Product Description
| Product Name | Oil-Free Booster Compressor |
| Model No | BW-3/5/10/15/20/30… |
| Inlet Pressure | 0.4Mpa( G ) |
| Exhaust Pressure | 150/200Mpa( G ) |
| Type | High Pressure Oil Free |
| Accessories | Filling Manifold, Piston ring, Etc |
If you have compressor inquiry please tell us follows information when you send inquiry:
*Compressor working medium: If single gas ,how many purity ? if mixed gas , what’s gas content lit ?
*Suction pressure(gauge pressure):_____bar
*Exhaust pressure(gauge pressure):_____bar
*Flow rate per hour for compressor: _____Nm³/h
Compressor gas suction temperature:_____ºC
Compressor working hours per day :_____hours
Compressor working site altitude :_____m
Environment temperature : _____ºC
Has cooling water in the site or not ?______
Voltage and frequency for 3 phase :____________
Do not has water vapor or H2S in the gas ?______
Application for compressor?__________
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | 1year |
|---|---|
| Warranty: | 1year |
| Product Name: | Oxygen,Nitrogen Compressor |
| Gas Type: | Oxygen,Nitrogen,Special Gas |
| Cooling Method: | Air Cooling Water Cooling |
| Application: | Filling Cylinder |
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|
.webp)
Can Gas Air Compressors Be Used for Well Drilling?
Gas air compressors can be used for well drilling, and they are commonly employed in drilling operations. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Air Drilling Method:
Gas air compressors are often utilized in the air drilling method, also known as pneumatic drilling. In this drilling technique, compressed air is used to create a high-velocity airflow that carries the drill cuttings to the surface. The high-pressure air also aids in cooling the drill bit and providing additional force for efficient drilling.
2. Benefits of Gas Air Compressors:
Gas air compressors offer several advantages for well drilling:
- Portability: Gas air compressors can be easily transported to remote drilling sites, allowing for flexibility in well location.
- Power: Gas air compressors provide high-pressure air output, which is essential for effective drilling in various geological formations.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Gas air compressors can be more cost-effective compared to other drilling methods, as they eliminate the need for drilling mud and associated disposal costs.
- Environmental Considerations: Air drilling with gas compressors produces minimal waste and does not require the use of potentially harmful drilling fluids, making it an environmentally friendly option.
3. Compressor Selection:
When selecting a gas air compressor for well drilling, several factors should be considered:
- Pressure and Flow Requirements: Evaluate the pressure and flow requirements of the drilling operation to ensure that the gas air compressor can deliver the necessary air output.
- Compressor Size and Power: Choose a compressor with adequate size and power output to match the drilling demands. Factors such as borehole depth, drill bit type, and drilling speed will influence the compressor’s power requirements.
- Portability: Consider the portability features of the gas air compressor, such as its weight, dimensions, and mobility options, to facilitate transportation to drilling sites.
4. Safety Considerations:
It is essential to follow safety guidelines when using gas air compressors for well drilling. These may include proper ventilation to prevent the accumulation of exhaust fumes, adherence to equipment operating limits, and the use of personal protective equipment (PPE) for drilling personnel.
5. Other Considerations:
While gas air compressors are commonly used for well drilling, it is worth noting that the suitability of a gas air compressor for a specific drilling project depends on various factors such as geological conditions, well depth, and drilling objectives. It is recommended to consult with drilling experts and professionals to determine the most suitable drilling method and equipment for a particular project.
In summary, gas air compressors can be effectively used for well drilling, particularly in the air drilling method. They offer portability, power, cost-effectiveness, and environmental advantages. Proper selection, considering pressure and flow requirements, as well as safety precautions, is crucial to ensure successful and safe drilling operations.
.webp)
How Do Gas Air Compressors Contribute to Energy Savings?
Gas air compressors can contribute to energy savings in several ways. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Efficient Power Source:
Gas air compressors are often powered by gasoline or diesel engines. Compared to electric compressors, gas-powered compressors can provide higher power output for a given size, resulting in more efficient compression of air. This efficiency can lead to energy savings, especially in applications where a significant amount of compressed air is required.
2. Reduced Electricity Consumption:
Gas air compressors, as standalone units that don’t rely on electrical power, can help reduce electricity consumption. In situations where the availability of electricity is limited or expensive, using gas air compressors can be a cost-effective alternative. By utilizing fuel-based power sources, gas air compressors can operate independently from the electrical grid and reduce dependence on electricity.
3. Demand-Sensitive Operation:
Gas air compressors can be designed to operate on demand, meaning they start and stop automatically based on the air requirements. This feature helps prevent unnecessary energy consumption during periods of low or no compressed air demand. By avoiding continuous operation, gas air compressors can optimize energy usage and contribute to energy savings.
4. Energy Recovery:
Some gas air compressors are equipped with energy recovery systems. These systems capture and utilize the heat generated during the compression process, which would otherwise be wasted. The recovered heat can be redirected and used for various purposes, such as space heating, water heating, or preheating compressed air. This energy recovery capability improves overall energy efficiency and reduces energy waste.
5. Proper Sizing and System Design:
Selecting the appropriate size and capacity of a gas air compressor is crucial for energy savings. Over-sizing a compressor can lead to excessive energy consumption, while under-sizing can result in inefficient operation and increased energy usage. Properly sizing the compressor based on the specific air demands ensures optimal efficiency and energy savings.
6. Regular Maintenance:
Maintaining gas air compressors in good working condition is essential for energy efficiency. Regular maintenance, including cleaning or replacing air filters, checking and repairing leaks, and ensuring proper lubrication, helps optimize compressor performance. Well-maintained compressors operate more efficiently, consume less energy, and contribute to energy savings.
7. System Optimization:
For larger compressed air systems that involve multiple compressors, implementing system optimization strategies can further enhance energy savings. This may include employing advanced control systems, such as variable speed drives or sequencers, to match compressed air supply with demand, minimizing unnecessary energy usage.
In summary, gas air compressors contribute to energy savings through their efficient power sources, reduced electricity consumption, demand-sensitive operation, energy recovery systems, proper sizing and system design, regular maintenance, and system optimization measures. By utilizing gas-powered compressors and implementing energy-efficient practices, businesses and industries can achieve significant energy savings in their compressed air systems.
.webp)
Can Gas Air Compressors Be Used in Remote Locations?
Yes, gas air compressors are well-suited for use in remote locations where access to electricity may be limited or unavailable. Their portability and reliance on gas engines make them an ideal choice for providing a reliable source of compressed air in such environments. Here’s a detailed explanation of how gas air compressors can be used in remote locations:
1. Independence from Electrical Grid:
Gas air compressors do not require a direct connection to the electrical grid, unlike electric air compressors. This independence from the electrical grid allows gas air compressors to be used in remote locations, such as wilderness areas, remote job sites, or off-grid locations, where it may be impractical or cost-prohibitive to establish electrical infrastructure.
