Product Description
| Model | HK-D04/08-A4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Operation control mode | Pressure start and stop | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rated pressure (MPa) | 0.8 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Maximum pressure ( MPa) | 1.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Air flow (M³/min) | 0.4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Running speed ( R/min) | 3200 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drive mode | Belt drive | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Exhaust air temperature ( ºC ) | ≤ambient temperature
Can air compressors be used for gas compression and storage?Yes, air compressors can be used for gas compression and storage. While air compressors are commonly used to compress and store air, they can also be utilized for compressing and storing other gases, depending on the specific application requirements. Here’s how air compressors can be used for gas compression and storage: Gas Compression: Air compressors can compress various gases by utilizing the same principles applied to compressing air. The compressor takes in the gas at a certain pressure, and through the compression process, it increases the pressure and reduces the volume of the gas. This compressed gas can then be used for different purposes, such as in industrial processes, gas pipelines, or storage systems. Gas Storage: Air compressors can also be used for gas storage by compressing the gas into storage vessels or tanks. The compressed gas is stored at high pressure within these vessels until it is needed for use. Gas storage is commonly employed in industries where a continuous and reliable supply of gas is required, such as in natural gas storage facilities or for storing compressed natural gas (CNG) used as a fuel for vehicles. Gas Types: While air compressors are primarily designed for compressing air, they can be adapted to handle various gases, including but not limited to:
It’s important to note that when using air compressors for gas compression and storage, certain considerations must be taken into account. These include compatibility of the compressor materials with the specific gas being compressed, ensuring proper sealing to prevent gas leaks, and adhering to safety regulations and guidelines for handling and storing compressed gases. By leveraging the capabilities of air compressors, it is possible to compress and store gases efficiently, providing a reliable supply for various industrial, commercial, and residential applications.
How does the horsepower of an air compressor affect its capabilities?The horsepower of an air compressor is a crucial factor that directly impacts its capabilities and performance. Here’s a closer look at how the horsepower rating affects an air compressor: Power Output: The horsepower rating of an air compressor indicates its power output or the rate at which it can perform work. Generally, a higher horsepower rating translates to a greater power output, allowing the air compressor to deliver more compressed air per unit of time. This increased power output enables the compressor to operate pneumatic tools and equipment that require higher air pressure or greater airflow. Air Pressure: The horsepower of an air compressor is directly related to the air pressure it can generate. Air compressors with higher horsepower ratings have the capacity to produce higher air pressures. This is particularly important when operating tools or machinery that require specific air pressure levels to function optimally. For example, heavy-duty pneumatic tools like jackhammers or impact wrenches may require higher air pressure to deliver the necessary force. Air Volume: In addition to air pressure, the horsepower of an air compressor also affects the air volume or airflow it can provide. Higher horsepower compressors can deliver greater volumes of compressed air, measured in cubic feet per minute (CFM). This increased airflow is beneficial when using pneumatic tools that require a continuous supply of compressed air, such as paint sprayers or sandblasters. Duty Cycle: The horsepower rating of an air compressor can also influence its duty cycle. The duty cycle refers to the amount of time an air compressor can operate continuously before it needs to rest and cool down. Higher horsepower compressors often have larger and more robust components, allowing them to handle heavier workloads and operate for longer periods without overheating. This is particularly important in demanding applications where continuous and uninterrupted operation is required. Size and Portability: It’s worth noting that the horsepower rating can also affect the physical size and portability of an air compressor. Higher horsepower compressors tend to be larger and heavier due to the need for more substantial motors and components to generate the increased power output. This can impact the ease of transportation and maneuverability, especially in portable or mobile applications. When selecting an air compressor, it is essential to consider the specific requirements of your intended applications. Factors such as desired air pressure, airflow, duty cycle, and portability should be taken into account. It’s important to choose an air compressor with a horsepower rating that aligns with the demands of the tools and equipment you plan to operate, ensuring optimal performance and efficiency. Consulting the manufacturer’s specifications and guidelines can provide valuable information on how the horsepower rating of an air compressor corresponds to its capabilities and suitability for different tasks.
How is air pressure measured in air compressors?Air pressure in air compressors is typically measured using one of two common units: pounds per square inch (PSI) or bar. Here’s a brief explanation of how air pressure is measured in air compressors: 1. Pounds per Square Inch (PSI): PSI is the most widely used unit of pressure measurement in air compressors, especially in North America. It represents the force exerted by one pound of force over an area of one square inch. Air pressure gauges on air compressors often display pressure readings in PSI, allowing users to monitor and adjust the pressure accordingly. 2. Bar: Bar is another unit of pressure commonly used in air compressors, particularly in Europe and many other parts of the world. It is a metric unit of pressure equal to 100,000 pascals (Pa). Air compressors may have pressure gauges that display readings in bar, providing an alternative measurement option for users in those regions. To measure air pressure in an air compressor, a pressure gauge is typically installed on the compressor’s outlet or receiver tank. The gauge is designed to measure the force exerted by the compressed air and display the reading in the specified unit, such as PSI or bar. It’s important to note that the air pressure indicated on the gauge represents the pressure at a specific point in the air compressor system, typically at the outlet or tank. The actual pressure experienced at the point of use may vary due to factors such as pressure drop in the air lines or restrictions caused by fittings and tools. When using an air compressor, it is essential to set the pressure to the appropriate level required for the specific application. Different tools and equipment have different pressure requirements, and exceeding the recommended pressure can lead to damage or unsafe operation. Most air compressors allow users to adjust the pressure output using a pressure regulator or similar control mechanism. Regular monitoring of the air pressure in an air compressor is crucial to ensure optimal performance, efficiency, and safe operation. By understanding the units of measurement and using pressure gauges appropriately, users can maintain the desired air pressure levels in their air compressor systems.
China OEM Hot Sale Oil-Free Rotary Screw Gas Air Compressor Large Air Displacement mini air compressorProduct Description
OFAC oil-free screw air compressor used Japanese Mitsui’s original technology, who is the only maintenance service provider in China.
F– air cooling method S– water cooling method FAQ Q1: Warranty terms of your machine? Q2: Will you provide some spare parts of the machines? Q3: What about product package? Q4: Can you use our brand? Q5: How long will you take to arrange production? Q6: How Many Staff Are There In your Factory? Q8: What the exactly address of your factory?
.shipping-cost-tm .tm-status-off{background: none;padding:0;color: #1470cc}
Can Gas Air Compressors Be Used in Construction Projects?Gas air compressors are widely used in construction projects due to their portability, versatility, and ability to provide the necessary compressed air for various applications. They are an essential tool in the construction industry, enabling the efficient and effective operation of pneumatic tools and equipment. Here’s a detailed explanation of how gas air compressors are used in construction projects: 1. Powering Pneumatic Tools: Gas air compressors are commonly used to power a wide range of pneumatic tools on construction sites. These tools include jackhammers, nail guns, impact wrenches, concrete breakers, air drills, sanders, grinders, and paint sprayers. The compressed air generated by the gas air compressor provides the necessary force and power for efficient operation of these tools, enabling tasks such as concrete demolition, fastening, surface preparation, and finishing. 2. Air Blow and Cleaning Operations: In construction projects, there is often a need to clean debris, dust, and dirt from work areas, equipment, and surfaces. Gas air compressors are used to generate high-pressure air for air blow and cleaning operations. This helps maintain cleanliness, remove loose materials, and prepare surfaces for further work, such as painting or coating. 3. Operating Pneumatic Systems: Gas air compressors are employed to operate various pneumatic systems in construction projects. These systems include pneumatic control devices, pneumatic cylinders, and pneumatic actuators. Compressed air from the gas air compressor is used to control the movement of equipment, such as gates, doors, and barriers, as well as to operate pneumatic lifts, hoists, and other lifting mechanisms. 4. Concrete Spraying and Shotcreting: Gas air compressors are utilized in concrete spraying and shotcreting applications. Compressed air is used to propel the concrete mixture through a nozzle at high velocity, ensuring proper adhesion and distribution on surfaces. This technique is commonly employed in applications such as tunnel construction, slope stabilization, and repair of concrete structures. 5. Sandblasting and Surface Preparation: In construction projects that require surface preparation, such as removing old paint, rust, or coatings, gas air compressors are often used in conjunction with sandblasting equipment. Compressed air powers the sandblasting process, propelling abrasive materials such as sand or grit onto the surface to achieve effective cleaning and preparation before applying new coatings or finishes. 6. Tire Inflation and Equipment Maintenance: Gas air compressors are utilized for tire inflation and equipment maintenance on construction sites. They provide compressed air for inflating and maintaining proper tire pressure in construction vehicles and equipment. Additionally, gas air compressors are used for general equipment maintenance, such as cleaning, lubrication, and powering pneumatic tools for repair and maintenance tasks. 7. Portable and Remote Operations: Gas air compressors are particularly beneficial in construction projects where electricity may not be readily available or feasible. Portable gas air compressors provide the flexibility to operate in remote locations, allowing construction crews to utilize pneumatic tools and equipment without relying on a fixed power source. Gas air compressors are an integral part of construction projects, facilitating a wide range of tasks and enhancing productivity. Their ability to power pneumatic tools, operate pneumatic systems, and provide compressed air for various applications makes them essential equipment in the construction industry.
Can Gas Air Compressors Be Used for Pneumatic Tools?Yes, gas air compressors can be used for pneumatic tools. Here’s a detailed explanation: 1. Versatile Power Source: Gas air compressors, powered by gasoline or diesel engines, provide a portable and versatile power source for operating pneumatic tools. They eliminate the need for electrical power supply, making them suitable for remote locations or construction sites where electricity may not be readily available. 2. High Power Output: Gas air compressors typically offer higher power output compared to electric compressors of similar size. This high power output enables gas compressors to deliver the necessary air pressure and volume required by pneumatic tools, ensuring optimal tool performance. 3. Mobility and Portability: Gas air compressors are often designed with mobility and portability in mind. They are compact and equipped with wheels or handles, allowing for easy transportation to different job sites. This mobility is advantageous when using pneumatic tools in various locations or when working in confined spaces. 4. Continuous Operation: Gas air compressors can provide continuous air supply for pneumatic tools without the need for frequent pauses or recharging. As long as there is an adequate fuel supply, gas compressors can operate for extended periods, allowing uninterrupted use of pneumatic tools for tasks such as drilling, nailing, sanding, or painting. 5. Suitable for High-Demand Applications: Pneumatic tools used in heavy-duty applications often require a robust air supply to meet their performance requirements. Gas air compressors can generate higher air flow rates and maintain higher operating pressures, making them suitable for high-demand pneumatic tools like jackhammers, impact wrenches, or sandblasters. 6. Flexibility in Compressor Size: Gas air compressors are available in various sizes and capacities, allowing users to choose the compressor that best matches the air demands of their pneumatic tools. From small portable compressors for light-duty tasks to larger industrial-grade compressors for heavy-duty applications, there is a wide range of options to suit different tool requirements. 7. Reduced Dependency on Electrical Infrastructure: Using gas air compressors for pneumatic tools reduces reliance on electrical infrastructure. In situations where the electrical power supply is limited, unreliable, or expensive, gas compressors offer a viable alternative, ensuring consistent tool performance without concerns about power availability. It’s important to note that gas air compressors emit exhaust gases during operation, so proper ventilation is necessary when using them in enclosed spaces to ensure the safety of workers. In summary, gas air compressors can effectively power pneumatic tools, offering mobility, high power output, continuous operation, and suitability for various applications. They provide a reliable and portable solution for utilizing pneumatic tools in locations where electrical power supply may be limited or unavailable.
