosing the right air compressor depends on your specific needs.
Electric motor
While purchasing an electric motor for air compressor, compatibility is a key factor. Not all motors work with the same type of air compressor, so it’s important to check the manufacturer’s instructions before purchasing. By doing this, you can avoid wasting money on an incompatible motor. Another important consideration is speed. A motor’s speed is its rate of rotation, measured in revolutions per minute. It is critical that you purchase a motor with sufficient speed to meet the needs of your air compressor.
Typically, an electric motor for air compressor is 1.5 hp. It is ideal for use with medical equipment and metal-cutting machines. It also performs well under continuous operation and offers a high efficiency and energy-saving performance. Moreover, it features an attractive price, making it a good choice for a wide range of applications. If you are looking for a motor for an air compressor, look no further than a ZYS series.
A motor’s protection class indicates how the motor will operate. Protection classes are specified by the IEC 60034-5. These are stated with two digits and represent the protection against solid objects and water. For example, an IP23 rating means that the motor will be protected from solid objects, while IP54 means that it will protect from dust and water sprayed from all directions. It is vital to choose a motor with the correct protection class for your air compressor.
When choosing an electric motor, you should consider whether it’s compatible with the brand of air compressor. Some may be compatible, while others may require advanced electronics skills to repair. However, most air compressors are covered by warranty, so it’s important to check with the manufacturer if the warranty is still in effect before you spend a dime on a replacement. The motor should be replaced if it has failed to perform as designed.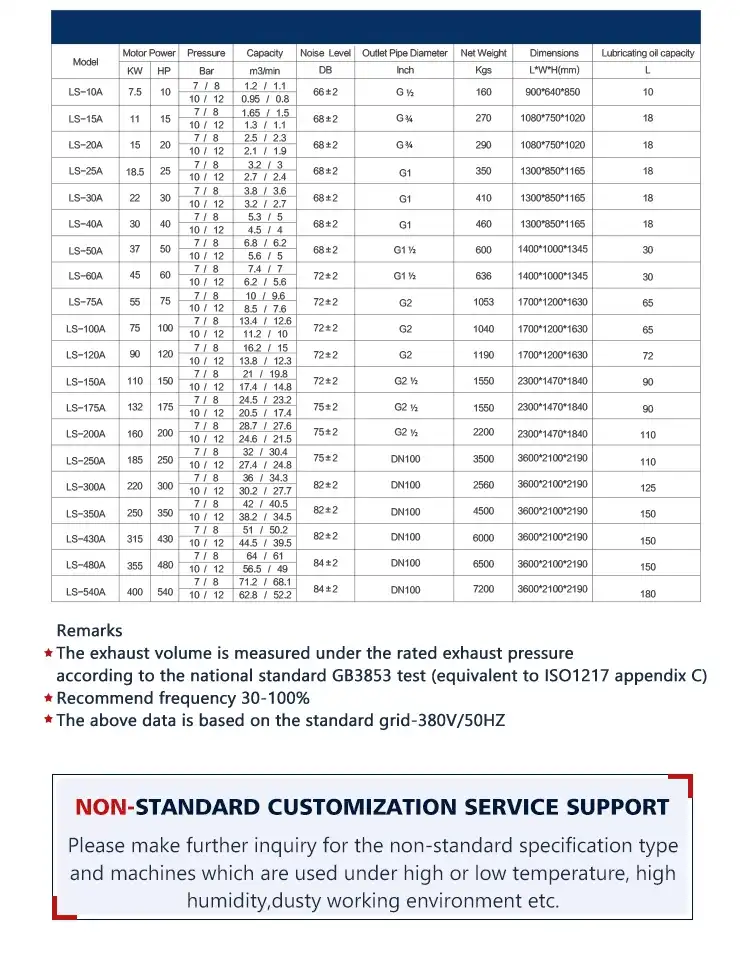
Oil bath
Air compressors require proper lubrication to function efficiently. The piston must draw air with minimal friction. Depending on their design, air compressors can either be oil-lubricated or oil-free. The former uses oil to reduce piston friction, while the latter splashes it on the cylinder bearings and walls. Such air compressors are commonly known as oil-flooded air compressors. In order to keep their oil baths clean, they are recommended for use in locations with high dust levels.