2. Mobility and Portability:
Gas air compressors are designed to be portable and easy to transport. They are often equipped with handles, wheels, or trailers, making them suitable for remote locations. The gas engine powering the compressor provides mobility, allowing the compressor to be moved to different areas within the remote location as needed.
3. Fuel Versatility:
Gas air compressors can be fueled by various types of combustible gases, including gasoline, diesel, natural gas, or propane. This fuel versatility ensures that gas air compressors can adapt to the available fuel sources in remote locations. For example, if gasoline or diesel is readily available, the gas air compressor can be fueled with these fuels. Similarly, if natural gas or propane is accessible, the compressor can be configured to run on these gases.
4. On-Site Power Generation:
In remote locations where electricity is limited, gas air compressors can serve as on-site power generators. They can power not only the compressor itself but also other equipment or tools that require electricity for operation. This versatility makes gas air compressors useful for a wide range of applications in remote locations, such as powering lights, tools, communication devices, or small appliances.
5. Off-Grid Operations:
Gas air compressors enable off-grid operations, allowing tasks and activities to be carried out in remote locations without relying on external power sources. This is particularly valuable in industries such as mining, oil and gas exploration, forestry, or construction, where operations may take place in remote and isolated areas. Gas air compressors provide the necessary compressed air for pneumatic tools, drilling equipment, and other machinery required for these operations.
6. Emergency Preparedness:
Gas air compressors are also beneficial for emergency preparedness in remote locations. In situations where natural disasters or emergencies disrupt the power supply, gas air compressors can provide a reliable source of compressed air for essential equipment and systems. They can power emergency lighting, communication devices, medical equipment, or backup generators, ensuring operational continuity in critical situations.
7. Adaptability to Challenging Environments:
Gas air compressors are designed to withstand various environmental conditions, including extreme temperatures, humidity, dust, and vibrations. This adaptability to challenging environments makes them suitable for use in remote locations, where environmental conditions may be harsh or unpredictable.
Overall, gas air compressors can be effectively used in remote locations due to their independence from the electrical grid, mobility, fuel versatility, on-site power generation capabilities, suitability for off-grid operations, emergency preparedness, and adaptability to challenging environments. These compressors provide a reliable source of compressed air, enabling a wide range of applications in remote settings.


editor by CX 2024-03-28
China Standard Vehicle-Mounted Diesel Engine 40MPa Nitrogen Generator Injection System Membrane Nitrogen Production N2 Compressor air compressor CHINAMFG freight
Product Description
Company Profile
The company’s main products include desulfurization, dehydrocarbons, separation, compression, filling, storage and transportation equipment for natural gas extraction in oil and gas fields; complete sets of wellhead gas recovery equipment; complete sets of vented natural gas recovery equipment; complete sets of coalbed methane, shale gas and biogas development and utilization equipment Equipment; CNG filling station complete equipment; LNG complete equipment; BOG compressor; large-displacement screw-piston compound compressor; membrane nitrogen and adsorption nitrogen production complete equipment; in addition, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, argon, carbon monoxide gas, carbon dioxide gas, coal gas, hydrogen sulfide gas, propylene gas, ethylene gas, methyl chloride gas, trifluoropropane gas, liquefied petroleum gas and other special gases, low-temperature gases and air compressors. Among them, the W and V series non-lubricated compressors produced by introducing advanced foreign technology have reached the international advanced level.
Product Description
Membrane nitrogen production
In order to meet the requirements of downhole nitrogen filling, underbalanced drilling technology, pipeline nitrogen replacement and other requirements. Our company has developed a screw low-pressure air compressor + membrane nitrogen production system + high-pressure nitrogen booster and compression system. It can provide users with high-pressure nitrogen with a flow rate of 600-2000Nm3/h and a pressure of 15-40MPa.
The nitrogen production system is designed to be skid-mounted and installed on 2 skids. The system is divided into 3 modules, screw low-pressure air compressor module, membrane nitrogen production system module, and high-pressure nitrogen booster compressor module. The screw low-pressure air compressor module and membrane nitrogen generation system module are installed on 1 skid, and the high-pressure nitrogen booster compressor system is on another skid. The system is air-cooled and driven by a diesel engine. The skid is equipped with a metal cover, which can be easily installed on the chassis of the car and is suitable for field operations.
Adsorption ammonia production
Our company produces various adsorption ammonia production equipment. Among them, adsorption ammonia production, special gas recovery, purification, and purification are our company’s unique technologies. They have the advantages of reasonable configuration, complete functions, high reliability, and easy operation.
Processing capacity: 50-600Nm3/h
Ammonia purity: 95-9939%
Ammonia final outlet pressure: 0.7-40MPa
Recovery, purification and purification of special gases
Medium: ammonia, argon, etc.
Processing capacity: 400-600Nm3/h
Purification purity: can be purified from 75% to 95-99.95%
Purified gas loss rate: ≤5%
After purification, the pressure will be increased to 25-40MPa according to user needs.
Parameters of nitrogen production system
| Nitrogen flow rate: | 600-2000NM3/H |
| Nitrogen purity: | ≥95% (Vol1%) (no oxygen N, Ar content, ) (95%-99.9% continuously adjustable) |
| Nitrogen pressure: | 40Mpa |
| Power: | Motors/ Diesel engine |
| Cooling | Air/water |
| Skid size: | 9500*2500*2400(mm) Adapted to high wind and sand working conditions in the wild, the whole body is skid-mounted on the vehicle. |
| Design altitude: | 2000M |
| Work time: | 24 hours continuously |
| Nitrogen generation time after startup: | 10min |
| Ambient temperature range: | -20ºC-+45ºC |
| Ambient humidity range: | ≤85% |
| Type | Nitrogen production Nm3/h | Exhaust pressure Mpa |
| KZD-600/40 | 600 | 40 |
| KZD-900/40 | 900 | 40 |
| KZD-1200/40 | 1200 | 40 |
| KZD-2000/25 | 2000 | 25 |
| KZD-2000/40 | 2000 | 40 |
Detailed Photos
After Sales Service
In addition to the high-quality performance of our products, we also attach great importance to providing customers with comprehensive services. We have an independent service operation and maintenance team, providing customers with various support and services, including technical support, debugging services, spare parts supply, renovation and upgrading, and major maintenance. We always adhere to the principle of customer-centrism, ensuring the safe and stable operation of customer equipment. Our service team is committed to providing reliable support for customers’ operations 24/7.
Training plan
Technical training is divided into 2 parts: company training and on-site training.
1)Company training
Before the unit is delivered, that is during the unit assembly period, users will be provided with a one-week on-site training by the company. Provide local accommodation and transportation facilities, and provide free venues, teaching materials, equipment, tools, etc. required for training. The company training content is as follows:
The working principle, structure and technical performance of the unit.