How Does a Gas Air Compressor Work?A gas air compressor works by utilizing a gas engine to power a compressor pump, which draws in air and compresses it to a higher pressure. The compressed air can then be used for various applications. Here’s a detailed explanation of how a gas air compressor operates: 1. Gas Engine: A gas air compressor is equipped with a gas engine as its power source. The gas engine is typically fueled by gasoline, diesel, natural gas, or propane. When the engine is started, the fuel is combusted within the engine’s cylinders, generating mechanical energy in the form of rotational motion. 2. Compressor Pump: The gas engine drives the compressor pump through a mechanical linkage, such as a belt or direct coupling. The compressor pump is responsible for drawing in atmospheric air and compressing it to a higher pressure. There are different types of compressor pumps used in gas air compressors, including reciprocating, rotary screw, or centrifugal, each with its own operating principles. 3. Intake Stroke: In a reciprocating compressor pump, the intake stroke begins when the piston moves downward within the cylinder. This creates a vacuum, causing the inlet valve to open and atmospheric air to be drawn into the cylinder. In rotary screw or centrifugal compressors, air is continuously drawn in through the intake port as the compressor operates. 4. Compression Stroke: During the compression stroke in a reciprocating compressor, the piston moves upward, reducing the volume within the cylinder. This compression action causes the air to be compressed and its pressure to increase. In rotary screw compressors, two interlocking screws rotate, trapping and compressing the air between them. In centrifugal compressors, air is accelerated and compressed by high-speed rotating impellers. 5. Discharge Stroke: Once the air is compressed, the discharge stroke begins in reciprocating compressors. The piston moves upward, further reducing the volume and forcing the compressed air out of the cylinder through the discharge valve. In rotary screw compressors, the compressed air is discharged through an outlet port as the interlocking screws continue to rotate. In centrifugal compressors, the high-pressure air is discharged from the impeller into the surrounding volute casing. 6. Pressure Regulation: Gas air compressors often include pressure regulation mechanisms to control the output pressure of the compressed air. This can be achieved through pressure switches, regulators, or control systems that adjust the compressor’s operation based on the desired pressure setting. These mechanisms help maintain a consistent and controlled supply of compressed air for the specific application requirements. 7. Storage and Application: The compressed air produced by the gas air compressor is typically stored in a receiver tank or used directly for applications. The receiver tank helps stabilize the pressure and provides a reservoir of compressed air for immediate use. From the receiver tank, the compressed air can be distributed through pipelines to pneumatic tools, machinery, or other devices that require the compressed air for operation. Overall, a gas air compressor operates by using a gas engine to power a compressor pump, which draws in air and compresses it to a higher pressure. The compressed air is then regulated and used for various applications, providing a reliable source of power for pneumatic tools, machinery, and other equipment.
China best High Lower Pressure Rotary Water Lubrication Laser Cutting Oilless Oil-Free Screw Scroll Piston Air Compressor for Dental Hospital Bus Truck Blowing Bottle mini air compressorProduct Description
High Lower Pressure Rotary Water Lubrication Laser Cutting Oilless Oil-Free Screw Scroll Piston Air Compressor for Dental Hospital Bus Truck Blowing Bottle
Product Description
Main uses and guarantees: Energy saving: energy saving more than 15% compared with dry oil-free compressor. Because the purified water takes part into the compressing process to seal, cool and lubricate, it increases efficiency. With the same motor power, comparing with dry oil-free air compress, there is 15% more air production of oil-free screw air compressor of water lubrication, it reduces the energy consumption greatly. The consumption material of oil-free screw air compressor is only water, air filter and water filter, the maintenance cost is very low. 100% oil-free compressed air, 100% purified compressed air, 100% no oil pollution risk. In the process of food and drink industry, medical industry, packing industry, electronic manufacture, painting industry, powder coating industry and textile manufacturing, it must avoid any risk of oil pollution, otherwise it would cause serious consequences such as manufacture damages and stop, brand and credit losing. CMN oil-free screw air compressor takes water for lubrication, there is not any lubricate oil in the air end, and at the meantime, because the purified water clean the air, the compressor air is absolutely clear and not any pollution. Guarantee: High precision, high wear resistance, low noise, smooth and steady, high strength
Our OEM/ODM company provides you what best matches your needs
Our product can be adapted. Please give us the required model name so we can provide you the most accurate quotation. This chart if for reference, if you need different features, provide us all relevant details for your project and we will be glad to help you finding the product matching your need at the best quality with the lowest price. Please note the price and the MOQ may vary regarding the product you chose: do not hesitate to contact us to know more!
Main Features
1) Simple structure in linear type ,easy in installation and maintation.
Company Profile In the early stage, we carried out technical cooperation with Simeon of France on high-end oil-free compressors and gradually established a complete set of innovation and R&D systems in China.
Certifications
How are air compressors employed in the petrochemical industry?Air compressors play a vital role in the petrochemical industry, where they are employed for various applications that require compressed air. The petrochemical industry encompasses the production of chemicals and products derived from petroleum and natural gas. Here’s an overview of how air compressors are utilized in the petrochemical industry: 1. Instrumentation and Control Systems: Air compressors are used to power pneumatic instrumentation and control systems in petrochemical plants. These systems rely on compressed air to operate control valves, actuators, and other pneumatic devices that regulate processes such as flow control, pressure control, and temperature control. Compressed air provides a reliable and clean source of energy for these critical control mechanisms. 2. Pneumatic Tools and Equipment: Petrochemical plants often utilize pneumatic tools and equipment for various tasks such as maintenance, repair, and construction activities. Air compressors supply the necessary compressed air to power these tools, including pneumatic drills, impact wrenches, grinders, sanders, and painting equipment. The versatility and convenience of compressed air make it an ideal energy source for a wide range of pneumatic tools used in the industry. 3. Process Air and Gas Supply: Petrochemical processes often require a supply of compressed air and gases for specific applications. Air compressors are employed to generate compressed air for processes such as oxidation, combustion, and aeration. They may also be used to compress gases like nitrogen, hydrogen, and oxygen, which are utilized in various petrochemical reactions and treatment processes. 4. Cooling and Ventilation: Petrochemical plants require adequate cooling and ventilation systems to maintain optimal operating conditions and ensure the safety of personnel. Air compressors are used to power cooling fans, blowers, and air circulation systems that help maintain the desired temperature, remove heat generated by equipment, and provide ventilation in critical areas. 5. Nitrogen Generation: Nitrogen is widely used in the petrochemical industry for applications such as blanketing, purging, and inerting. Air compressors are utilized in nitrogen generation systems, where they compress atmospheric air, which is then passed through a nitrogen separation process to produce high-purity nitrogen gas. This nitrogen is used for various purposes, including preventing the formation of explosive mixtures, protecting sensitive equipment, and maintaining the integrity of stored products. 6. Instrument Air: Instrument air is essential for operating pneumatic instruments, analyzers, and control devices throughout the petrochemical plant. Air compressors supply compressed air that is treated and conditioned to meet the stringent requirements of instrument air quality standards. Instrument air is used for tasks such as pneumatic conveying, pneumatic actuators, and calibration of instruments. By employing air compressors in the petrochemical industry, operators can ensure reliable and efficient operation of pneumatic systems, power various tools and equipment, support critical processes, and maintain safe and controlled environments.
How do you troubleshoot common air compressor problems?Troubleshooting common air compressor problems can help identify and resolve issues that may affect the performance and functionality of the compressor. Here are some steps to troubleshoot common air compressor problems: 1. No Power:
2. Low Air Pressure:
3. Excessive Noise or Vibration:
4. Air Leaks:
5. Excessive Moisture in Compressed Air:
6. Motor Overheating:
If troubleshooting these common problems does not resolve the issue, it may be necessary to consult the manufacturer’s manual or seek assistance from a qualified technician. Regular maintenance, such as cleaning, lubrication, and inspection, can also help prevent common problems and ensure the optimal performance of the air compressor.
How does an air compressor work?An air compressor works by using mechanical energy to compress and pressurize air, which is then stored and used for various applications. Here’s a detailed explanation of how an air compressor operates: 1. Air Intake: The air compressor draws in ambient air through an intake valve or filter. The air may pass through a series of filters to remove contaminants such as dust, dirt, and moisture, ensuring the compressed air is clean and suitable for its intended use. 2. Compression: The intake air enters a compression chamber, typically consisting of one or more pistons or a rotating screw mechanism. As the piston moves or the screw rotates, the volume of the compression chamber decreases, causing the air to be compressed. This compression process increases the pressure and reduces the volume of the air. 3. Pressure Build-Up: The compressed air is discharged into a storage tank or receiver where it is held at a high pressure. The tank allows the compressed air to be stored for later use and helps to maintain a consistent supply of compressed air, even during periods of high demand. 4. Pressure Regulation: Air compressors often have a pressure regulator that controls the output pressure of the compressed air. This allows the user to adjust the pressure according to the requirements of the specific application. The pressure regulator ensures that the compressed air is delivered at the desired pressure level. 5. Release and Use: When compressed air is needed, it is released from the storage tank or receiver through an outlet valve or connection. The compressed air can then be directed to the desired application, such as pneumatic tools, air-operated machinery, or other pneumatic systems. 6. Continued Operation: The air compressor continues to operate as long as there is a demand for compressed air. When the pressure in the storage tank drops below a certain level, the compressor automatically starts again to replenish the compressed air supply. Additionally, air compressors may include various components such as pressure gauges, safety valves, lubrication systems, and cooling mechanisms to ensure efficient and reliable operation. In summary, an air compressor works by drawing in air, compressing it to increase its pressure, storing the compressed air, regulating the output pressure, and releasing it for use in various applications. This process allows for the generation of a continuous supply of compressed air for a wide range of industrial, commercial, and personal uses.
China manufacturer Piston Type Oil-Free Dental Air Compressor Motor Medical Equipment Supply wholesalerProduct Description
Dental Silent Oil Free Air Compressor (piston type) You may also like:
Are there special considerations for air compressor installations in remote areas?Yes, there are several special considerations to take into account when installing air compressors in remote areas. These areas often lack access to infrastructure and services readily available in urban or well-developed regions. Here are some key considerations: 1. Power Source: Remote areas may have limited or unreliable access to electricity. It is crucial to assess the availability and reliability of the power source for operating the air compressor. In some cases, alternative power sources such as diesel generators or solar panels may need to be considered to ensure a consistent and uninterrupted power supply. 2. Environmental Conditions: Remote areas can present harsh environmental conditions that can impact the performance and durability of air compressors. Extreme temperatures, high humidity, dust, and corrosive environments may require the selection of air compressors specifically designed to withstand these conditions. Adequate protection, insulation, and ventilation must be considered to prevent damage and ensure optimal operation. 3. Accessibility and Transport: Transporting air compressors to remote areas may pose logistical challenges. The size, weight, and portability of the equipment should be evaluated to ensure it can be transported efficiently to the installation site. Additionally, the availability of suitable transportation infrastructure, such as roads or air transportation, needs to be considered to facilitate the delivery and installation process. 4. Maintenance and Service: In remote areas, access to maintenance and service providers may be limited. It is important to consider the availability of trained technicians and spare parts for the specific air compressor model. Adequate planning for routine maintenance, repairs, and troubleshooting should be in place to minimize downtime and ensure the longevity of the equipment. 5. Fuel and Lubricants: For air compressors that require fuel or lubricants, ensuring a consistent and reliable supply can be challenging in remote areas. It is necessary to assess the availability and accessibility of fuel or lubricant sources and plan for their storage and replenishment. In some cases, alternative or renewable fuel options may need to be considered. 6. Noise and Environmental Impact: Remote areas are often characterized by their natural beauty and tranquility. Minimizing noise levels and environmental impact should be a consideration when installing air compressors. Selecting models with low noise emissions and implementing appropriate noise reduction measures can help mitigate disturbances to the surrounding environment and wildlife. 7. Communication and Remote Monitoring: Given the remote location, establishing reliable communication channels and remote monitoring capabilities can be essential for effective operation and maintenance. Remote monitoring systems can provide real-time data on the performance and status of the air compressor, enabling proactive maintenance and troubleshooting. By addressing these special considerations, air compressor installations in remote areas can be optimized for reliable operation, efficiency, and longevity.