Start/stop control
An air compressor can be controlled by a start/stop control. This type of control sends a signal to the main motor that activates the compressor when the demand for air falls below a preset limit. This control strategy is effective for smaller air compressors and can be useful for reducing energy costs. Start/stop control is most effective in applications where air pressure does not change frequently and where the compressor is not required to run continuously.
To troubleshoot this problem, you need to check the power supply of your compressor. To check the supply side, use a voltage monitor to determine if power is flowing to the compressor. Ensure that the power supply to the compressor is steady and stable at all times. If it fluctuates, the compressor may not start or stop as expected. If you cannot find the problem with the air compressor power supply, it may be time to replace it.
In addition to the start/stop control, you may want to purchase additional air receivers for your air compressor. These can increase the capacity of air stored and reduce the number of times it starts and stops. Another way to decrease the number of starts per hour is to add more air receivers. Then, you can adjust the control to match your requirements. You can also install a pressure gauge that monitors the compressor’s performance.
Start/stop control for air compressors can be complex, but the basic components are relatively easy to understand. One way to test them is to turn the compressor on or off. It is usually located on the exterior of the motor. If you’re unsure of the location of these components, check the capacitors and make sure that the air compressor is not running while you’re not using it. If it does, try to remove the capacitor.
Variable displacement control is another way to adjust the amount of air flowing into the compressor. By controlling the amount of air, the control can delay the use of additional compressors until more required air is available. In addition to this, the device can also monitor the energy used in the compressor. This control method can result in substantial energy savings. You can even save on the amount of electricity by using variable displacement control. It is essential for efficient compressed air systems.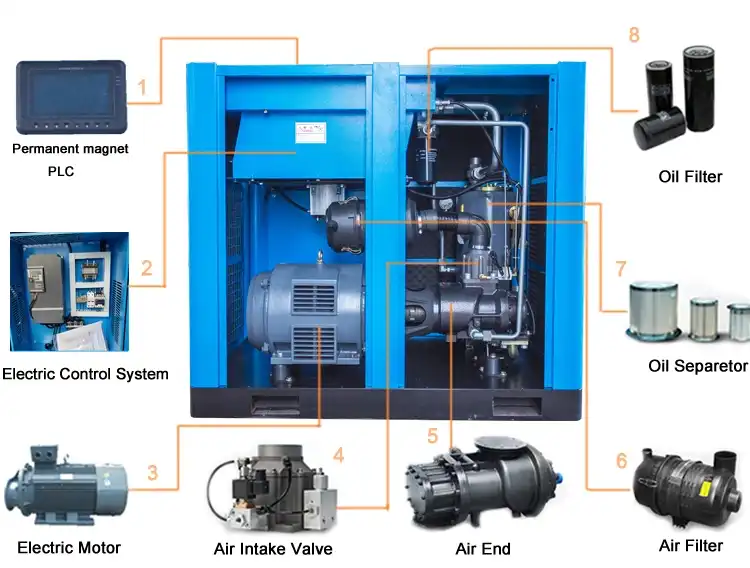
Variable speed drive
A VFD, or variable frequency drive, is a type of electric motor that adjusts its speed to match the demand for air. It is an efficient way to reduce energy costs and improve system reliability. In fact, studies have shown that a 20% reduction in motor speed can save up to 50% of energy. In addition, a VFD can monitor additional variables such as compressor oil pressure and motor temperature. By eliminating manual checks, a VFD will improve the performance of the application and reduce operating costs.
In addition to reducing energy costs, variable-speed drives also increase productivity. A variable-speed air compressor reduces the risk of system leaks by 30 percent. It also reduces the risk of system leaks by reducing pressure in the system. Because of these advantages, many governments are promoting this technology in their industries. Many even offer incentives to help companies upgrade to variable-speed drives. Therefore, the variable-speed drive can benefit many air compressor installations.
One major benefit of a variable-speed drive is its ability to optimize energy use. Variable frequency drives are able to ramp up and down to match the demand for air. The goal is to optimize the pressure and flow in the system so that the best “dead band” occurs between forty percent and eighty percent of full load. A variable-speed compressor will also increase energy efficiency because of its programmability.