Unit assembly and adjustment, unit testing.
Operation of the unit, remote/local operation, manual/automatic operation, daily operation and management, familiar with the structure of each system of the unit.
Routine maintenance and upkeep of the unit, and precautions for operation and maintenance.
Analysis and troubleshooting of common faults, and emergency handling methods.
2) On-site training
During the installation and trial operation of the unit, on-site training will be conducted to teach the principles, structure, operation, maintenance, troubleshooting of common faults and other knowledge of the unit, so as to further become familiar with the various systems of the unit, so that the purchaser can independently and correctly operate the unit. Operation, maintenance and management.
Packaging & Shipping
/* March 10, 2571 17:59:20 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | 12 Month |
|---|---|
| Warranty: | 12 Month |
| Lubrication Style: | Lubricated |
.shipping-cost-tm .tm-status-off{background: none;padding:0;color: #1470cc}
|
Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
about shipping cost and estimated delivery time. |
|---|
| Payment Method: |
|
|---|---|
|
Initial Payment Full Payment |
| Currency: | US$ |
|---|
| Return&refunds: | You can apply for a refund up to 30 days after receipt of the products. |
|---|
.webp)
What Is the Noise Level of Gas Air Compressors?
The noise level of gas air compressors can vary depending on several factors, including the compressor’s design, engine type, operating conditions, and the presence of noise-reducing features. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Compressor Design:
The design of the gas air compressor can influence its noise level. Some compressors are engineered with noise reduction in mind, utilizing features such as sound insulation, vibration dampening materials, and mufflers to minimize noise generation. Compressors with enclosed cabinets or acoustic enclosures tend to have lower noise levels compared to open-frame compressors.
2. Engine Type:
The type of engine used in the gas air compressor can impact the noise level. Gas air compressors typically use internal combustion engines powered by gasoline or propane. Gasoline engines tend to produce higher noise levels compared to diesel engines or electric motors. However, advancements in engine technology have led to quieter gasoline engines with improved noise control.
3. Operating Conditions:
The operating conditions of the gas air compressor can affect the noise level. Factors such as the load capacity, speed of operation, and ambient temperature can influence the amount of noise generated. Compressors operating at higher loads or speeds may produce more noise compared to those running at lower levels.
4. Noise-Reducing Features:
Some gas air compressors are equipped with noise-reducing features to minimize sound emissions. These may include built-in silencers, acoustic enclosures, or noise-absorbing materials. Such features help dampen the noise produced by the compressor and reduce its overall noise level.
5. Manufacturer Specifications:
Manufacturers often provide noise level specifications for their gas air compressors. These specifications typically indicate the sound pressure level (SPL) in decibels (dB) at a specific distance from the compressor. It is important to refer to these specifications to get an idea of the expected noise level of a particular compressor model.
6. Distance and Location:
The distance between the gas air compressor and the listener can impact the perceived noise level. As sound waves disperse, the noise level decreases with distance. Locating the compressor in an area that is isolated or distant from occupied spaces can help minimize the impact of noise on the surrounding environment.
It is important to note that gas air compressors, especially those used in industrial or heavy-duty applications, can generate substantial noise levels. Occupational health and safety regulations may require the use of hearing protection for individuals working in close proximity to loud compressors.
Overall, the noise level of gas air compressors can vary, and it is advisable to consult the manufacturer’s specifications and consider noise-reducing features when selecting a compressor. Proper maintenance, such as regular lubrication and inspection of components, can also help minimize noise levels and ensure optimal performance.
.webp)
Can Gas Air Compressors Be Used for Gas Line Maintenance?
Gas air compressors can be used for certain aspects of gas line maintenance, primarily for tasks that require compressed air. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Clearing Debris and Cleaning:
Gas air compressors can be utilized to clear debris and clean gas lines. Compressed air can be directed through the gas lines to dislodge and remove dirt, dust, rust particles, or other contaminants that may accumulate over time. This helps maintain the integrity and efficiency of the gas lines.
2. Pressure Testing:
Gas line maintenance often involves pressure testing to ensure the lines can withstand the required operating pressures. Gas air compressors can provide the necessary compressed air to pressurize the lines for testing purposes. By pressurizing the gas lines with compressed air, technicians can identify any leaks or weaknesses in the system.
3. Leak Detection:
Gas air compressors can also be used in conjunction with appropriate leak detection equipment to identify and locate gas leaks in the gas lines. Compressed air can be introduced into the lines, and the detection equipment can then identify any areas where the compressed air escapes, indicating a potential gas leak.
4. Valve and Equipment Maintenance:
Gas line maintenance may involve the inspection, maintenance, or replacement of valves and associated equipment. Compressed air can be used to clean and blow out debris from valves, purge lines, or assist in the disassembly and reassembly of components.
5. Pipe Drying:
Gas air compressors can aid in drying gas lines after maintenance or repairs. By blowing compressed air through the lines, any residual moisture can be removed, ensuring the gas lines are dry before being put back into service.
6. Precautions and Regulations:
When using gas air compressors for gas line maintenance, it is essential to follow safety precautions and adhere to relevant regulations. Gas line maintenance often involves working in hazardous environments, and proper training, equipment, and procedures must be followed to ensure the safety of personnel and the integrity of the gas system.
It is important to note that gas air compressors should not be used directly for pressurizing or transporting natural gas or other combustible gases. Gas line maintenance tasks involving gas air compressors primarily focus on using compressed air for specific maintenance and testing purposes, as outlined above.
In summary, gas air compressors can be useful for certain aspects of gas line maintenance, including clearing debris, pressure testing, leak detection, valve and equipment maintenance, and pipe drying. However, it is crucial to follow safety guidelines and regulations when working with gas lines and compressed air to ensure the safety and integrity of the gas system.
.webp)
Can Gas Air Compressors Be Used in Remote Locations?
Yes, gas air compressors are well-suited for use in remote locations where access to electricity may be limited or unavailable. Their portability and reliance on gas engines make them an ideal choice for providing a reliable source of compressed air in such environments. Here’s a detailed explanation of how gas air compressors can be used in remote locations:
1. Independence from Electrical Grid:
Gas air compressors do not require a direct connection to the electrical grid, unlike electric air compressors. This independence from the electrical grid allows gas air compressors to be used in remote locations, such as wilderness areas, remote job sites, or off-grid locations, where it may be impractical or cost-prohibitive to establish electrical infrastructure.
2. Mobility and Portability:
Gas air compressors are designed to be portable and easy to transport. They are often equipped with handles, wheels, or trailers, making them suitable for remote locations. The gas engine powering the compressor provides mobility, allowing the compressor to be moved to different areas within the remote location as needed.