How do you maintain proper air quality in compressed air systems?Maintaining proper air quality in compressed air systems is essential to ensure the reliability and performance of pneumatic equipment and the safety of downstream processes. Here are some key steps to maintain air quality: 1. Air Filtration: Install appropriate air filters in the compressed air system to remove contaminants such as dust, dirt, oil, and water. Filters are typically placed at various points in the system, including the compressor intake, aftercoolers, and before point-of-use applications. Regularly inspect and replace filters to ensure their effectiveness. 2. Moisture Control: Excessive moisture in compressed air can cause corrosion, equipment malfunction, and compromised product quality. Use moisture separators or dryers to remove moisture from the compressed air. Refrigerated dryers, desiccant dryers, or membrane dryers are commonly employed to achieve the desired level of dryness. 3. Oil Removal: If the compressed air system utilizes oil-lubricated compressors, it is essential to incorporate proper oil removal mechanisms. This can include coalescing filters or adsorption filters to remove oil aerosols and vapors from the air. Oil-free compressors eliminate the need for oil removal. 4. Regular Maintenance: Perform routine maintenance on the compressed air system, including inspections, cleaning, and servicing of equipment. This helps identify and address any potential issues that may affect air quality, such as leaks, clogged filters, or malfunctioning dryers. 5. Air Receiver Tank Maintenance: Regularly drain and clean the air receiver tank to remove accumulated contaminants, including water and debris. Proper maintenance of the tank helps prevent contamination from being introduced into the compressed air system. 6. Air Quality Testing: Periodically test the quality of the compressed air using appropriate instruments and methods. This can include measuring particle concentration, oil content, dew point, and microbial contamination. Air quality testing provides valuable information about the effectiveness of the filtration and drying processes and helps ensure compliance with industry standards. 7. Education and Training: Educate personnel working with compressed air systems about the importance of air quality and the proper procedures for maintaining it. Provide training on the use and maintenance of filtration and drying equipment, as well as awareness of potential contaminants and their impact on downstream processes. 8. Documentation and Record-Keeping: Maintain accurate records of maintenance activities, including filter replacements, drying system performance, and air quality test results. Documentation helps track the system’s performance over time and provides a reference for troubleshooting or compliance purposes. By implementing these practices, compressed air systems can maintain proper air quality, minimize equipment damage, and ensure the integrity of processes that rely on compressed air.
Can air compressors be used for automotive applications?Yes, air compressors can be used for various automotive applications and are commonly found in automotive repair shops, garages, and even in some vehicles. Here are some automotive applications where air compressors are frequently utilized: 1. Tire Inflation: Air compressors are commonly used to inflate tires in automotive applications. They provide a convenient and efficient way to inflate tires to the recommended pressure, ensuring optimal tire performance, fuel efficiency, and safety. 2. Air Tools: Air compressors power a wide range of pneumatic tools used in automotive repair and maintenance. These tools include impact wrenches, ratchet wrenches, air hammers, pneumatic drills, and sanders. Air-powered tools are favored for their high torque and power-to-weight ratio, making them suitable for heavy-duty automotive tasks. 3. Spray Painting: Air compressors are commonly used in automotive painting applications. They power airbrushes and spray guns that are used to apply paint, primer, and clear coats. Air compressors provide the necessary air pressure to atomize the paint and deliver a smooth and even finish. 4. Brake System Maintenance: Air compressors play a crucial role in maintaining and diagnosing automotive brake systems. They are used to pressurize the brake lines, allowing for proper bleeding of the system and detection of leaks or faults. 5. Suspension Systems: Some automotive suspension systems, such as air suspensions, rely on air compressors to maintain the desired air pressure in the suspension components. The compressor inflates or deflates the suspension as needed to provide a comfortable ride and optimal handling. 6. Cleaning and Dusting: Air compressors are used for cleaning automotive parts, blowing away dust and debris, and drying surfaces. They provide a high-pressure stream of air that effectively cleans hard-to-reach areas. 7. Air Conditioning Systems: Air compressors are a key component in automotive air conditioning systems. They compress and circulate refrigerant, allowing the system to cool and dehumidify the air inside the vehicle. When using air compressors for automotive applications, it’s important to consider the specific requirements of the task at hand. Ensure that the air compressor has the necessary pressure and capacity to meet the demands of the application. Additionally, use appropriate air hoses, fittings, and tools that are compatible with the compressor’s output. Overall, air compressors are versatile and valuable tools in the automotive industry, providing efficient power sources for a wide range of applications, from tire inflation to powering pneumatic tools and supporting various automotive systems.
China Best Sales Silent Electric Screw Air Rotary Compressor Price 30 Kw 40HP 7bar 175 Cfm Oil-Free Screw Mini Gas Compressor small air compressorProduct Description
OFAC oil-free screw air compressor used Japanese Mitsui’s original technology, who is the only maintenance service provider in China.
F– air cooling method S– water cooling method FAQ Q1: Warranty terms of your machine? Q2: Will you provide some spare parts of the machines? Q3: What about product package? Q4: Can you use our brand? Q5: How long will you take to arrange production? Q6: How Many Staff Are There In your Factory? Q8: What the exactly address of your factory?
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Can Gas Air Compressors Be Used for Well Drilling?
Gas air compressors can be used for well drilling, and they are commonly employed in drilling operations. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Air Drilling Method:
Gas air compressors are often utilized in the air drilling method, also known as pneumatic drilling. In this drilling technique, compressed air is used to create a high-velocity airflow that carries the drill cuttings to the surface. The high-pressure air also aids in cooling the drill bit and providing additional force for efficient drilling.
2. Benefits of Gas Air Compressors:
Gas air compressors offer several advantages for well drilling:
- Portability: Gas air compressors can be easily transported to remote drilling sites, allowing for flexibility in well location.
- Power: Gas air compressors provide high-pressure air output, which is essential for effective drilling in various geological formations.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Gas air compressors can be more cost-effective compared to other drilling methods, as they eliminate the need for drilling mud and associated disposal costs.
- Environmental Considerations: Air drilling with gas compressors produces minimal waste and does not require the use of potentially harmful drilling fluids, making it an environmentally friendly option.
3. Compressor Selection:
When selecting a gas air compressor for well drilling, several factors should be considered:
- Pressure and Flow Requirements: Evaluate the pressure and flow requirements of the drilling operation to ensure that the gas air compressor can deliver the necessary air output.
- Compressor Size and Power: Choose a compressor with adequate size and power output to match the drilling demands. Factors such as borehole depth, drill bit type, and drilling speed will influence the compressor’s power requirements.
- Portability: Consider the portability features of the gas air compressor, such as its weight, dimensions, and mobility options, to facilitate transportation to drilling sites.
4. Safety Considerations:
It is essential to follow safety guidelines when using gas air compressors for well drilling. These may include proper ventilation to prevent the accumulation of exhaust fumes, adherence to equipment operating limits, and the use of personal protective equipment (PPE) for drilling personnel.
5. Other Considerations:
While gas air compressors are commonly used for well drilling, it is worth noting that the suitability of a gas air compressor for a specific drilling project depends on various factors such as geological conditions, well depth, and drilling objectives. It is recommended to consult with drilling experts and professionals to determine the most suitable drilling method and equipment for a particular project.
In summary, gas air compressors can be effectively used for well drilling, particularly in the air drilling method. They offer portability, power, cost-effectiveness, and environmental advantages. Proper selection, considering pressure and flow requirements, as well as safety precautions, is crucial to ensure successful and safe drilling operations.
Can Gas Air Compressors Be Used in Agriculture?
Yes, gas air compressors can be used in various agricultural applications. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Pneumatic Tools and Equipment:
Gas air compressors can power a wide range of pneumatic tools and equipment used in agriculture. These tools include pneumatic drills, impact wrenches, nail guns, staplers, and pneumatic pumps. Gas air compressors provide the necessary compressed air to operate these tools, making various tasks more efficient and convenient on the farm.
2. Irrigation Systems:
Gas air compressors can be used to power irrigation systems in agriculture. They can supply compressed air to operate pneumatic valves, which control the flow of water in irrigation networks. Gas air compressors ensure reliable and efficient operation of irrigation systems, facilitating the distribution of water to crops in a controlled manner.
3. Grain Handling and Storage:
Air compressors play a vital role in grain handling and storage facilities. They are used to power aeration systems that provide airflow to grains stored in silos or bins. Aeration helps control the temperature and moisture levels, preventing spoilage and maintaining grain quality. Gas air compressors provide the airflow necessary for effective aeration in grain storage operations.
4. Cleaning and Maintenance:
In agriculture, gas air compressors are commonly used for cleaning and maintenance tasks. They can power air blowers or air guns to remove dust, debris, or chaff from machinery, equipment, or storage areas. Gas air compressors provide a high-pressure stream of compressed air, facilitating efficient cleaning and maintenance operations.
5. Livestock Operations:
Gas air compressors find applications in livestock operations as well. They can power pneumatic equipment used for animal care, such as pneumatic nail guns for building or repairing livestock enclosures, pneumatic pumps for water distribution, or pneumatic tools for general maintenance tasks.
6. Portable and Versatile:
Gas air compressors are often portable and can be easily transported around the farm, allowing flexibility in agricultural operations. Their versatility makes them suitable for various tasks, from powering tools and equipment in the field to providing compressed air for maintenance or cleaning in different farm locations.
7. Remote Locations:
In agricultural settings where access to electricity may be limited, gas air compressors offer a reliable alternative. They can be powered by gasoline or diesel engines, providing compressed air even in remote areas without electrical infrastructure.
8. Considerations:
When using gas air compressors in agriculture, it is essential to consider factors such as compressor size, capacity, and maintenance requirements. Selecting the right compressor based on the specific needs of the agricultural applications ensures optimal performance and efficiency.
In summary, gas air compressors have various applications in agriculture. They can power pneumatic tools and equipment, operate irrigation systems, facilitate grain handling and storage, assist in cleaning and maintenance tasks, support livestock operations, and offer portability and versatility. Gas air compressors contribute to increased efficiency, convenience, and productivity in agricultural operations.
How Do You Choose the Right Size Gas Air Compressor for Your Needs?
Choosing the right size gas air compressor is crucial to ensure optimal performance and efficiency for your specific needs. Selecting a compressor that is too small may result in insufficient airflow or pressure, while choosing one that is too large can lead to unnecessary energy consumption and higher costs. Here’s a detailed explanation of the factors to consider when choosing the right size gas air compressor:
1. Required Airflow:
Determine the airflow requirements of your applications. Consider the tools, equipment, or processes that will be powered by the compressor and their respective airflow demands. The required airflow is typically measured in cubic feet per minute (CFM). Determine the total CFM required, taking into account any simultaneous or intermittent tool usage.
2. Operating Pressure:
Identify the operating pressure required for your applications. Different tools and systems have specific pressure requirements, measured in pounds per square inch (PSI). Ensure that the compressor you choose can deliver the required pressure consistently.
3. Duty Cycle:
Consider the duty cycle, which refers to the amount of time the compressor will be in operation within a given period. Some applications may require continuous operation, while others involve intermittent or occasional use. Take into account the duty cycle to ensure that the compressor can handle the expected workload without overheating or experiencing excessive wear.
4. Tank Size:
The tank size of a gas air compressor determines its ability to store compressed air and provide a steady supply. A larger tank can help accommodate fluctuations in demand and reduce the frequency of the compressor cycling on and off. Consider the required storage capacity based on the specific applications and the desired balance between continuous operation and storage capacity.
5. Power Source:
Gas air compressors can be powered by different fuels, such as gasoline, diesel, natural gas, or propane. Consider the availability and cost of the fuel options in your location, as well as the specific requirements of your applications. Choose a compressor that is compatible with a power source that suits your needs.
6. Portability:
Determine if portability is a requirement for your applications. If you need to move the compressor to different job sites or locations, consider a portable model with features like wheels, handles, or a compact design that facilitates easy transportation.
7. Noise Level:
If noise is a concern in your working environment, consider the noise level of the compressor. Gas air compressors can vary in their noise output, and certain models may have noise-reducing features or insulation to minimize sound emissions.
8. Manufacturer Recommendations:
Consult the manufacturer’s recommendations and guidelines for selecting the appropriate compressor size for your specific needs. Manufacturers often provide guidelines based on the anticipated applications, airflow requirements, and other factors to help you make an informed decision.
By considering these factors and carefully assessing your specific requirements, you can choose the right size gas air compressor that meets your airflow, pressure, duty cycle, and other operational needs. It’s advisable to consult with industry professionals or compressor experts for guidance, especially for complex or specialized applications.