A variable-speed air compressor can also be used to control the amount of air that is compressed by the system. This feature adjusts the frequency of power supplied to the motor based on the demand. If the demand for air is low, the frequency of the motor will reduce to save energy. On the other hand, if there is an excess demand for air, the variable-speed compressor will increase its speed. In addition, this type of air compressor is more efficient than its fixed-speed counterpart.
A VFD has many benefits for compressed air systems. First, it helps stabilize the pressure in the pipe network, thereby reducing the power losses due to upstream pressure. It also helps reduce the power consumption caused by fluctuations in upward pressure. Its benefits are also far-reaching. And as long as the air pressure and air supply is properly sized, a VFD will help optimize the efficiency of compressed air systems.


editor by CX 2023-05-16
China 0.55KW0.75HP Low noise oil free reciprocating piston air compressor pump head with high quality
Error:获取session失败,

Choosing an Air Compressor
Considering a new Air Compressor? Here are some tips to make the decision easier. Learn the pros and cons of each type, including the differences between oil-injected and oil-free models, single stage and positive displacement. In addition, learn more about the different technologies that are available for your air compressor. It is important to choose an appropriate unit for the type of work you do. Here are some of the best compressors available today.
Positive displacement
There are several different types of air compressors, but most are positive displacement air compressors. They use a rotary or reciprocating component to compress air. The reciprocating component compresses air by reducing the volume of the chamber. Positive displacement compressors are used in bicycle pumps, chemical plants, and refrigerators. Positive displacement air compressors use multiple inlet ports. Despite the various types, the principle of operation remains the same.
Another type of positive displacement air compressor is a reciprocating piston. The piston inside a cylinder moves up and down, causing the compressed air to fill the upper part of the cylinder. These air compressors are used in a variety of different applications, including blowing bottles and gas pipelines. These air compressors can be water-cooled, lubricated, or non-lubricated. Different types have different capacities and air pressures.
A positive displacement flowmeter uses a rotating chamber that divides continuous fluid into discrete portions. The number of times the chamber is filled and discharged can be used to estimate the flow rate. The rotation speed of the measuring chamber is directly proportional to the flow rate. The drawbacks of this type of positive displacement flowmeter are that it is prone to jamming. If the fluid contains particles, it may be too thick for the meter to determine flow rate.
A negative displacement air compressor was invented in 1860 and is the oldest type of compressor. It uses two lobes positioned in a circular cavity. One rotor is connected to an engine, while the other pushes the other one to spin in the opposite direction. Negative displacement compressors are low-maintenance, but they do require more precision. They are often used in nuclear power plants because they use the kinetic energy of the rotating elements to produce pressure.
Oil-injected
Oil-flooded or oil-injected air compressors use liquid to seal and lubricate moving parts and reduce noise. Oil-flooded air compressors are effective for a variety of pneumatic tools and accessories. Some models have a thermostat that controls the amount of oil used during operation. Other types of oil-flooded air compressors are piston-type models. Here is an overview of the basic differences between these two air compressors.
An oil-injected air compressor is more expensive than a comparable oil-free air compressor, but its advantages far outweigh its disadvantages. An oil-free compressor is quieter, requires less maintenance, and has a lower price tag. It also offers a greater degree of air purity. A number of other advantages may also make this type of air compressor the better choice for many industrial settings. If you need a high-pressure compressor in a tight space, consider the benefits of an oil-free system.
Oil-injected air compressors require more maintenance than oil-free models. Both types of air compressors offer similar capacity and ISO 8573-1 Class 0 and 1-2 purity, but the oil-injected systems require more air-treatment components. They require an activated carbon filter and coalescing filter. Oil-injected air compressors will likely remain the standard for industrial air compressors for many years. And since their performance and efficiency are comparable, it may be worthwhile to invest in some point-of-use air treatment.