3. Fuel Versatility:
Gas air compressors can be fueled by various types of combustible gases, including gasoline, diesel, natural gas, or propane. This fuel versatility ensures that gas air compressors can adapt to the available fuel sources in remote locations. For example, if gasoline or diesel is readily available, the gas air compressor can be fueled with these fuels. Similarly, if natural gas or propane is accessible, the compressor can be configured to run on these gases.
4. On-Site Power Generation:
In remote locations where electricity is limited, gas air compressors can serve as on-site power generators. They can power not only the compressor itself but also other equipment or tools that require electricity for operation. This versatility makes gas air compressors useful for a wide range of applications in remote locations, such as powering lights, tools, communication devices, or small appliances.
5. Off-Grid Operations:
Gas air compressors enable off-grid operations, allowing tasks and activities to be carried out in remote locations without relying on external power sources. This is particularly valuable in industries such as mining, oil and gas exploration, forestry, or construction, where operations may take place in remote and isolated areas. Gas air compressors provide the necessary compressed air for pneumatic tools, drilling equipment, and other machinery required for these operations.
6. Emergency Preparedness:
Gas air compressors are also beneficial for emergency preparedness in remote locations. In situations where natural disasters or emergencies disrupt the power supply, gas air compressors can provide a reliable source of compressed air for essential equipment and systems. They can power emergency lighting, communication devices, medical equipment, or backup generators, ensuring operational continuity in critical situations.
7. Adaptability to Challenging Environments:
Gas air compressors are designed to withstand various environmental conditions, including extreme temperatures, humidity, dust, and vibrations. This adaptability to challenging environments makes them suitable for use in remote locations, where environmental conditions may be harsh or unpredictable.
Overall, gas air compressors can be effectively used in remote locations due to their independence from the electrical grid, mobility, fuel versatility, on-site power generation capabilities, suitability for off-grid operations, emergency preparedness, and adaptability to challenging environments. These compressors provide a reliable source of compressed air, enabling a wide range of applications in remote settings.


editor by CX 2024-02-20
China Good quality 30nm3/H 300bar High Quality Oil-Free Oxygen Nitrogen Gas Compressors air compressor portable
Product Description
High Quality Oil-free Oxygen Nitrogen Gas Compressors
Minwen high pressure industrial gas compressor belongs to oil-free reciprocating piston type construction. It is divided into three-stage, four-stage or five-stage compression according to the displacement and pressure. It is divided into air-cooled type and water-cooled type according to the cooling type.
An oil-free compressor is a type of gas compressor that operates without the need for lubricating oil in the compression chamber. Traditional gas compressors use oil to lubricate the moving parts and provide a better seal between the compression chamber and the piston or rotor. However, in certain applications where oil contamination is a concern, such as medical and dental facilities, food processing, electronics manufacturing, and painting, oil-free compressors are preferred.
There is no lubricating oil inside the gas compressors, grease lubricated sealing type bearing is adopted for the rotary moving components, the moving seals inside the cylinder are made of self-lubricating material so as to ensure that the compressed gas will never contact any oil.
The machine adopts automatic control mode with low leakage and noise and without the need to arrange dedicated person for attention, and can operate over long term reliably.
Our Advantages
1. Oil-Free Gas: They deliver high-quality, oil-free compressed gases, which is essential in applications where oil contamination can be detrimental to the end product or process.
2. Reduced Maintenance: Oil-free compressors eliminate the need for oil changes, filter replacements, and oil disposal, resulting in lower maintenance requirements and costs.
3. Environmental Friendliness: The absence of oil reduces the risk of oil leaks or spills, making oil-free compressors environmentally friendly.
4. Improved gas Quality: Oil-free compressors provide cleaner gases, free from oil aerosols or vapors, which is essential in sensitive applications like medical and dental procedures or electronics manufacturing.
Product Parameters
| Model | Inlet pressure Bar |
Outlet pressure Bar |
Capacity Nm3/h |
Power kW |
Inlet size |
Outlet size |
Dimension mm |
Weight kg |
Speed r/min |
| WWY-(1- 5)/4-150/200 | 4.0 | 150/ 200 | 5 | 4.0 | Rc1/2 | G5/8 | 1350 *850 *1100 | 380 | 470 |
| WWY- 10/4-150/200 | 4.0 | 150/ 200 | 10 | 5.5 | Rc1/2 | G5/8 | 1350 *1050 *1100 | 410 | 470 |
| WWY- 15/4-150/200 | 4.0 | 150/ 200 | 15 | 7.5 | Rc1/2 | G5/8 | 1350 *1050 *1100 | 420 | 640 |
| WWY-20/4-150/200 | 4.0 | 150/ 200 | 20 | 11 | Rc1/2 | G5/8 | 1350 *1050 *1100 | 430 | 580 |
| WWY-25/4-150/200 | 4.0 | 150/ 200 | 25 | 11 | Rc1/2 | G5/8 | 1350 *1050 *1100 | 430 | 640 |
| WWY-30/4-150/200 | 4.0 | 150/ 200 | 30 | 15 | Rc1/2 | G5/8 | 1350 *1050 *1100 | 450 | 470 |
| WWY-35/4-150/200 | 4.0 | 150/ 200 | 35 | 15 | Rc1/2 | G5/8 | 1350 *1050 *1100 | 450 | 470 |
| WWY-40/4-150/200 | 4.0 | 150/ 200 | 40 | 15 | Rc1/2 | G5/8 | 1350 *1050 *1100 | 450 | 580 |
| SWY- 45/4-150/200 | 4.0 | 150/ 200 | 45 | 18.5 | Rc1 | G5/8 | 1450 *1100 *1250 | 520 | 580 |
| SWY- 50/4-150/200 | 4.0 | 150/ 200 | 50 | 18.5 | Rc1 | G5/8 | 1450 *1100 *1250 | 520 | 580 |
| SWY- 55/4-150/200 | 4.0 | 150/ 200 | 55 | 18.5 | Rc1 | G5/8 | 1450 *1100 *1250 | 520 | 580 |
| SWY- 60/4-150/200 | 4.0 | 150/ 200 | 60 | 22 | Rc1 | G5/8 | 1450 *1100 *1250 | 540 | 640 |
| SWY- 65/4-150/200 | 4.0 | 150/ 200 | 65 | 22 | Rc1 | G5/8 | 1450 *1100 *1250 | 540 | 720 |
| SWY- 70/4-150/200 | 4.0 | 150/ 200 | 70 | 22 | Rc1 | G5/8 | 1450 *1100 *1250 | 540 | 720 |
| SWY-75/4-150/200 | 4.0 | 150/ 200 | 75 | 22 | Rc1 | G5/8 | 1450*1100*1250 | 540 | 720 |
Notes: More specification are available based on clients‘ special requirement.