editor by CX 2023-09-29
China Good quality Totally Oil-Free Air Gas Compressor air compressor repair near me
Product Description
CHINAMFG Oil-free Air Compressor
BROTIE oil-free lubricated air compressors belong to reciprocating, piston, single action and air-cooled portable air compressors, they are designed for the departments which need pure air source and higher environmental requirements. There is no need to add lubricating oil for this product, the exhaust gas does not contain oil and oil vapor and won’t pollute environment, compressed air consuming equipment and its product, therefore, it is an environment-friendly energy-saving product.
1. When it is used as a general power gas source, it is more convenient in use than oil lubricated air compressor and its maintenance cost is lower.
2. As the simplest and optimum equipment which provides high-quality oilless compressed air, it saves complicated oil filtering and treatment equipment, thus saving a lot of equipment expenditure and maintenance cost.
Select a machine type with at least 20% allowance when determining compressed air consumption.
Please take into account the condition that consumption of compressed air may be increased in the future. Correct type selection will reduce purchase and use cost.
For detailed models, please contact with CHINAMFG with no hesitation.
| Model | Capacity (m 3 /min) |
Discharge pressure (Mpa) |
Speed (r/min) |
Noise bd(A) |
Motor Power (KW) |
Size of discharge | Air Container Volume (M3) |
dimensions (L*W*H) |
| ZW-0.1/7 | 0.1 | 0.7 | 980 | ≤ 78 | 1.5(220V) | G1/4″ | 0.04 | 750*350*750 |
| ZW-0.24/7 | 0.24 | 0.24 | 950 | ≤ 81 | 2.2(380V) | G1/2″ | 0.08 | 1140*400*900 |
| ZW-0.3/7 | 0.3 | 0.7 | 950 | ≤ 81 | 2.2(380V) | G1/2″ | 0.08 | 1140*400*900 |
| VW-0.45/7 | 0.45 | 0.7 | 920 | ≤ 83 | 4(380V) | G1/2″ | 0.12 | 1300*460*960 |
| VW-0.6/7 | 0.6 | 0.7 | 950 | ≤ 84 | 5.5(380V) | G1/2″ | 0.12 | 1300*460*960 |
| VW-0.42/10 | 0.42 | 1.0 | 920 | ≤ 84 | 4(380V) | G1/2″ | 0.12 | 1300*460*960 |
| VW-0.5/14 | 0.5 | 1.4 | 670 | ≤ 84 | 5.5(380V) | G1/2″ | 0.18 | 1450*500*1100 |
| WW-0.6/10 | 0.6 | 1.0 | 740 | ≤ 84 | 5.5(380V) | G1/2″ | 0.18 | 1450*500*1100 |
| WW-0.9/7 | 0.9 | 0.7 | 810 | ≤ 84 | 7.5(380V) | G1/2″ | 0.18 | 1450*500*1100 |
| WW-0.9/10 | 0.9 | 1.0 | 810 | ≤ 84 | 7.5(380V) | G1/2″ | 0.18 | 1450*500*1100 |
| WW-0.7/12.5 | 0.7 | 1.25 | 740 | ≤ 84 | 7.5(380V) | G1/2″ | 0.18 | 1450*500*1100 |
| WW-1.25/7 | 1.25 | 0.7 | 860 | ≤ 85 | 11(380V) | G3/4″ | 0.28 | 1600*650*1200 |
| WW-1.25/10 | 1.25 | 1.0 | 770 | ≤ 85 | 11(380V) | G3/4″ | 0.28 | 1600*650*1200 |
| WW-1.6/10 | 1.6 | 1.0 | 820 | ≤ 85 | 15(380V) | G3/4″ | 0.32 | 1660*650*1220 |
| WW-1.8/10 | 1.8 | 1.0 | 900 | ≤ 86 | 15(380V) | G3/4″ | 0.32 | 1660*650*1220 |
| WW-1.2/10 | 1.2 | 1.0 | 740 | ≤ 84 | 5.5*2(380V) | G1″ | 0.30 | 1850*1250*1400 |
| WW-1.8/7 | 1.8 | 0.7 | 810 | ≤ 84 | 7.5*2(380V) | G1″ | 0.30 | 1850*1250*1400 |
| WW-1.8/10 | 1.8 | 1.0 | 810 | ≤ 84 | 7.5*2(380V) | G1″ | 0.30 | 1850*1250*1400 |
| WW-1.4/12.5 | 1.4 | 1.25 | 740 | ≤ 84 | 7.5*2(380V) | G1″ | 0.30 | 1850*1250*1400 |
| WW-2.5/7 | 2.5 | 0.7 | 860 | ≤ 86 | 11*2(380V) | G1″ | 0.30 | 1850*1250*1400 |
| WW-2.5/10 | 2.5 | 1.0 | 770 | ≤ 86 | 11*2(380V) | G1″ | 0.30 | 1850*1250*1400 |
| WW-3.0/7 | 3.0 | 0.7 | 770 | ≤ 86 | 11*2(380V) | G1″ | 0.32 | 1850*1250*1400 |
| WW-3.0/10 | 3.0 | 1.0 | 810 | ≤ 86 | 11*2(380V) | G1″ | 0.32 | 1850*1250*1400 |
| WW-3.2/7 | 3.2 | 0.7 | 820 | ≤ 86 | 15*2(380V) | G1″ | 0.32 | 1900*1500*1500 |
| WW-3.2/10 | 3.2 | 1.0 | 820 | ≤ 86 | 15*2(380V) | G1″ | 0.32 | 1900*1500*1500 |
| WW-3.6/7 | 3.6 | 0.7 | 900 | ≤ 86 | 15*2(380V) | G1″ | 0.32 | 1900*1500*1500 |
| WW-3.6/10 | 3.6 | 1.0 | 900 | ≤ 86 | 15*2(380V) | G1″ | 0.32 | 1900*1500*1500 |
| WW-4.8/10 | 4.8 | 1.0 | 900 | ≤ 86 | 15*2(380V) 11*1(380V) | G3/2″ | / | 2210*1360*1050 |
| Lubrication Style: | Oil-free |
|---|---|
| Compressed Grade: | 1-4 |
| Place of Origin: | China |
| Working Principle: | Oil-Free Lubrication Reciprocating Type Booster |
| Cooling Type: | Wind or Water Cooling |
| Mute: | Yes |
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|
What Is the Noise Level of Gas Air Compressors?
The noise level of gas air compressors can vary depending on several factors, including the compressor’s design, engine type, operating conditions, and the presence of noise-reducing features. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Compressor Design:
The design of the gas air compressor can influence its noise level. Some compressors are engineered with noise reduction in mind, utilizing features such as sound insulation, vibration dampening materials, and mufflers to minimize noise generation. Compressors with enclosed cabinets or acoustic enclosures tend to have lower noise levels compared to open-frame compressors.
2. Engine Type:
The type of engine used in the gas air compressor can impact the noise level. Gas air compressors typically use internal combustion engines powered by gasoline or propane. Gasoline engines tend to produce higher noise levels compared to diesel engines or electric motors. However, advancements in engine technology have led to quieter gasoline engines with improved noise control.
3. Operating Conditions:
The operating conditions of the gas air compressor can affect the noise level. Factors such as the load capacity, speed of operation, and ambient temperature can influence the amount of noise generated. Compressors operating at higher loads or speeds may produce more noise compared to those running at lower levels.
4. Noise-Reducing Features:
Some gas air compressors are equipped with noise-reducing features to minimize sound emissions. These may include built-in silencers, acoustic enclosures, or noise-absorbing materials. Such features help dampen the noise produced by the compressor and reduce its overall noise level.
5. Manufacturer Specifications:
Manufacturers often provide noise level specifications for their gas air compressors. These specifications typically indicate the sound pressure level (SPL) in decibels (dB) at a specific distance from the compressor. It is important to refer to these specifications to get an idea of the expected noise level of a particular compressor model.
6. Distance and Location:
The distance between the gas air compressor and the listener can impact the perceived noise level. As sound waves disperse, the noise level decreases with distance. Locating the compressor in an area that is isolated or distant from occupied spaces can help minimize the impact of noise on the surrounding environment.
It is important to note that gas air compressors, especially those used in industrial or heavy-duty applications, can generate substantial noise levels. Occupational health and safety regulations may require the use of hearing protection for individuals working in close proximity to loud compressors.
Overall, the noise level of gas air compressors can vary, and it is advisable to consult the manufacturer’s specifications and consider noise-reducing features when selecting a compressor. Proper maintenance, such as regular lubrication and inspection of components, can also help minimize noise levels and ensure optimal performance.
What Are the Key Components of a Gas Air Compressor Control Panel?
A gas air compressor control panel typically consists of several key components. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Power Switch:
The power switch allows the operator to turn the compressor on or off. It is usually a toggle switch or a push-button switch located on the control panel.
2. Pressure Gauges:
Pressure gauges display the compressed air pressure at different stages of the compression process. Commonly, there are two pressure gauges: one to measure the incoming air pressure (suction pressure) and another to measure the outgoing compressed air pressure (discharge pressure).
3. Control Knobs or Buttons:
Control knobs or buttons are used to adjust and set various parameters of the compressor operation. These controls may include pressure settings, on/off timers, automatic start/stop functions, and other operational parameters specific to the compressor model.
4. Emergency Stop Button:
An emergency stop button is a critical safety feature that immediately shuts down the compressor in case of an emergency. Pressing the emergency stop button cuts off power to the compressor and stops its operation.
5. Motor Start/Stop Buttons:
Motor start and stop buttons allow the operator to manually start or stop the compressor motor. These buttons are used when manual control of the motor is required, such as during maintenance or troubleshooting.
6. Control Indicators:
Control indicators include various lights or LEDs that provide visual feedback about the compressor’s status and operation. These indicators may include power indicators, motor running indicators, pressure indicators, and fault indicators to signal any malfunctions or abnormal conditions.
7. Control Panel Display:
Some gas air compressors feature a control panel display that provides real-time information and feedback on the compressor’s performance. The display may show parameters such as operating pressure, temperature, maintenance alerts, fault codes, and other relevant information.
8. Start/Stop Control Circuit:
The start/stop control circuit is responsible for initiating and controlling the motor start and stop sequences. It typically includes relays, contactors, and other electrical components that enable the control panel to safely start and stop the compressor motor.
9. Safety and Protection Devices:
Gas air compressor control panels may incorporate safety and protection devices to safeguard the compressor and prevent potential damage or hazardous situations. These devices can include overload relays, thermal protection, pressure relief valves, and other safety features.
10. Control Panel Enclosure:
The control panel enclosure houses and protects the electrical components and wiring of the control panel. It provides insulation, protection from dust and moisture, and ensures the safety of the operator.
In summary, a gas air compressor control panel typically includes a power switch, pressure gauges, control knobs or buttons, emergency stop button, motor start/stop buttons, control indicators, control panel display (if applicable), start/stop control circuit, safety and protection devices, and a control panel enclosure. These components work together to monitor and control the compressor’s operation, ensure safety, and provide essential information to the operator.
What Fuels Are Commonly Used in Gas Air Compressors?
Gas air compressors can be powered by various fuels depending on the specific model and design. The choice of fuel depends on factors such as availability, cost, convenience, and environmental considerations. Here’s a detailed explanation of the fuels commonly used in gas air compressors:
1. Gasoline:
Gasoline is a widely used fuel in gas air compressors, particularly in portable models. Gasoline-powered compressors are popular due to the widespread availability of gasoline and the convenience of refueling. Gasoline engines are generally easy to start, and gasoline is relatively affordable in many regions. However, gasoline-powered compressors may emit more exhaust emissions compared to some other fuel options.
2. Diesel:
Diesel fuel is another common choice for gas air compressors, especially in larger industrial models. Diesel engines are known for their efficiency and durability, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications. Diesel fuel is often more cost-effective than gasoline, and diesel-powered compressors typically offer better fuel efficiency and longer runtime. Diesel compressors are commonly used in construction sites, mining operations, and other industrial settings.
3. Natural Gas:
Natural gas is a clean-burning fuel option for gas air compressors. It is a popular choice in areas where natural gas infrastructure is readily available. Natural gas compressors are often used in natural gas processing plants, pipeline operations, and other applications where natural gas is abundant. Natural gas-powered compressors offer lower emissions compared to gasoline or diesel, making them environmentally friendly.