Both types of air compressors have their benefits. However, choosing between oil-free and oil-injected air compressors is not as straightforward as you might think. Whichever type you choose, make sure it will meet your needs. The benefits of an oil-injected air compressor outweigh their disadvantages. In general, oil-injected air compressors are more durable and can last longer than oil-free models. The only downside is their higher price.
Oil-free
When choosing an air compressor for your company, you’ll need to determine what it is going to be used for. For example, if you’re planning on using it to power multiple workers, you should consider getting an oil-free compressor. An oil-free compressor, on the other hand, is quieter and can power several workers at a time. If you’re a contractor, the most important consideration will be the type of jobs you’ll be doing. Higher air pressure means greater demand for air flow, and more pressure can damage the equipment.
Oil-free compressed air is certified 100% free of contaminants. Technically, oil-free air is not completely free of foreign matter, but it is extremely low within the limits of practical air quality. A technically oil-free air compressor might have a total oil level of 0.003 mg/m3. If you’re in need of a technically oil-free air compressor, you must install an air treatment equipment after your current compressor.
If you’re in the manufacturing industry, a good oil-free air compressor will save you money and reduce your environmental impact. Many of these tools require air compressors to work, and this equipment will ensure that they don’t get contaminated. To buy the best oil-free compressor, you should learn a bit about the different terms used by compressor repair companies. ACFM, for example, is the amount of air that can be compressed in one minute at rated conditions.
When you’re using an oil-free air compressor, you should know that the overall life of the device will be much shorter. Compared to an oil-flooded rotary screw air compressor, an oil-free compressor typically has a lifespan of 50 thousand hours. But it’s important to understand that this type of compressor can still cause damage to piping and processes. Therefore, you should choose an oil-free compressor when you need to clean air for your business.
Single-stage
A single-stage air compressor, also known as a piston air compressor, compresses air only once before storing it in a cylinder. This stored air has enough energy to power a variety of pneumatic tools, such as screwdrivers, chisels, and wrenches. These units are also ideally suited for low-flow applications and are widely used in gas stations, auto shops, and various manufacturing plants.
A single-stage air compressor uses two valves – one for inlet and one for outlet – to transfer compressed air. Both valves are actuated by springs. The inlet valve has a slight curvature to provide protection from damage. The compressor’s outlet valve opens when the pressure in the cylinder is higher than the pressure in the storage tank. The piston moves very quickly inside the cylinder, exerting a high amount of force throughout the compression process. This high piston speed is a common cause of compressor wear and tear.
A single-stage air compressor is ideal for smaller tradesmen and small construction crews. Its lightweight and compact design make it easier to transport and store. While it may be tempting to buy the first cheap air compressor you see, it’s important to balance the price against performance to choose the right air compressor for your needs. The best single-stage air compressor is one that provides excellent performance and durability. Its two-stage counterpart is designed for larger construction teams and large applications.
The main difference between a single-stage and a two-stage air compressor lies in their capacity. A single-stage air compressor compresses air only once and delivers it into the storage tank, while a two-stage compressor compresses it twice, creating double the pressure. Because of this, single-stage air compressors are cheaper and versatile than their counterparts, which means that they can be used for multiple purposes.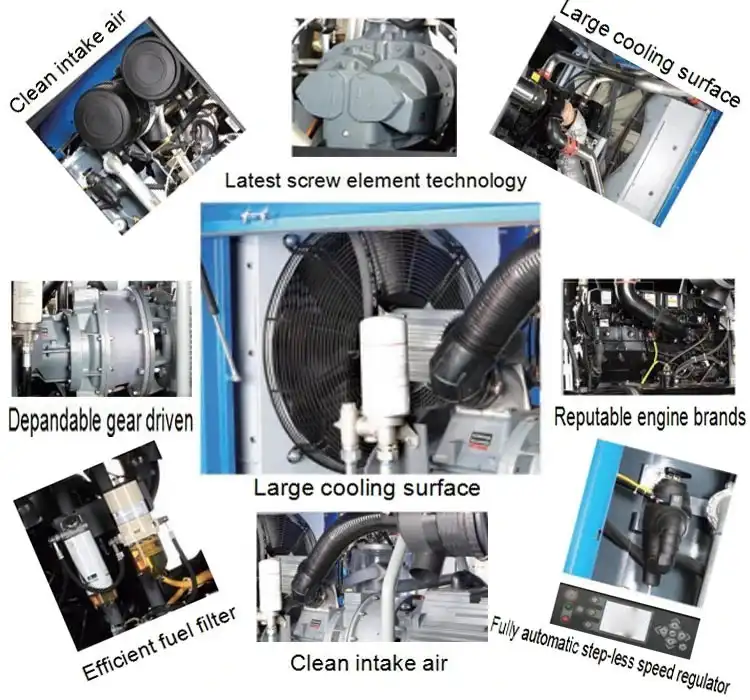
Low-noise
A low-noise air compressor is a type of industrial compressor that is less noisy than regular air compressors. These are generally smaller machines designed for smaller factories and workshops with a few to several employees. They are designed to handle mid-weight volumes of compressed air per day. This type of compressor is especially useful for smaller manufacturing businesses that need to produce compressed air for medical applications. Small breweries can also benefit from the low-noise capabilities of these compressors.