Company Profile
HangZhou Minwen Cryogenic Equipment Co., Ltd. is an established company specializing in industrial gas equipment and cryogenic solutions. With stable economy development in China, Minwen constantly strengthens its supply chain capabilities and resource integration capabilities. We are always on the way of promoting the efficiency and competitiveness, to guarantee high-quality performance of our services.
With advanced technologies and strict quality management, our products have passed the major international third-party quality control certifications such as ASME, CE, and Famous classification society such like BV, TUV, Lloyds and etc.
At Minwen, we pride ourselves on building long-lasting relationships with our clients. We will work with you every step of the way to ensure that your needs are met and your expectations are exceeded. We are committed to providing you with the best price and service we can offer, and we are confident in our ability to deliver top-quality solutions that cater to your specific set of requirements.
FAQ
1. Which countries you can ship the equipment to?
We ship to worldwide, such as Russia, Paraguay, Brazil, Colombia, Indonesia, Middle East, Africa, etc.
2. May I have the best price from you?
Sure. We are always on the way of promoting our competitiveness on products price and service.
3. Is your equipment quality good?
Yes. With advanced technologies and strict quality management, our products have passed the major international third-party quality control certifications such as ASME, CE, and Famous classification society such like BV, TUV, Lloyds
4. Do you provide one-stop service so I can save my time and labor?
Yes. Minwen constantly strengthens its supply chain capabilities and resource integration capabilities. You will own a professional team in China by cooperating with Minwen.
5. Where is your company located?
Our Export Office is located in HangZhou, with associated factories across China. This helps our international clients to integrate all the high quality resources together with Minwen.
/* March 10, 2571 17:59:20 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | Lifetime Aftersales Service |
|---|---|
| Warranty: | Lifetime Aftersales Service |
| Lubrication Style: | Oil-free |
| Cooling System: | Water/ Air Cooling |
| Cylinder Arrangement: | Balanced Opposed Arrangement |
| Cylinder Position: | Vertical |
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|
.webp)
How Do You Troubleshoot Common Issues with Gas Air Compressors?
Troubleshooting common issues with gas air compressors involves identifying and addressing potential problems that may arise during operation. Here’s a detailed explanation of the troubleshooting process:
1. Start with Safety Precautions:
Prior to troubleshooting, ensure that the gas air compressor is turned off and disconnected from the power source. Follow proper safety procedures, such as wearing appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), to avoid accidents or injuries.
2. Check Power Supply and Connections:
Verify that the compressor is receiving power and that all electrical connections are secure. Inspect the power cord, plug, and any switches or controls to ensure they are functioning properly. If the compressor is equipped with a battery, check its charge level and connections.
3. Check Fuel Supply:
For gas air compressors that use gasoline or propane, ensure that there is an adequate fuel supply. Check the fuel tank level and verify that the fuel shut-off valve is open. If the compressor has been sitting idle for an extended period, old or stale fuel may cause starting issues. Consider draining and replacing the fuel if necessary.
4. Inspect Air Filters:
Dirty or clogged air filters can restrict airflow and affect the compressor’s performance. Check the intake air filters and clean or replace them as needed. Clogged filters can be cleaned with compressed air or washed with mild detergent and water, depending on the type of filter.
5. Check Oil Level and Quality:
If the gas air compressor has an engine with an oil reservoir, verify the oil level using the dipstick or oil level indicator. Insufficient oil can lead to engine damage or poor performance. Additionally, check the oil quality to ensure it is clean and within the recommended viscosity range. If needed, change the oil following the manufacturer’s guidelines.
6. Inspect Spark Plug:
If the gas air compressor uses a spark plug ignition system, inspect the spark plug for signs of damage or fouling. Clean or replace the spark plug if necessary, following the manufacturer’s recommendations for gap setting and torque.
7. Check Belts and Pulleys:
Inspect the belts and pulleys that drive the compressor pump. Loose or worn belts can cause slippage and affect the compressor’s performance. Tighten or replace any damaged belts, and ensure that the pulleys are properly aligned.
8. Listen for Unusual Noises:
During operation, listen for any unusual or excessive noises, such as grinding, rattling, or squealing sounds. Unusual noises could indicate mechanical issues, loose components, or improper lubrication. If identified, consult the compressor’s manual or contact a qualified technician for further inspection and repair.
9. Consult the Owner’s Manual:
If troubleshooting steps do not resolve the issue, refer to the compressor’s owner’s manual for specific troubleshooting guidance. The manual may provide additional troubleshooting steps, diagnostic charts, or recommended maintenance procedures.
10. Seek Professional Assistance:
If the issue persists or if you are unsure about performing further troubleshooting steps, it is recommended to seek assistance from a qualified technician or contact the manufacturer’s customer support for guidance.
Remember to always prioritize safety and follow proper maintenance practices to prevent issues and ensure the reliable performance of the gas air compressor.
.webp)
Can Gas Air Compressors Be Used for Gas Line Maintenance?
Gas air compressors can be used for certain aspects of gas line maintenance, primarily for tasks that require compressed air. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Clearing Debris and Cleaning:
Gas air compressors can be utilized to clear debris and clean gas lines. Compressed air can be directed through the gas lines to dislodge and remove dirt, dust, rust particles, or other contaminants that may accumulate over time. This helps maintain the integrity and efficiency of the gas lines.
2. Pressure Testing:
Gas line maintenance often involves pressure testing to ensure the lines can withstand the required operating pressures. Gas air compressors can provide the necessary compressed air to pressurize the lines for testing purposes. By pressurizing the gas lines with compressed air, technicians can identify any leaks or weaknesses in the system.
3. Leak Detection:
Gas air compressors can also be used in conjunction with appropriate leak detection equipment to identify and locate gas leaks in the gas lines. Compressed air can be introduced into the lines, and the detection equipment can then identify any areas where the compressed air escapes, indicating a potential gas leak.
4. Valve and Equipment Maintenance:
Gas line maintenance may involve the inspection, maintenance, or replacement of valves and associated equipment. Compressed air can be used to clean and blow out debris from valves, purge lines, or assist in the disassembly and reassembly of components.
5. Pipe Drying:
Gas air compressors can aid in drying gas lines after maintenance or repairs. By blowing compressed air through the lines, any residual moisture can be removed, ensuring the gas lines are dry before being put back into service.
6. Precautions and Regulations:
When using gas air compressors for gas line maintenance, it is essential to follow safety precautions and adhere to relevant regulations. Gas line maintenance often involves working in hazardous environments, and proper training, equipment, and procedures must be followed to ensure the safety of personnel and the integrity of the gas system.
It is important to note that gas air compressors should not be used directly for pressurizing or transporting natural gas or other combustible gases. Gas line maintenance tasks involving gas air compressors primarily focus on using compressed air for specific maintenance and testing purposes, as outlined above.