4. Propane:
Propane, also known as liquefied petroleum gas (LPG), is commonly used as a fuel in gas air compressors. Propane-powered compressors are popular in construction, agriculture, and other industries where propane is used for various applications. Propane is stored in portable tanks, making it convenient for use in portable compressors. Propane-powered compressors are known for their clean combustion, low emissions, and easy availability.
5. Biogas:
In specific applications, gas air compressors can be fueled by biogas, which is produced from the decomposition of organic matter such as agricultural waste, food waste, or wastewater. Biogas compressors are used in biogas production facilities, landfills, and other settings where biogas is generated and utilized as a renewable energy source. The use of biogas as a fuel in compressors contributes to sustainability and reduces dependence on fossil fuels.
It’s important to note that the availability and suitability of these fuel options may vary depending on the region, infrastructure, and specific application requirements. When selecting a gas air compressor, it’s crucial to consider the compatibility of the compressor with the available fuel sources and to follow the manufacturer’s guidelines regarding fuel selection, storage, and safety precautions.


editor by CX 2023-09-28
China Best Sales 55kw 75HP Oil Free Water Lubricated Screw Air Compressor for Mining Industrial with Good quality
Product Description
|
Product name |
Oil Free Water Lubricated Screw Air Compressor |
|
Model |
WLS |
|
Cooling Method |
Air Cooling |
|
Pressure |
8/1013 bar |
|
Power |
5.5-250 kw |
|
Capacity |
0.3~33.97 m3/min |
|
Voltage |
380V/50HZ, 220V/60HZ, 400V/50HZ, 415V/50HZ or Customer′s Requirements |
|
Color |
Customized |
Advantage
1.Clean air 100% oil-free
2.Use water instead of oil, higher cooling efficiency and compression efficiency
3.Optimal isothermal compression
4.Powerful MAM microcomputer controller and touch screen
5.Reasonable Structure, with perfect balancing
6.Components made of anti-rust and anti-corrosion materials ensure the durability
7.Significant energy saving, environmental-friendly and pollution-free
8.Designed especially for medical, pharmacy, instrument, coating, chemical industry and food processing, etc.
| Model | Pressure (mpa) |
Displacement (m³/min) |
Power (kw) |
Noise (db) |
Water Inlet Diameter | Lubricating Water (L) |
Air Outlet |
| WLS-0.8/5.5 | 0.8 | 0.3-0.78 | 5.5 | 57 | 3/4″ | 10 | 3/4″ |
| WLS-1.0/5.5 | 1.0 | 0.2-0.65 | |||||
| WLS-0.8/7.5 | 0.8 | 0.35-0.17 | 7.5 | 57 | 3/4″ | 10 | 3/4″ |
| WLS-1.0/7.5 | 1.0 | 0.3-1.05 | |||||
| WLS-1.25/7.5 | 1.25 | 0.24-0.81 | |||||
| WLS-0.8/11 | 0.8 | 0.54-1.72 | 11 | 60 | 1″ | 26 | 3/4″ |
| WLS-1.0/11 | 1 | 0.45-1.42 | |||||
| WLS-1.25/11 | 1.3 | 0.35-1.10 | |||||
| WLS-0.8/15 | 0.8 | 0.75-2.43 | 15 | 60 | 1″ | 26 | 1″ |
| WLS-1.0/15 | 1.0 | 0.65-2.17 | |||||
| WLS-1.25/15 | 1.25 | 0.6-1.80 | |||||
| WLS-0.8/18.5 | 0.8 | 0.9-3.31 | 18.5 | 63 | 1″ | 30 | 1″ |
| WLS-1.0/18.5 | 1 | 0.9-2.82 | |||||
| WLS-1.25/18.5 | 1.3 | 0.6-2.05 | |||||
| WLS-0.8/22 | 0.8 | 1.1-3.7 | 22 | 63 | 1″ | 30 | 1″ |
| WLS-1.0/22 | 1.0 | 0.97-3.21 | |||||
| WLS-1.25/22 | 1.25 | 0.85-2.87 | |||||
| WLS-0.8/30 | 0.8 | 1.55-5.2 | 30 | 63 | 1 1/2″ | 40 | 1 1/2″ |
| WLS-1.0/30 | 1 | 1.255-4.43 | |||||
| WLS-1.25/30 | 1.3 | 1.1-3.63 | |||||
| WLS-0.8/37 | 0.8 | 1.91-6.50 | 37 | 66 | 1 1/2″ | 40 | 1 1/2″ |
| WLS-1.0/37 | 1.0 | 1.6-5.53 | |||||
| WLS-1.25/37 | 1.25 | 1.42-4.47 | |||||
| WLS-0.8/45 | 0.8 | 2.5-8.3 | 45 | 66 | 1 1/2″ | 90 | 2″ |
| WLS-1.0/45 | 1 | 1.91-6.3 | |||||
| WLS-1.25/45 | 1.3 | 1.7-5.56 | |||||
| WLS-0.8/55 | 0.8 | 3.0-10.3 | 55 | 69 | 1 1/2″ | 100 | 2″ |
| WLS-1.0/55 | 1.0 | 2.6-8.55 | |||||
| WLS-1.25/55 | 1.25 | 2.3-7.67 | |||||
| WLS-0.8/75 | 0.8 | 3.95-13 | 75 | 72 | 1 1/2″ | 100 | 2″ |
| WLS-1.0/75 | 1 | 3.4-11.5 | |||||
| WLS-1.25/75 | 1.3 | 3.0-9.7 | |||||
| WLS-0.8/90 | 0.8 | 5.0-16.6 | 90 | 73 | 1 1/2″ | 120 | 2 1/2″ |
| WLS-1.0/90 | 1.0 | 4.3-14.66 | |||||
| WLS-1.25/90 | 1.25 | 3.72-12.6 | |||||
| WLS-0.8/110 | 0.8 | 6.0-20.2 | 110 | 77 | 2″ | 120 | 2 1/2″ |
| WLS-1.0/110 | 1 | 5.0-16.66 | |||||
| WLS-1.25/110 | 1.3 | 4.65-15.56 | |||||
| WLS-0.8/132 | 0.8 | 6.75-22.52 | 132 | 77 | 2″ | 120 | 2 1/2″ |
| WLS-1.0/132 | 1.0 | 6.0-19.97 | |||||
| WLS-1.25/132 | 1.25 | 5.07-16.90 | |||||
| WLS-0.8/160 | 0.8 | 8.5-28.11 | 160 | 79 | 3″ | 160 | 3″ |
| WLS-1.0/160 | 1 | 7.6-25.45 | |||||
| WLS-1.25/160 | 1.3 | 6.7-22.52 | |||||
| WLS-0.8/185 | 0.8 | 10-33.97 | 185 | 79 | 3″ | 160 | 3″ |
| WLS-1.0/185 | 1.0 | 8.72-29 | |||||
| WLS-1.25/185 | 1.25 | 7.75-25.21 | |||||
| WLS-0.8/200 | 0.8 | 11.2-36.75 | 200 | 80 | 4″ | 200 | 4″ |
| WLS-1.0/200 | 1 | 9.68-32.78 | |||||
| WLS-1.25/200 | 1.3 | 9.2-29.24 | |||||
| WLS-0.8/250 | 0.8 | 13.5-45 | 250 | 80 | 4″ | 200 | 4″ |
| WLS-1.25/250 | 1.3 | 10.2-33.97 |
ZheJiang CHINAMFG Gas Compressor Manufacturing Co.,Ltd. founded in 2005, is a leading high technology of machine and equipment manufacturer integrating the design, R&D, production, sales and service for air compressors & Mining Equipment. Adopting advanced technology, design concept and quality control, and we are able to provide customized products to meet customers’ OEM needs.
Our company has more than 520 employees, including 86 senior technicians and professional engineers. Our technical team provides our customers with professional air system solutions. With the total 15000 square meters of the facility, 4 modern advanced production lines are built up to ensure production capacity to meet customer requirements.
Our company has been awarded the honorary title of “ZheJiang high-tech enterprise” and our products enjoy high honors in the industry. Our company has the ISO9001 certification and was awarded the qualification certificate of equipment through military contracts in 2018.
We offer the following products and services:
1. Screw air compressor
1.1 Oil-free screw air compressor
1.2 Oil-injected air compressor
2. Reciprocating piston air compressor
2.1 Piston air compressor
2.2 Oil-free piston air compressor
2.3 Piston medium & high-pressure air compressor
3.Portable air compressor & Mining Equipment
3.1 Diesel or Electric portable screw air compressor
3.2 Air Pick, Rock Drill, DTH Drilling Rig, Crawler Drilling Rig
4. Air compressor accessories
4.1 CHINAMFG or Adsorption compressed air drier
4.2 Compressed air filter or tank
4.3 Lubrication oil
We have a complete system of after-sales service and quality assurance. The company’s material purchase, inspection, manufacturing, installation, and testing are strictly in accordance with the ISO procedures. which will ensure each compressor has reliable quality and has a complete record to trace, if needed.
Q: Do you test all your goods before delivery?
A: Yes, we have 100% test before delivery.
Q: How can we start order with your factory?
A: First, leave us an inquiry and advise which item you’re interested, and then we will contact you in 24 hours. You’re so kind if provide all detailed information, will better for us to know exactly what you need.
Q: What are your MOQ?
A: Different products have different MOQ, most is 1 set.
Q: What is your terms of payment?
A: T/T 30% as deposit, and 70% before delivery. We’ll show you the photos of the products and packages.
Q: How about your delivery time?
A: Generally, it will take 90 days after receiving your advance payment. The specific delivery time depends on the items and the quantity of your order.
Q: Do you a trade company or real factory?
A: We are 100% factory; we located in ZheJiang city, China.
|
Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
To be negotiated |
|---|
| After-sales Service: | Online Support |
|---|---|
| Warranty: | Unit 1 Year, Air End 2 Years |
| Lubrication Style: | Oil-free |
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|
.webp)
How are air compressors employed in the petrochemical industry?
Air compressors play a vital role in the petrochemical industry, where they are employed for various applications that require compressed air. The petrochemical industry encompasses the production of chemicals and products derived from petroleum and natural gas. Here’s an overview of how air compressors are utilized in the petrochemical industry:
1. Instrumentation and Control Systems:
Air compressors are used to power pneumatic instrumentation and control systems in petrochemical plants. These systems rely on compressed air to operate control valves, actuators, and other pneumatic devices that regulate processes such as flow control, pressure control, and temperature control. Compressed air provides a reliable and clean source of energy for these critical control mechanisms.
2. Pneumatic Tools and Equipment:
Petrochemical plants often utilize pneumatic tools and equipment for various tasks such as maintenance, repair, and construction activities. Air compressors supply the necessary compressed air to power these tools, including pneumatic drills, impact wrenches, grinders, sanders, and painting equipment. The versatility and convenience of compressed air make it an ideal energy source for a wide range of pneumatic tools used in the industry.
3. Process Air and Gas Supply:
Petrochemical processes often require a supply of compressed air and gases for specific applications. Air compressors are employed to generate compressed air for processes such as oxidation, combustion, and aeration. They may also be used to compress gases like nitrogen, hydrogen, and oxygen, which are utilized in various petrochemical reactions and treatment processes.
4. Cooling and Ventilation:
Petrochemical plants require adequate cooling and ventilation systems to maintain optimal operating conditions and ensure the safety of personnel. Air compressors are used to power cooling fans, blowers, and air circulation systems that help maintain the desired temperature, remove heat generated by equipment, and provide ventilation in critical areas.
5. Nitrogen Generation:
Nitrogen is widely used in the petrochemical industry for applications such as blanketing, purging, and inerting. Air compressors are utilized in nitrogen generation systems, where they compress atmospheric air, which is then passed through a nitrogen separation process to produce high-purity nitrogen gas. This nitrogen is used for various purposes, including preventing the formation of explosive mixtures, protecting sensitive equipment, and maintaining the integrity of stored products.
6. Instrument Air:
Instrument air is essential for operating pneumatic instruments, analyzers, and control devices throughout the petrochemical plant. Air compressors supply compressed air that is treated and conditioned to meet the stringent requirements of instrument air quality standards. Instrument air is used for tasks such as pneumatic conveying, pneumatic actuators, and calibration of instruments.
By employing air compressors in the petrochemical industry, operators can ensure reliable and efficient operation of pneumatic systems, power various tools and equipment, support critical processes, and maintain safe and controlled environments.