Low-noise air compressors come in various sizes and features. For smaller jobs, you can purchase a one-gallon model that is lightweight and portable. For larger jobs, you can purchase one with a larger tank that can provide more pressure for longer jobs. However, a larger tank will make the compressor heavier and harder to transport. To avoid this, make sure to check the size of the tank and how much power it can handle.
Considering a low-noise air compressor for your business? If so, you’ve come to the right place. There are a variety of affordable and dependable low-noise options to choose from. A CAT 10020C, for example, is designed to provide high-volume air to many outlets at once. A CAT 10020C comes with a 10-gallon tank, wheels, and a carrying handle.
Noise levels can also affect the productivity of employees. When employees work with air compressors in close proximity to each other, they may develop tinnitus. If employees are free from tinnitus because of the loud noise, they are likely to work more efficiently. Moreover, it will be easier for them to focus and communicate efficiently. If you need a compressor, a low-noise one is an excellent choice.


editor by CX 2023-04-23
China High Pressure Reciprocating Piston High Pressure Air Compressor (K80SH-15150) manufacturer
Solution Description
Large Pressure Reciprocating Piston High Stress Air Compressor (K80SH-15150)
The ADEKOM High Force Air Compressor with the software of a series of most recent systems including” polygon cylindrical straight-movement valve” and strict high quality handle, high Oil-Totally free Air Compressor is a product developed for ongoing procedure even in harsh atmosphere. Pressure Air Compressor is CZPT to run 24 hour all around-the-clock securely as a classic weighty piston kind air compressor.
This specially made compressor employs considerably less gas, has a longer working existence, operates considerably quieter and operates almost vibration-totally free. The ADEKOM Piston Air Compressor is a superior designed item outstanding in its class.
Quite reduced oil use to be eco-friendly
Reduced pace for power saving
Prolonged upkeep cycle for high reliability
Stable stress provide
Complex Parameters:
| model | Model | Discharge ability | Discharge strain | Compression stage | Motor output (Kw) | Speed | Weight (kg) | Proportions | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (Nm3/min) | (Mpa) | (r.p.m) | L×W×H(mm) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| K80SH | 80SH-15150 | 0.seventy five | 15 | 4 | 15 | 630 | 680 | 1678×1035×998 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| K80SH | 80SH-15250 | 0.seventy five | 25 | 630 | 1678×1035×998 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| K81SH | 81SH-15350 | 0.7 | 35 | 630 | 17 Fax : 769 88803230 Web : dgadekom
###
###
###
###
###
###
How to Choose the Right Air CompressorAn air compressor uses pressurized air to power a variety of tools. They are most commonly used to power nailers and impact wrenches. Other popular uses for air compressors include paint sprayers and impact wrenches. While all air compressors have the same basic construction, their specialty differs. Ultimately, their differences come down to the amount of air they can push. Read on for information on each type of air compressor. These tools are great for many different purposes, and choosing the right air compressor depends on your specific needs. Electric motorWhile purchasing an electric motor for air compressor, compatibility is a key factor. Not all motors work with the same type of air compressor, so it’s important to check the manufacturer’s instructions before purchasing. By doing this, you can avoid wasting money on an incompatible motor. Another important consideration is speed. A motor’s speed is its rate of rotation, measured in revolutions per minute. It is critical that you purchase a motor with sufficient speed to meet the needs of your air compressor. Oil bathAir compressors require proper lubrication to function efficiently. The piston must draw air with minimal friction. Depending on their design, air compressors can either be oil-lubricated or oil-free. The former uses oil to reduce piston friction, while the latter splashes it on the cylinder bearings and walls. Such air compressors are commonly known as oil-flooded air compressors. In order to keep their oil baths clean, they are recommended for use in locations with high dust levels. Start/stop controlAn air compressor can be controlled by a start/stop control. This type of control sends a