In summary, gas air compressors can be useful for certain aspects of gas line maintenance, including clearing debris, pressure testing, leak detection, valve and equipment maintenance, and pipe drying. However, it is crucial to follow safety guidelines and regulations when working with gas lines and compressed air to ensure the safety and integrity of the gas system.
.webp)
What Safety Precautions Should Be Taken When Operating Gas Air Compressors?
Operating gas air compressors safely is essential to prevent accidents, injuries, and equipment damage. It’s important to follow proper safety precautions to ensure a safe working environment. Here’s a detailed explanation of the safety precautions that should be taken when operating gas air compressors:
1. Read and Follow the Manufacturer’s Instructions:
Before operating a gas air compressor, carefully read and understand the manufacturer’s instructions, user manual, and safety guidelines. Follow the recommended procedures, maintenance schedules, and any specific instructions provided by the manufacturer.
2. Provide Adequate Ventilation:
Gas air compressors generate exhaust fumes and heat during operation. Ensure that the operating area is well-ventilated to prevent the accumulation of exhaust gases, which can be harmful or even fatal in high concentrations. If operating indoors, use ventilation systems or open windows and doors to allow fresh air circulation.
3. Wear Personal Protective Equipment (PPE):
Wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) when operating a gas air compressor. This may include safety glasses, hearing protection, gloves, and sturdy footwear. PPE helps protect against potential hazards such as flying debris, noise exposure, and hand injuries.
4. Perform Regular Maintenance:
Maintain the gas air compressor according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. Regularly inspect the compressor for any signs of wear, damage, or leaks. Keep the compressor clean and free from debris. Replace worn-out parts and components as needed to ensure safe and efficient operation.
5. Preventive Measures for Fuel Handling:
If the gas air compressor is powered by fuels such as gasoline, diesel, or propane, take appropriate precautions for fuel handling:
- Store fuel in approved containers and in well-ventilated areas away from ignition sources.
- Refuel the compressor in a well-ventilated outdoor area, following proper refueling procedures and avoiding spills.
- Handle fuel with caution, ensuring that there are no fuel leaks or spills near the compressor.
- Never smoke or use open flames near the compressor or fuel storage areas.
6. Use Proper Electrical Connections:
If the gas air compressor requires electrical power, follow these electrical safety precautions:
- Ensure that the electrical connections and wiring are properly grounded and in compliance with local electrical codes.
- Avoid using extension cords unless recommended by the manufacturer.
- Inspect electrical cords and plugs for damage before use.
- Do not overload electrical circuits or use improper voltage sources.
7. Secure the Compressor:
Ensure that the gas air compressor is securely positioned and stable during operation. Use appropriate mounting or anchoring methods, especially for portable compressors. This helps prevent tipping, vibrations, and movement that could lead to accidents or injuries.
8. Familiarize Yourself with Emergency Procedures:
Be familiar with emergency procedures and know how to shut off the compressor quickly in case of an emergency or malfunction. Have fire extinguishers readily available and know how to use them effectively. Develop an emergency action plan and communicate it to all personnel working with or around the compressor.
It’s crucial to prioritize safety when operating gas air compressors. By following these safety precautions and using common sense, you can minimize the risks associated with compressor operation and create a safer work environment for yourself and others.


editor by CX 2024-02-08
China manufacturer Nitrogen Gas Diaphragm Compressor Nitrogen Air Compressor for Tires (GZ-30/32~170) air compressor repair near me
Product Description
Product Introduction
5Nm3/h 120bar High Pressure Nitrogen Gas Diaphragm Compressor GZ-5/30-120
Product Parameters
|
Product Name |
5Nm3/h 120bar High Pressure Nitrogen Gas Diaphragm Compressor GZ-5/30-120 | ||
|
Compress Medium |
High purity Nitrogen Gas |
||
|
Model No. |
GZ-5/30-120 | ||
|
Type |
diaphragm compressor |
||
|
Rated flow rate (F.A.D) |
5Nm3/h |
||
|
Power |
5.5KW |
||
|
Suction pressure(G) |
3.0Mpa(G) |
|
|
|
Rated outlet pressure |
12.0Mpa(G) |
||
|
Lubricating mode |
Oil Free , 100% high purity |
||
|
Transmission mode |
Belt Driven/ Direct driven |
||
|
Cooling method |
Industrial circulating water cooling tower |
||
|
Dimension |
1240*840*1060mm |
||
|
Weight |
600KG |
||
|
Motor Speed |
400 r/min |
||
|
Voltage |
380V, other voltage for special customize for each order |
||
|
After-sales Service |
Engineers available to service overseas |
||
|
OEM |
Welcomed (we have 5professional R&D engineers to do design & customizing service according to client’s different requirement) |
||
High purity oxygen compressor Oil Free Diaphragm Compressor
The diaphragm compressor booster is a special structure of the volume-type compressor with high compression ratio, good leak tightness, compressed gas without lubricating oil and other CHINAMFG impurities contaminated features, So it’s suitable for high purity compression, rare, valuable, inflammable, explosive, toxic, harmful, corrosive, and high pressure gas.
GZ Type Diaphragm Compressor Features
As a displacement compressor with special,diaphragm compressor is characterized by large compression ratio,good sealing performace,and that the compress air will not be polluted by lubricant or other CHINAMFG impurities.Therefore diaphragm compressor is applicable to compress high-purity,rare and precious,flammable and explosive,toxic and hazardous,corrosive and high_pressure gases.
Keepwin diaphragm compressors consist of 4 types that are Z type, V type, L type and D type.The exhaust pressure ranges from 1.3 to 49Mpa. The products are widely used in the industries of national defense,scientific research,petrochemical,nuclear power,parmaceutical,food-stuff and gas separation.
How does a diaphragm compressor work?
Diaphragm compressor. A diaphragm compressor is a variant of the classic reciprocating compressor with backup and piston rings and rod seal. The compression of gas occurs by means of a flexible membrane, instead of an intake element. The back and forth moving membrane is driven by a rod and a crankshaft mechanism.
Oil Free Diaphragm Compressor VS Reciprocating Piston Compressor
1. The diaphragm compressor is essentially different from the piston machine in structure.
2. Diaphragm machine separates oil and gas completely through diaphragm to ensure that the gas in cylinder is 100% pure and oil-free. The filler part of piston compressor needs oil injection lubrication. Once the filler wears too much, oil will inevitably leak out and make the gas impure. In addition, the cylinder of high pressure chamber is often lubricated with oil.
3. Diaphragm compressor only needs two-stage compression to achieve 150 bar pressure, while piston engine needs three-stage compression to achieve 150 bar pressure, which increases the maintenance workload and maintenance cost.
4. Diaphragm compressor vulnerable parts usually only diaphragm and valve, simple maintenance and low cost.
FAQ
Q1: What’s your delivery time?