.webp)
Can air compressors be used for inflating tires and sporting equipment?
Yes, air compressors can be used for inflating tires and sporting equipment, providing a convenient and efficient method for achieving the desired air pressure. Here’s how air compressors are used for these purposes:
1. Tire Inflation:
Air compressors are commonly used for inflating vehicle tires, including car tires, motorcycle tires, bicycle tires, and even larger truck or trailer tires. Air compressors provide a continuous source of pressurized air, allowing for quick and accurate inflation. They are often used in automotive repair shops, gas stations, and by individuals who regularly need to inflate tires.
2. Sporting Equipment Inflation:
Air compressors are also useful for inflating various types of sporting equipment. This includes inflatable balls such as soccer balls, basketballs, footballs, and volleyballs. Additionally, air compressors can be used to inflate inflatable water toys, air mattresses, inflatable kayaks, and other recreational items that require air for proper inflation.
3. Air Tools for Inflation:
Air compressors can power air tools specifically designed for inflation purposes. These tools, known as inflators or air blow guns, provide controlled airflow for inflating tires and sporting equipment. They often have built-in pressure gauges and nozzles designed to fit different types of valves, making them versatile and suitable for various inflation tasks.
4. Adjustable Pressure:
One advantage of using air compressors for inflation is the ability to adjust the pressure. Most air compressors allow users to set the desired pressure level using a pressure regulator or control knob. This feature ensures that tires and sporting equipment are inflated to the recommended pressure, promoting optimal performance and safety.
5. Efficiency and Speed:
Air compressors provide a faster and more efficient inflation method compared to manual pumps. The continuous supply of compressed air allows for quick inflation, reducing the time and effort required to inflate tires and sporting equipment manually.
6. Portable Air Compressors:
For inflating tires and sporting equipment on the go, portable air compressors are available. These compact and lightweight compressors can be easily carried in vehicles or taken to sports events and outdoor activities, ensuring convenient access to a reliable air supply.
It is important to note that when using air compressors for inflating tires, it is recommended to follow manufacturer guidelines and proper inflation techniques to ensure safety and avoid overinflation.
.webp)
How do oil-lubricated and oil-free air compressors differ?
Oil-lubricated and oil-free air compressors differ in terms of their lubrication systems and the presence of oil in their operation. Here are the key differences:
Oil-Lubricated Air Compressors:
1. Lubrication: Oil-lubricated air compressors use oil for lubricating the moving parts, such as pistons, cylinders, and bearings. The oil forms a protective film that reduces friction and wear, enhancing the compressor’s efficiency and lifespan.
2. Performance: Oil-lubricated compressors are known for their smooth and quiet operation. The oil lubrication helps reduce noise levels and vibration, resulting in a more comfortable working environment.
3. Maintenance: These compressors require regular oil changes and maintenance to ensure the proper functioning of the lubrication system. The oil filter may need replacement, and the oil level should be regularly checked and topped up.
4. Applications: Oil-lubricated compressors are commonly used in applications that demand high air quality and continuous operation, such as industrial settings, workshops, and manufacturing facilities.
Oil-Free Air Compressors:
1. Lubrication: Oil-free air compressors do not use oil for lubrication. Instead, they utilize alternative materials, such as specialized coatings, self-lubricating materials, or water-based lubricants, to reduce friction and wear.
2. Performance: Oil-free compressors generally have a higher airflow capacity, making them suitable for applications where a large volume of compressed air is required. However, they may produce slightly more noise and vibration compared to oil-lubricated compressors.
3. Maintenance: Oil-free compressors typically require less maintenance compared to oil-lubricated ones. They do not need regular oil changes or oil filter replacements. However, it is still important to perform routine maintenance tasks such as air filter cleaning or replacement.
4. Applications: Oil-free compressors are commonly used in applications where air quality is crucial, such as medical and dental facilities, laboratories, electronics manufacturing, and painting applications. They are also favored for portable and consumer-grade compressors.
When selecting between oil-lubricated and oil-free air compressors, consider the specific requirements of your application, including air quality, noise levels, maintenance needs, and expected usage. It’s important to follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for maintenance and lubrication to ensure the optimal performance and longevity of the air compressor.


editor by CX 2023-09-28
China 100 1500cfm Screw 500 1000 L Scroll 270 cfm Piston 10 25 Bar Diesel Oil Free Air Compressor lowes air compressor
Error:获取返回内容失败,
Your session has expired. Please reauthenticate.
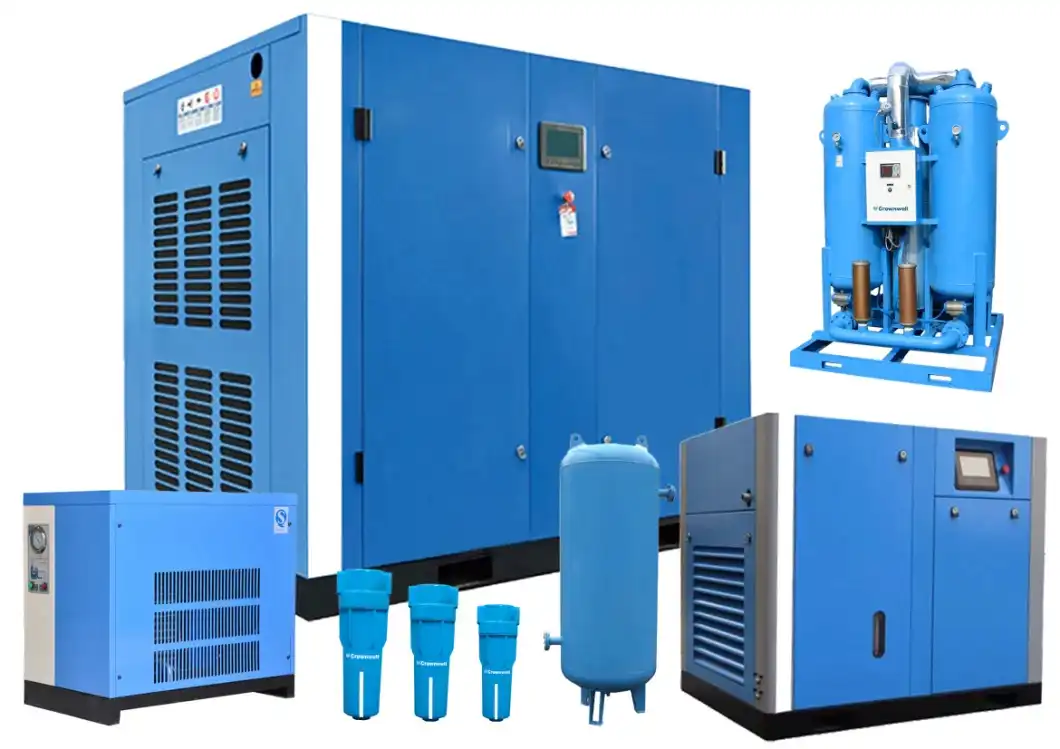

How to Repair and Maintain an Air Compressor
A compressor is a device used to move air from one place to another. Air enters the air compressor through the intake valve. Inside the compressor, the vanes on the inner rotor rotate within an eccentric cavity. The self-adjusting length arm divides the space into multiple cavities of different sizes. As the rotor rotates, air fills the cavity. As air flows around the cavity, it builds pressure and is squeezed out of the compressor output.
Positive displacement
Positive displacement air compressors use reciprocating pistons to compress air. Gas is drawn in during the suction stroke and compressed by moving the piston in the opposite direction. It then discharges the compressed air by moving it in the opposite direction. This type of air compressor is most commonly found in automobiles, refrigerators, and other applications that require high pressure. However, it is not as efficient as a centrifugal compressor.
Most modern air compressors use positive displacement. Positive displacement models capture a volume of air in the compression chamber and distribute it when the pump is operating at maximum capacity. They are more economical than their negative displacement counterparts. Reciprocating screw air compressors are the most common positive displacement compressors. The reciprocating screw air compressor adopts a water jacket around the cylinder and is often used in processes such as oil drilling.
A bicycle pump is an example of positive displacement compression. Air is drawn into the cylinder and compressed by the moving piston. A piston compressor works on the same principle, but it uses a rotating crankshaft or connecting rod to complete the movement of the pistons. There are two types of positive displacement compressors: single-acting and double-acting. Both types work on the same principle, both are positive displacement compressors. The difference between the two types is the pressure ratio.
In air compression, positive displacement compression reduces the volume of the fluid and reduces its viscosity. This results in higher pressure ratios and is used in centrifugal, axial, and scroll compressors. Positive displacement is a common feature of most air compressors. Positive displacement compressors offer the same benefits and are more energy-efficient when applied to oil-free and gas applications. This type of compression is usually the best choice for low-pressure applications.
oil free
If you’re looking for an air compressor for your business, consider an oil-free air compressor. These models offer cleaner, quieter operation than traditional air compressors and require less maintenance. They also meet ISO Class 0 or Class 1 air purity requirements. Oil-free air compressors are also quieter, with fewer moving parts and less noise. These advantages make oil-free air compressors an ideal solution for many commercial applications.
Air purity is critical in many industries. Even the tiniest drop of oil can damage production equipment or damage products. The best way to find an oil-free air compressor for your business is to consider the process and end product. As air quality improves, more and more businesses are turning to oil-free compressors. Some of the advantages and disadvantages of these air compressors are:
When choosing an oil-free air compressor, it is important to understand the terminology used in the industry. Knowing these terms will make it easier for you to choose the right compressor for your needs. ACTFM, or actual cubic feet per minute, is an industry term for measuring the amount of air pumped in one minute under rated conditions. Although a simple number, it can be very useful in determining which type of air compressor is best for your application.
The ISO 8573-1 international standard defines air quality and provides air purity classifications. The strictest classification is air purity class 0. Many manufacturers claim that oil-free air compressors meet this standard. However, a class 0 oil-free air compressor does not necessarily mean that the air is free of contaminants. In fact, Class 0 is the benchmark for air purity. While zero air quality is the highest level, that doesn’t mean it’s completely oil-free.
double acting
A double-acting air compressor is a device that uses compressed air to generate electricity. Its working principle is based on piston and connecting rod. The connecting rod connects the crankshaft to the piston through pins and caps. The piston moves as the piston moves. Rods are usually made of forged carbon steel. In terms of service and maintenance, double-acting compressors require regular vise maintenance and proper cleaning.
The displacement of the compressor is a measure of the displacement that the piston can produce in a certain period of time. Displacement is usually expressed in actual cubic feet per minute. The exact calculation depends on the type of cylinder and the configuration of the compressor. Single-acting cylinders can have head-end or crank-end displacement, both of which can be measured using the displacement equation. A double-acting air compressor will use this equation. 4 and 6 calculate the displacement.
Double-acting air compressors have multiple cylinders and are made of cast iron. They are water-cooled and have a mechanical connection between the piston and connecting rod. A double-acting compressor compresses air twice per revolution of the motor. One cylinder moves up, while the other cylinder moves down. The piston moves down, allowing air to enter through valve #1. During the operation of the compressor, the temperature of the air and gas increases.
Double-acting air compressors typically have high pressure and are considered workhorses. Double-acting compressors also feature intercooling and double compression. As a result, these machines tend to last longer than single-acting compressors. Its low speed and dual compression make it a workhorse in the compressor industry. Double-acting air compressors are workhorses and versatile devices.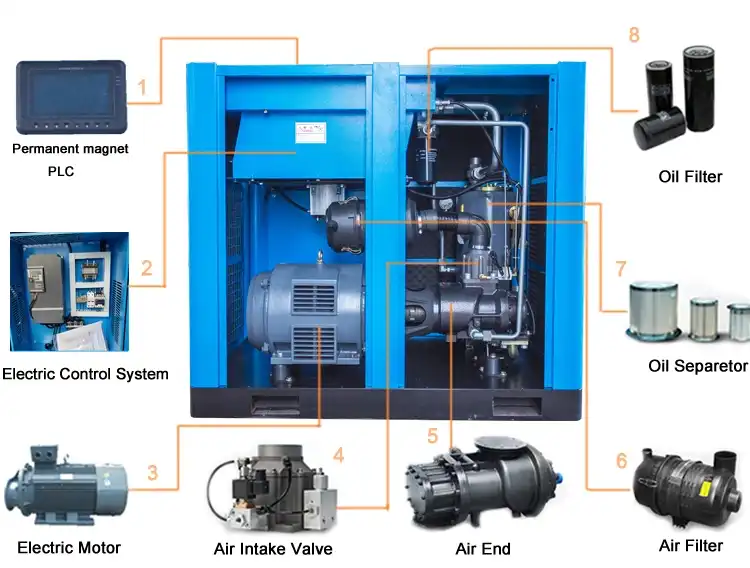
fuel tank pressure switch
You can adjust the pressure in the air compressor tank by adjusting the differential pressure. You can turn the mainspring clockwise or counterclockwise to increase or decrease the pressure. This valve will open when the pressure is low enough to start the compressor. If the pressure is too low, the valve should be closed. The cut-in and cut-out pressures should be set to appropriate values. After adjusting the tank pressure, check the hysteresis of the tank pressure switch and set the desired shutoff pressure.