signal to the main motor that activates the compressor when the demand for air falls below a preset limit. This control strategy is effective for smaller air compressors and can be useful for reducing energy costs. Start/stop control is most effective in applications where air pressure does not change frequently and where the compressor is not required to run continuously. Variable speed driveA VFD, or variable frequency drive, is a type of electric motor that adjusts its speed to match the demand for air. It is an efficient way to reduce energy costs and improve system reliability. In fact, studies have shown that a 20% reduction in motor speed can save up to 50% of energy. In addition, a VFD can monitor additional variables such as compressor oil pressure and motor temperature. By eliminating manual checks, a VFD will improve the performance of the application and reduce operating costs.
China Xinya CE Approved 220V 8bar 24L 50L Electrical Direct-Connected Reciprocating Portable Piston Oil Lubricated Direct Driven Air Compressor 12v air compressorMerchandise Description
Considering that 1988 Solution Description
Xinya CEFL Style 24L 50L CE Immediate Pushed Air Compressor
Electric powered immediate pushed oil lubricated air compressors
Set up Instructions Software Packaging & Transport
For Design: CEFL24/fifty
Similar products Organization Profile Excellent Maker We are ZHangZhoug crucial non-public company and groundbreaking backbone company. We have the most sophisticated engineering in each manufacturing and management. We have a quite powerful Analysis& Advancement staff. We carry on stringent checking and management to merchandise by a lot of varieties of advanced equipment with third-social gathering certified laboratory.Welcome to inquiry! Certifications Exhibitions FAQ Q: Are you producer or buying and selling factory? Q: What is your MOQ?
Q: May OEM? Q: May I get 1pc sample first? And How extended? Q: What is your Payment conditions? Q: What about the guarantee? Q: Exactly where is the landing port? Q: May I go to your manufacturing facility? In which? You should truly feel cost-free to contact us,thank you.
###
###
###
###
###
###
###
###
###
###
###
###
A Buyer’s Guide to Air Compressor TypesThere are many types of Air Compressors, and it’s important to understand what each type has to offer. In this article, we’ll discuss single stage air compressors, low-noise compressors, and models with two pistons. But, before you buy an Air Compressor, be sure to read our buyer’s guide to the various types. This way, you’ll have all of the information you need to make the right decision for your business. Single-stage air compressorsA single-stage air compressor is an excellent choice for most general-purpose purposes. They provide enough power to operate pneumatic tools, and they produce less heat. Single-stage air compressors, however, are not suitable for heavy-duty industrial uses. However, they can be used in various applications, including auto shops, gas stations, and various manufacturing facilities. They are also suitable for borewells and other high-pressure places. Rotary vane compressorsRotary vane compressors use a centrifugal pump to compress air. The rotor is set eccentrically in the housing, which almost touches the vane. As the rotor turns, the air that enters the pump is trapped between the vanes. This compressed air undergoes compression as the rotor rotates. Vanes are small pieces of carbon fiber or graphite composite. Vanes may be made of different materials depending on the application. Rotary vane compressors with low-noise modelsIf you are looking for a rotary vane air compressor, you have come to the right place. CZPT’s LV Series rotary vane compressors offer low-noise models, compact size, and robust integration. In addition to their low-noise features, they feature large filter systems to deliver high-quality compressed air. The LV Series models also feature CZPT’s reputation for reliability and quality. Rotary vane compressors with two pistonsThe rotary vane and rotary screw compressors are similar in application, but both have different advantages and disadvantages. This article will compare the benefits of each and highlight the differences between them. While both are commonly used in industrial applications, rotary vane compressors are preferred by many industries. These compressors also have a wide range of uses, ranging from automotive air tool operation to milking machines. These compressors also have the advantage of being quieter than piston-powered ones.