A: Generally 5-10 days if the goods are in stock. Or it is 20-35 days if the goods are not in stock, it is according to quantity.
Q2: How long is your air compressor warranty?
A: Usually 1 year /12 Months for whole compressor machine, 2years/24months for air end (except maintenance spare parts.). And we can provide further warranty if necessary.
Q3: How long could your air compressor be used?
A: Generally, more than 10 years.
Q4: Can you do OEM for us?
A: Yes, of course. We have around 2 decades OEM experience.And also we can do ODM for you.
Q5: What’s payment term?
A: T/T, L/C, D/P, Western Union, Paypal, Credit Card, Trade Assurance and etc. Also we could accept USD, RMB, GBP, Euro and other currency.
Q6: How about your customer service?
A: 24 hours on-line service available. 48hours problem sovled promise.
Q7: How about your after-sales service?
A: 1. Provide customers with intallation and commissioning online instructions.
2. Well-trained engineers available to overseas after-sales service.
Q8. Are you factory?
A4: Absolutely! You have touched the primary sources of Air /Gas Compressor. We are factory.
How to contact with us?
/* March 10, 2571 17:59:20 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Lubrication Style: | Oil-free |
|---|---|
| Cooling System: | Water Cooling |
| Cylinder Arrangement: | Parallel Arrangement |
| Cylinder Position: | Angular |
| Structure Type: | Closed Type |
| Compress Level: | Single-Stage |
| Samples: |
US$ 19999/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|
.webp)
How Do You Troubleshoot Common Issues with Gas Air Compressors?
Troubleshooting common issues with gas air compressors involves identifying and addressing potential problems that may arise during operation. Here’s a detailed explanation of the troubleshooting process:
1. Start with Safety Precautions:
Prior to troubleshooting, ensure that the gas air compressor is turned off and disconnected from the power source. Follow proper safety procedures, such as wearing appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), to avoid accidents or injuries.
2. Check Power Supply and Connections:
Verify that the compressor is receiving power and that all electrical connections are secure. Inspect the power cord, plug, and any switches or controls to ensure they are functioning properly. If the compressor is equipped with a battery, check its charge level and connections.
3. Check Fuel Supply:
For gas air compressors that use gasoline or propane, ensure that there is an adequate fuel supply. Check the fuel tank level and verify that the fuel shut-off valve is open. If the compressor has been sitting idle for an extended period, old or stale fuel may cause starting issues. Consider draining and replacing the fuel if necessary.
4. Inspect Air Filters:
Dirty or clogged air filters can restrict airflow and affect the compressor’s performance. Check the intake air filters and clean or replace them as needed. Clogged filters can be cleaned with compressed air or washed with mild detergent and water, depending on the type of filter.
5. Check Oil Level and Quality:
If the gas air compressor has an engine with an oil reservoir, verify the oil level using the dipstick or oil level indicator. Insufficient oil can lead to engine damage or poor performance. Additionally, check the oil quality to ensure it is clean and within the recommended viscosity range. If needed, change the oil following the manufacturer’s guidelines.
6. Inspect Spark Plug:
If the gas air compressor uses a spark plug ignition system, inspect the spark plug for signs of damage or fouling. Clean or replace the spark plug if necessary, following the manufacturer’s recommendations for gap setting and torque.
7. Check Belts and Pulleys:
Inspect the belts and pulleys that drive the compressor pump. Loose or worn belts can cause slippage and affect the compressor’s performance. Tighten or replace any damaged belts, and ensure that the pulleys are properly aligned.
8. Listen for Unusual Noises:
During operation, listen for any unusual or excessive noises, such as grinding, rattling, or squealing sounds. Unusual noises could indicate mechanical issues, loose components, or improper lubrication. If identified, consult the compressor’s manual or contact a qualified technician for further inspection and repair.
9. Consult the Owner’s Manual:
If troubleshooting steps do not resolve the issue, refer to the compressor’s owner’s manual for specific troubleshooting guidance. The manual may provide additional troubleshooting steps, diagnostic charts, or recommended maintenance procedures.
10. Seek Professional Assistance:
If the issue persists or if you are unsure about performing further troubleshooting steps, it is recommended to seek assistance from a qualified technician or contact the manufacturer’s customer support for guidance.
Remember to always prioritize safety and follow proper maintenance practices to prevent issues and ensure the reliable performance of the gas air compressor.
.webp)
Can Gas Air Compressors Be Used for Natural Gas Compression?
Gas air compressors are not typically used for natural gas compression. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Different Compressed Gases:
Gas air compressors are specifically designed to compress atmospheric air. They are not typically designed or suitable for compressing natural gas. Natural gas, which is primarily composed of methane, requires specialized compressors designed to handle the unique properties and characteristics of the gas.
2. Safety Considerations:
Natural gas compression involves handling a flammable and potentially hazardous substance. Compressing natural gas requires specialized equipment that meets stringent safety standards to prevent leaks, minimize the risk of ignition or explosion, and ensure the safe handling of the gas. Gas air compressors may not have the necessary safety features or materials to handle natural gas safely.
3. Equipment Compatibility:
Natural gas compression systems typically include components such as gas compressors, gas coolers, separators, and control systems that are specifically designed and engineered for the compression and handling of natural gas. These components are built to withstand the specific demands and conditions associated with natural gas compression, including the high pressures and potential presence of impurities.
4. Efficiency and Performance:
Compressing natural gas requires specialized compressors that can handle the high-pressure ratios and volumetric flow rates associated with the gas. Gas air compressors are generally not designed to achieve the same compression ratios and performance levels required for natural gas compression. Using gas air compressors for natural gas compression would likely result in inefficient operation and suboptimal performance.
5. Regulatory Compliance:
Compressing natural gas is subject to various regulations and standards to ensure safety, environmental protection, and compliance with industry guidelines. These regulations often dictate specific requirements for equipment, materials, and operating procedures in natural gas compression systems. Gas air compressors may not meet these regulatory requirements for natural gas compression.
6. Industry Standards and Practices:
The natural gas industry has well-established standards and best practices for equipment selection, installation, and operation in gas compression systems. These standards are based on the specific requirements and characteristics of natural gas. Gas air compressors do not align with these industry standards and practices, which are essential for safe and efficient natural gas compression.
In summary, gas air compressors are not suitable for natural gas compression. Natural gas compression requires specialized equipment designed to handle the unique properties and safety considerations associated with the gas. Compressors specifically engineered for natural gas compression offer the necessary performance, safety features, and regulatory compliance required for efficient and reliable operation in natural gas compression systems.
.webp)
Can Gas Air Compressors Be Used in Remote Locations?