If the pressure in the tank falls below the cut-in level, the tank pressure switch must be replaced. You can test the switch with a multimeter. Make sure the switch is not damaged. If you can’t find the switch, you can look at the other sections. If you find any damaged or missing parts, you should replace them. Otherwise, it may be time to check the tank pressure switch. You may need to disassemble the compressor and remove the switch.
The fuel tank pressure switch is an important part of the air compressor. It keeps you informed of the amount of air delivered by the compressor. If your tank or tank is damaged, your readings will be wrong. If the pressure switch is damaged, it will not function properly and result in incorrect readings. Fortunately, there are some easy ways to fix this. To prevent this from happening, keep the tank pressure switch in good condition.
When the air pressure in the tank drops to the cut-in pressure setting, the switch allows power to flow through it. This will start the motor and pump of the air compressor. Then, if the pressure in the tank rises above the cut-off level, the switch will trip and stop the compressor. This will prevent it from being over-pressurized. Power flow will continue to flow to the motor. Depending on your compressor model, you can change the cut-in and cut-out pressures as needed.
energy source
The power supply of the air compressor is very important. Most air compressors run on 12 VDC, which is ideal for automotive use. Alternatively, you can buy a switching power supply for around $20. No matter which power supply you choose, you must ensure that it can support the maximum current of the compressor. You can find power supplies in all sizes, from quarter-horsepower to five-horsepower.
The voltage required for a three-phase air compressor will vary. Three-phase air compressors require three separate power cords and a three-phase electrical service panel. This is because a standard 120/240-volt electrical service panel is not sufficient to power a three-phase compressor. Additionally, three-phase compressors require three separate isolated wires for the engine and motor circuits. Three-phase compressors do not require a neutral wire.


editor by Cx 2023-06-30
China 109 cfm Screw or piston & oil free 18.5kw air compressor manufacturer
Applicable Industries: Resorts, Garment Shops, Developing Material Retailers, Producing Plant, Machinery Restore Shops, Foods & Beverage Factory, Printing Retailers, Construction works , Power & Mining, Advertising and marketing Firm
Showroom Place: Uzbekistan
Condition: New, New
Kind: Screw, Screw
Configuration: Stationary, Stationary
Power Supply: AC Electricity, AC Power
Lubrication Type: Oil-totally free, Undercarriage PartsExcavator Spare Elements Observe Drive Sprocket For HitachiKobelcoVolvoHyundaiDoosanDeawooKato Lubricated
Mute: Sure
Design Amount: eighteen.5kw air compressor
Voltage: 380V
Dimension(L*W*H): 1180*800*1100
Fat: 550kg
Warranty: 1 Year
Functioning Strain: 8 bar, 13 bar, ten bar
Air potential: 109 cfm
Machinery Test Report: Provided
Online video outgoing-inspection: Presented
Advertising and marketing Type: New Merchandise 2571
Guarantee of core factors: 1 Calendar year
Core Elements: PLC, Strain vessel, Engine, Gear, Motor, Pump, Bearing, Gearbox
Fuel Kind: Air
Soon after-product sales Service Offered: Overseas third-social gathering support accessible, Free spare areas
Equivalent requirements 1: 92CFM air compressor
Similar technical specs 2: 94CFM air compressor
Related requirements 3: 95CFM air compressor
Similar technical specs 4: 97CFM air compressor
After Warranty Support: Movie technical help, On-line assistance, Spare elements, Discipline routine maintenance and repair support
Neighborhood Service Location: Uzbekistan
Certification: CE Certification
Packaging Details: 109 cfm Screw or piston & oil free eighteen.5kw air compressor & Custom made packaging OR Export normal wooden box
| Design | Compressed gas movement | Working strain | Speed | Cylinders number x diamater | Piston stroke | Tank quantity |
| m3/min | Mpa | r/min | z x mm | mm | L | |
| W1.8/five | 1.eight | 0.five | 1180 | 3 X100 | 80 | 130 |
| W2.8/5 | 2.eighty five | 0.5 | 1070 | 3 X115 | 100 | 200 |
| W3./5 | 3. | 0.five | 1070 | 3 X120 | 100 | 200 |
| W3.5/5 | 3.5 | 0.five | 1070 | 3 X125 | 100 | 200 |
| W3108 | 2. | 0.seven | 1150 | 3 X108 | 80 | 130 |
| W3118 | 3 | 0.seven | 1080 | 3 X118 | 100 | 200 |
| W3128 | 3.5 | 0.seven | 990 | 3 X128 | 110 | 200 |
| HV-4./5 | 4 | 0.5 | 970 | 4 X a hundred and twenty | 100 | 230 |
| 2V-4./5 | 4 | 0.five | 980 | 4 X 125 | 100 | 230 |
| 2V-4./5C | 4 | 0.5 | 980 | 4 X 125 | 100 | 230 |
| 2V-4./5P | 4 | 0.five | 980 | 4 X one hundred twenty | 100 | 230 |
| HS-4.5/six | 4.five | 0.six | 980 | 4 X a hundred and twenty | 112 | 200 |
| HS-4.5/6C | 4.5 | 0.six | 980 | 4 X a hundred and twenty | 112 | 230 |
Small air screw compressors
———————————————————————————————————————————-Welcome to go to the EXCEED Drillimg Rigs & Air Compressor Website in alibaba.http:///———————————————————————————————————————————-Phone Session: -———————————————————————————————————————————-
Parameters
| one | 18.5kw 25HP screw air compressor |
| 2 | Doing work strain: .8-1.0Mpa |
| three | Compressed gasoline circulation :three.m3/min |
| four | Can be custom-made Long term magnetic screw & variable frequency |
| five | Weight: 550KG |
| six | Measurement:1180*800*1100 |
| one | 45kw 60HP screw air compressors ==》Click |
| two | 55kw 75HP screw air compressors ==》Click |
| 3 | 75KW 100HP screw air compressors ==》Click |
| four | 90KW 120HP screw air compressors ==》Click |
| five | 110KW 150HP screw air compressors ==》Click |
| 6 | 132KW 175HP screw air compressors ==》Click |
| 1 | 160KW 200HP screw air compressors ==》Click |
| two | 185KW 250HP screw air compressors ==》Click |
| three | 200KW 270HP screw air compressors ==》Click |
| four | 220KW 300HP screw air compressors ==》Click |
| five | 250KW 350HP screw air compressors ==》Click |
| 6 | 280KW 375HP screw air compressors ==》Click |
Company Video clip HongHangZhouan·ChinaHongHangZhouan Team business,Specialist R & D, manufacturing Drilling Rigs,Air compressors,Joint venture drilling rigs with CZPT in July 28, 2016.
20 years knowledge, 245 million registered funds,8 sequence product classes, countless numbers variety items,tens of millions sets air compressors and drilling rigs.
Tel: –
Solution Specifics Show ———————————————————————————————————————————-Welcome to check out the EXCEED Drillimg Rigs & Air Compressor Web site in alibaba.http:///———————————————————————————————————————————-Phone Session: -———————————————————————————————————————————
Why Pick Us Primary Products ———————————————————————————————————————————-Welcome to pay a visit to the EXCEED Drillimg Rigs & Air Compressor Website in alibaba.http:///———————————————————————————————————————————-Welcome to OEM & For KTM Duke Motorbike CNC Aluminum Front Sprocket Chain Protect Guard Safeguard Components ODMTelephone Consultation: -———————————————————————————————————————————-

How to Repair and Maintain an Air Compressor
A compressor is a device used to move air from one place to another. Air enters the air compressor through the intake valve. Inside the compressor, the vanes on the inner rotor rotate within an eccentric cavity. The self-adjusting length arm divides the space into multiple cavities of different sizes. As the rotor rotates, air fills the cavity. As air flows around the cavity, it builds pressure and is squeezed out of the compressor output.
Positive displacement
Positive displacement air compressors use reciprocating pistons to compress air. Gas is drawn in during the suction stroke and compressed by moving the piston in the opposite direction. It then discharges the compressed air by moving it in the opposite direction. This type of air compressor is most commonly found in automobiles, refrigerators, and other applications that require high pressure. However, it is not as efficient as a centrifugal compressor.
Most modern air compressors use positive displacement. Positive displacement models capture a volume of air in the compression chamber and distribute it when the pump is operating at maximum capacity. They are more economical than their negative displacement counterparts. Reciprocating screw air compressors are the most common positive displacement compressors. The reciprocating screw air compressor adopts a water jacket around the cylinder and is often used in processes such as oil drilling.
A bicycle pump is an example of positive displacement compression. Air is drawn into the cylinder and compressed by the moving piston. A piston compressor works on the same principle, but it uses a rotating crankshaft or connecting rod to complete the movement of the pistons. There are two types of positive displacement compressors: single-acting and double-acting. Both types work on the same principle, both are positive displacement compressors. The difference between the two types is the pressure ratio.
In air compression, positive displacement compression reduces the volume of the fluid and reduces its viscosity. This results in higher pressure ratios and is used in centrifugal, axial, and scroll compressors. Positive displacement is a common feature of most air compressors. Positive displacement compressors offer the same benefits and are more energy-efficient when applied to oil-free and gas applications. This type of compression is usually the best choice for low-pressure applications.
oil free
If you’re looking for an air compressor for your business, consider an oil-free air compressor. These models offer cleaner, quieter operation than traditional air compressors and require less maintenance. They also meet ISO Class 0 or Class 1 air purity requirements. Oil-free air compressors are also quieter, with fewer moving parts and less noise. These advantages make oil-free air compressors an ideal solution for many commercial applications.
Air purity is critical in many industries. Even the tiniest drop of oil can damage production equipment or damage products. The best way to find an oil-free air compressor for your business is to consider the process and end product. As air quality improves, more and more businesses are turning to oil-free compressors. Some of the advantages and disadvantages of these air compressors are:
When choosing an oil-free air compressor, it is important to understand the terminology used in the industry. Knowing these terms will make it easier for you to choose the right compressor for your needs. ACTFM, or actual cubic feet per minute, is an industry term for measuring the amount of air pumped in one minute under rated conditions. Although a simple number, it can be very useful in determining which type of air compressor is best for your application.
The ISO 8573-1 international standard defines air quality and provides air purity classifications. The strictest classification is air purity class 0. Many manufacturers claim that oil-free air compressors meet this standard. However, a class 0 oil-free air compressor does not necessarily mean that the air is free of contaminants. In fact, Class 0 is the benchmark for air purity. While zero air quality is the highest level, that doesn’t mean it’s completely oil-free.
double acting
A double-acting air compressor is a device that uses compressed air to generate electricity. Its working principle is based on piston and connecting rod. The connecting rod connects the crankshaft to the piston through pins and caps. The piston moves as the piston moves. Rods are usually made of forged carbon steel. In terms of service and maintenance, double-acting compressors require regular vise maintenance and proper cleaning.
The displacement of the compressor is a measure of the displacement that the piston can produce in a certain period of time. Displacement is usually expressed in actual cubic feet per minute. The exact calculation depends on the type of cylinder and the configuration of the compressor. Single-acting cylinders can have head-end or crank-end displacement, both of which can be measured using the displacement equation. A double-acting air compressor will use this equation. 4 and 6 calculate the displacement.