China best Italian Type H Belt Driven Reciprocating Air Compressor for Industrial Equipment near me supplier
Item Description
Merchandise Description
Item Parameters Packaging & Transport
1) Packing Specifics 2) Shipping Particulars Company Profile ZHangZhoug Jinjin Motor Co., Ltd, located in Zeguo City, HangZhou, HangZhou Metropolis, China, enjoys hassle-free land, sea and air transportation community. We are specialized in air compressor, pneumatic tools and spray gun For air compressore, there is oil totally free oiless air compressor and piston oil air compressore. Spray gun include washing gun, tire inflating gun and accessory ets. About pneumatic instruments, there are air influence wrench collection, pneumatic screwdriver series, air die grinder series, tire pressre gue, air angle sander. We have obtained ISO90001-2008 top quality certificate, CE certificate and CCC certificate. Our merchandise are widely exported to above 50 nations and areas, these kinds of as east Europe, Southeast Asia, South The us, Middle East, Africa and many others. In the meantime, we have stored well contact with a lot of buying and selling organizations at residence and abroad for cooperation connection. “Reliable high quality, Exceptional provider, Reasonable price tag, Well timed supply” is our business persistent pursuit. Hunting forward to be your long time period business companion. Set up Guidelines Comprehensive Pictures FAQ Q:Why choose us? Q:What is your MOQ? Q:What about your guarantee? Q:how about your payment way ? Q:Can you make OEM/ODM get?
what to see in an air compressorIf you need to have to acquire an air compressor, you need to know what to seem for. The kinds of air compressors on the market are categorised in accordance to their CFM ranking, safety devices, and pumps. There are several differences between lubricated and oil-free of charge air compressors that you ought to know before purchasing. To greater understand the distinction among these sorts of air compressors, study on. This article will guide you through these variances. PumpIf you are searching for a good quality air compressor, you have arrive to the right spot. A very good air compressor pump will supply substantial pressure for anything from tires to boats and far more. There are hundreds of diverse types to pick from, and the great issue about getting 1 from a Chinese maker is that they have so many possibilities. A lot more importantly, Chinese manufacturers can customise air equipment this sort of as air compressors at low rates. basic safety productsThere are a number of safety attributes you need to verify when making use of an air compressor. First, verify the link of the air filter to the air. If they occur unfastened, parts could separate and lead to harm. Yet another critical protection feature is the shut-off valve. When operating close to compressed air, the shut-off valve need to be within effortless attain and visibility. Relocating elements and other products have to be secured with protecting addresses. Verify security valve and replace ruined areas. CFM ScoreAn air compressor’s PSI and CFM rankings indicate the stress and volume it can provide. PSI stands for lbs for every square inch and measures the force and strain contained in 1 square inch of air. These two indicators are equally crucial when selecting an air compressor. If you need to have a great deal of compressed air for a distinct application, you will want a larger psi compressor. Also, if you are making use of compressed air in a more compact software, a low cfm compressor will not provide ample power to fulfill your wants. Lack of oil and lubricationOil-free of charge air compressors have a more compact footprint and demand less routine maintenance than oil-lubricated air compressors. Though oil-lubricated air compressors are a lot more costly and heavier than oil-cost-free air compressors, they are also excellent for stationary use. The positive aspects of oil-free of charge air compressors incorporate increased toughness and reduce routine maintenance charges. The positive aspects and drawbacks of every type are reviewed below. noise amountIf you are asking yourself what the sounds stage of an air compressor is, the solution relies upon on your certain tools and operating environment situations. Typically, air compressors create forty to ninety decibels of sounds. Though the decrease the decibel level, the quieter the compressor will be. Bigger, more potent air compressors generate higher sound amounts than their little brothers. But no matter how large the air compressors are, it really is a good idea to put on listening to safety although working about them. |