Double-acting air compressors have multiple cylinders and are made of cast iron. They are water-cooled and have a mechanical connection between the piston and connecting rod. A double-acting compressor compresses air twice per revolution of the motor. One cylinder moves up, while the other cylinder moves down. The piston moves down, allowing air to enter through valve #1. During the operation of the compressor, the temperature of the air and gas increases.
Double-acting air compressors typically have high pressure and are considered workhorses. Double-acting compressors also feature intercooling and double compression. As a result, these machines tend to last longer than single-acting compressors. Its low speed and dual compression make it a workhorse in the compressor industry. Double-acting air compressors are workhorses and versatile devices.
fuel tank pressure switch
You can adjust the pressure in the air compressor tank by adjusting the differential pressure. You can turn the mainspring clockwise or counterclockwise to increase or decrease the pressure. This valve will open when the pressure is low enough to start the compressor. If the pressure is too low, the valve should be closed. The cut-in and cut-out pressures should be set to appropriate values. After adjusting the tank pressure, check the hysteresis of the tank pressure switch and set the desired shutoff pressure.
If the pressure in the tank falls below the cut-in level, the tank pressure switch must be replaced. You can test the switch with a multimeter. Make sure the switch is not damaged. If you can’t find the switch, you can look at the other sections. If you find any damaged or missing parts, you should replace them. Otherwise, it may be time to check the tank pressure switch. You may need to disassemble the compressor and remove the switch.
The fuel tank pressure switch is an important part of the air compressor. It keeps you informed of the amount of air delivered by the compressor. If your tank or tank is damaged, your readings will be wrong. If the pressure switch is damaged, it will not function properly and result in incorrect readings. Fortunately, there are some easy ways to fix this. To prevent this from happening, keep the tank pressure switch in good condition.
When the air pressure in the tank drops to the cut-in pressure setting, the switch allows power to flow through it. This will start the motor and pump of the air compressor. Then, if the pressure in the tank rises above the cut-off level, the switch will trip and stop the compressor. This will prevent it from being over-pressurized. Power flow will continue to flow to the motor. Depending on your compressor model, you can change the cut-in and cut-out pressures as needed.
energy source
The power supply of the air compressor is very important. Most air compressors run on 12 VDC, which is ideal for automotive use. Alternatively, you can buy a switching power supply for around $20. No matter which power supply you choose, you must ensure that it can support the maximum current of the compressor. You can find power supplies in all sizes, from quarter-horsepower to five-horsepower.
The voltage required for a three-phase air compressor will vary. Three-phase air compressors require three separate power cords and a three-phase electrical service panel. This is because a standard 120/240-volt electrical service panel is not sufficient to power a three-phase compressor. Additionally, three-phase compressors require three separate isolated wires for the engine and motor circuits. Three-phase compressors do not require a neutral wire.


editor by Cx 2023-06-29
China 11Kw 15HP Industrial Cheap Energy Saving Silent Water Oil Free Oilless Direct Drive Screw Air Compressor supplier
Relevant Industries: Accommodations, Garment Outlets, Constructing Material Shops, Manufacturing Plant, Machinery Fix Stores, Foods & Beverage Manufacturing unit, Farms, Cafe, Residence Use, Retail, Meals Shop, Printing Retailers, Development works , Power & Mining, Meals & Beverage Shops, Other, Chain Sprocket Blacken Treatment method Harden Tooth C45 Steel Roller Chain Sprocket Advertising and marketing Company
Showroom Area: None
Condition: New
Kind: Screw
Configuration: Stationary
Energy Source: AC Electrical power
Lubrication Fashion: Oil-totally free
Mute: Sure
Product Quantity: HYWV-11G
Voltage: 380V/220V/415V/460V/440V
Dimension(L*W*H): 1135*800*1000mm
Weight: 500
Warranty: 1 12 months
Working Force: 7 bar, 8 bar, thirteen bar, ten bar
Air ability: 1-43 m3/min
Machinery Test Report: Presented
Video outgoing-inspection: Provided
Advertising Type: Hot Product 2571
Guarantee of main factors: eighteen months
Main Elements: Motor, Rotor, Oil and fuel separator
Fuel Variety: Air
Design: HYWV-11G
Product name: Screw compressor
Functioning stress: 7bar 8bar 10bar
Exhaust volume: 1-forty three m3/min
Energy: 11kw
Noise: 58±3
Air outlet pipe diameter: G1”
Cooling: Air/Drinking water cooling
Keywords and phrases: Screw
Dimension: 1135*800*1000mm
Packaging Information: Wooden box
Port: ZheJiang HangZhou HangZhou
Specification
| item | value |
| Working Strain | 7 bar, 8 bar, 10 bar, 13bar |
| 1-43Air capability | 8-ten m3/min |
| Gas Variety | Air |
| Model | HYWV-11G |
| Exhaust volume | 35-1519 cfm |
| Power | 55kw |
| Noise | 69±3 |
| Air outlet pipe diameter | G1” |
| Cooling | Air/H2o cooling |
| Keywords | Screw |
| Dimension | 1135*800*1000mm |
| Power | Minimum electricity conserving (KW – h) twenty% | Maximum electrical power preserving (KW – h) forty% |
| 7.5KW | 12000 | 24000 |
| 11KW | 17600 | 35200 |
| 15KW | 24000 | 48000 |
| 22KW | 35200 | 70400 |
| 37KW | 59200 | 118400 |
| 45KW | 72000 | 144000 |
| 55KW | 88000 | 176000 |
| 75KW | 120000 | 240000 |
| 90KW | 144000 | 288000 |

The Air Compressor Is a Versatile Tool
The Air Compressor is one of the most versatile tools in any garage or workshop. It is easy to use and can perform a variety of tasks, from jackhammering to drilling. These machines are available in a wide variety of sizes and types, making it an excellent choice for a variety of situations. With a single motor, you no longer need separate motors for each tool. Its lightweight, compact design makes it easy to handle, and the single motor also reduces wear on parts.
Oil-injected
Oil-injected air compressors require a large amount of lubricant, which needs to be added to the sump regularly to maintain optimum performance. As there are many types of industrial fluids, a well-intentioned maintenance technician may add the wrong lubricant to the compressor. If this happens, the compressor will become incompatible with the lubricant, resulting in excessive carryover and the need to flush and replace downstream air treatment components.
Typically, the G 110-250 oil-injected rotary screw compressor from Atlas Copco provides reliable compressed air, preventing costly downtime. The G110-250 oil-injected rotary screw compressor is highly reliable and durable, enabling it to function in temperatures up to 46degC/115degF. Despite the oil-injected air compressor’s robust design, this unit requires very little on-site installation, and it features simple operation.
The primary advantage of oil-injected air compressors is the reduced cost of running. The cost of oil-free compressors is less than half of that of oil-injected ones, and it will require fewer maintenance costs in the long run. Moreover, the oil-free system is more environmentally friendly than oil-injected air compressors. But the drawbacks of oil-injected air compressors are substantial, too. It can contaminate finished goods and cause a significant financial risk for the manufacturer.
An oil-injected rotary screw air compressor offers several advantages over its counterpart. First, it features an innovative vertical design with variable-speed drive, allowing it to run more efficiently. Second, oil-injected air compressors reduce energy consumption by up to 50% compared to non-oil-injected air compressors. They also have a thermostatic valve, allowing them to maintain an optimum temperature. Thermostatically-regulated oil coolers allow the compressor to run more quietly.
Oil-free
What is an oil-free air compressor? The name refers to a type of air compressor that does not contain oil in the compressor chamber. Oil-free air compressors still use oil for various purposes, including lubricating the moving parts and managing waste heat. However, many people do not realize that their air compressor still requires oil for proper functioning. This article will explore why this type of air compressor is preferable for many users.
First of all, oil-free air technology has many benefits. For one, it reduces the energy cost involved in filtering air, and it minimizes leaks. Moreover, it also reduces the oil costs associated with compressor refills. And finally, it reduces the risks of contamination. Oil-free air technology is the future of compressed air. If you’re looking for an oil-free air compressor, here’s what to look for in your search.
Depending on the purpose of your air compressor, it may be beneficial to invest in an oil-free air compressor. Oil-lubricated air compressors are generally more durable than their oil-free counterparts, but they may cost twice as much. You should still consider the cost of ownership before purchasing an oil-free compressor. The oil-free models can be easier to transport, and they are more powerful. Moreover, they’re quieter than oil-lubed models.
An oil-free air compressor also means less maintenance, as it doesn’t need oil to work. This type of air compressors also features fewer moving parts, which means fewer places for problems to develop. All oil-free air compressors are manufactured to meet ISO Class 0 and 1 air purity standards. They also have less noise and vibration compared to their oil-based counterparts. So, why not choose an oil-free air compressor for your business?
Gasoline
When choosing a gas-powered air compressor, it’s important to consider the advantages of gasoline. This energy source can power a large air compressor without electricity. However, this type of air compressor lacks electrical hookup, so you’ll need to run an extension cord if you need to use it at a distance. However, gas compressors are able to function with just a gas tank. This makes them ideal for medium to heavy-duty industrial applications.
Another important consideration when choosing a gas air compressor is its size. Larger compressors are typically larger than portable ones and require more space. This makes them easier to transport and operate on the go. However, if you’re not sure which type of air compressor is best for you, consider the gas-powered versions. While they may be lighter, they don’t run as smoothly as their electric counterparts. Gasoline-powered compressors are not as portable as their electric counterparts and require proper maintenance.
Electricity
Electricity in an air compressor is not cheap. A 25 HP air compressor runs for ten hours each day, five days a week. The motor in these machines consumes 746 watts per hour. To find out how much electricity the equipment uses, multiply the wattage by the running time. For example, if the compressor runs for three hours, then it will use 1.9 kilowatt hours of electricity. To determine how much electricity an air compressor uses per day, you can calculate the kilowatt hours and multiply the number by the utility rate. Considering this, you can determine the cost of running your air compressor once per month.
The cost of operating an air compressor depends on the type of compressor. Electric air compressors are often silent and can run without any maintenance. These tools can be left unattended for up to four thousand hours before requiring repair. Electric air compressors require higher power for higher pressure, so you should plan accordingly. Whether or not you need a maintenance visit is up to you, but the benefit of not having to spend a fortune on repairs is priceless.
Although compressed air is not an energy-efficient source, its use in a variety of applications may save you money and kilowatts. Since an air compressor uses power when it is running, the cost is lower than the cost of operating a power tool. If you plan to use your air compressor for a long time, make sure that it is maintained properly. Proper care will save you money and power, and you may even be able to get an extended warranty if the compressor breaks down.
Variable frequency drive
The main purpose of a variable frequency drive (VFD) in an air compressor is to reduce energy consumption in the process of compression. A single motor drag system cannot adjust its speed continuously according to the weight of the load. By applying frequency control to the compressor, the power consumption can be reduced while maintaining the same pressure level. Therefore, a VFD is an excellent choice for compressors. Its benefits are numerous.
A VFD can also monitor the temperature of the motor and send error signals if the motor is running too hot or too cold. This eliminates the need for a separate sensor to monitor the oil pressure. These functions are useful not only in lowering energy consumption, but also in improving the performance of an application. Moreover, a VFD can monitor additional variables such as temperature and motor speed. Hence, it is a useful investment.
When using a VFD, it is crucial to choose the right motor. The speed of the compressor should be within the maximum starting limit of the motor. The air tank may be of any size, but a constant pressure limit is required to keep the VFD running within the service factor of the motor. In addition to a VFD, a master controller should also include a remote pressure set point and a PID card for a master controller. The transmitter should incorporate all useful data from the VFD, including the speed and the oil temperature. The VFD must be tested before it is integrated with the master control. It should be tested for min and max speed, temperature, and current within the expected range.
The use of a VFD in an air compressor has many benefits. One of the most notable is the reduction in power consumption. Fixed-speed compressors run on set points of six to seven bar. An extra bar of compression uses 7 percent of energy. This energy is wasted. A VFD-powered air compressor can also increase the life span of compressor parts. It is one of the best investments in your compressor. So, why wait any longer?


editor by Cx 2023-06-25
.webp)
.webp)
.webp)
.webp)
.webp)
.webp)