Yes, gas air compressors are well-suited for use in remote locations where access to electricity may be limited or unavailable. Their portability and reliance on gas engines make them an ideal choice for providing a reliable source of compressed air in such environments. Here’s a detailed explanation of how gas air compressors can be used in remote locations:
1. Independence from Electrical Grid:
Gas air compressors do not require a direct connection to the electrical grid, unlike electric air compressors. This independence from the electrical grid allows gas air compressors to be used in remote locations, such as wilderness areas, remote job sites, or off-grid locations, where it may be impractical or cost-prohibitive to establish electrical infrastructure.
2. Mobility and Portability:
Gas air compressors are designed to be portable and easy to transport. They are often equipped with handles, wheels, or trailers, making them suitable for remote locations. The gas engine powering the compressor provides mobility, allowing the compressor to be moved to different areas within the remote location as needed.
3. Fuel Versatility:
Gas air compressors can be fueled by various types of combustible gases, including gasoline, diesel, natural gas, or propane. This fuel versatility ensures that gas air compressors can adapt to the available fuel sources in remote locations. For example, if gasoline or diesel is readily available, the gas air compressor can be fueled with these fuels. Similarly, if natural gas or propane is accessible, the compressor can be configured to run on these gases.
4. On-Site Power Generation:
In remote locations where electricity is limited, gas air compressors can serve as on-site power generators. They can power not only the compressor itself but also other equipment or tools that require electricity for operation. This versatility makes gas air compressors useful for a wide range of applications in remote locations, such as powering lights, tools, communication devices, or small appliances.
5. Off-Grid Operations:
Gas air compressors enable off-grid operations, allowing tasks and activities to be carried out in remote locations without relying on external power sources. This is particularly valuable in industries such as mining, oil and gas exploration, forestry, or construction, where operations may take place in remote and isolated areas. Gas air compressors provide the necessary compressed air for pneumatic tools, drilling equipment, and other machinery required for these operations.
6. Emergency Preparedness:
Gas air compressors are also beneficial for emergency preparedness in remote locations. In situations where natural disasters or emergencies disrupt the power supply, gas air compressors can provide a reliable source of compressed air for essential equipment and systems. They can power emergency lighting, communication devices, medical equipment, or backup generators, ensuring operational continuity in critical situations.
7. Adaptability to Challenging Environments:
Gas air compressors are designed to withstand various environmental conditions, including extreme temperatures, humidity, dust, and vibrations. This adaptability to challenging environments makes them suitable for use in remote locations, where environmental conditions may be harsh or unpredictable.
Overall, gas air compressors can be effectively used in remote locations due to their independence from the electrical grid, mobility, fuel versatility, on-site power generation capabilities, suitability for off-grid operations, emergency preparedness, and adaptability to challenging environments. These compressors provide a reliable source of compressed air, enabling a wide range of applications in remote settings.


editor by CX 2024-02-05
China Professional Nitrogen Gas Diaphragm Compressor Nitrogen Air Compressor for Tires air compressor parts
Product Description
Detailed Photos
Mixed Medium Water-Cooling Nitrogen Reciprocating Compressor
Description&Advantages
Product Descriptions:
The Nitrogen compressors manufactured by ASC Compressor Factory are oil-free lubrication reciprocating piston compressors developed in collaboration with the German company CHINAMFG DEMAG. These models are known for their low energy consumption, minimal noise, reduced vibration, high reliability, and easy operation.
Each unit primarily consists of the compressor mainframe, electric motor, common base frame, air system, cooling system, lubrication system, instrument control system, drainage system, and electrical system. All components are generally installed on a single common base frame, which is then mounted on a concrete foundation, making it a fixed-type gas station. The connections between the equipment and the fixing points to the base are detachable, making transportation, installation, operation, and maintenance extremely convenient.
As a specialty gas compressor, this model can also compress gases like helium, natural gas, LPG, associated petroleum gas, hydrogen, argon, ethylene, propylene, propane, chloromethane, chloroethane, ethylene oxide, perfluoroethane, carbon monoxide, ammonia, dimethyl ether, carbon dioxide, and coal gas. It’s widely used in industries like petroleum, chemical, fertilizer, metallurgy, industrial gases, fuel gas, food, and more.
Advantages:
Our products, incorporating technology from Germany’s CHINAMFG Demag companies, exhibit high reliability. Wearable parts like gas valves and piston rings use products from Austria’s Hoerbiger company, with a lifespan exceeding 8000 hours. The system supports soft starting, allowing frequent start and stop cycles for the compressor. It features a wide intake range for broad adaptability. The overall skid-mounted structure results in low noise and is easy to install in urban areas, leading to investment savings.
It is equipped with a CHINAMFG PLC control system for high automation, ABB soft start (or variable frequency), and features automatic shutdown with audible and visual alarms in case of faults
Product Parameters
| Model | Flow m3/h | Inlet Pressure (Mpa) |
Outlet Pressure (Mpa) |
Weight (Kg) |
Power (Kw) |
| VW-6/16-24 | 360 | 1.6 | 2.4 | 2600 | 110 |
| VW-6/(0-1.62)-(5-21) | 360 | 0-0.162 | 0.5-2.1 | 2350 | 75 |
| WW-26.7/0.5-10 | 1602 | 0.05 | 1 | 4500 | 250 |
| DW-2/0.2-16 | 120 | 0.02 | 1.6 | 1500 | 22 |
| WW-3/8 | 180 | normal pressure | 0.8 | 1500 | 22 |
| 2VW-50/3.5 | 3000 | normal pressure | 0.35 | 6000 | 220 |
| 2VW-16.7/0.5-20 | 1002 | 0.05 | 2 | 6500 | 185 |
| ZW-0.6/6-10 | 36 | 0.6 | 1 | 760 | 5.5 |
| ZW-0.8/12 | 48 | normal pressure | 1.2 | 1200 | 7.5 |
| DW-9.5/7 | 570 | normal pressure | 0.7 | 2600 | 55 |
| VW-4.5/0.5-10 | 270 | 0.05 | 1 | 2100 | 37 |
| 2VW-25/25 | 1500 | normal pressure | 2.5 | 2100 | 250 |
| 2VW-50/3.5 | 3000 | normal pressure | 0.35 | 6000 | 220 |
| DW-4.5/0.5-13 | 270 | 0.05 | 1.3 | 2500 | 18.5 |
| ZW-0.46/(5-10)-(15-20) | 27.6 | 0.5-1.0 | 1.5-2.0 | 850 | 11 |
| VW-5.6/(1.5-2)-25 | 27.6 | 0.15-0.2 | 2.5 | 2000 | 55 |
| V-6.5/(1-3)-7 | 390 | 0.1-0.3 | 0.7 | 1900 | 37 |
| WW-2.5/3-250 | 150 | 0.3 | 25 | 3500 | 110 |
Our Factory
Part of Customer Visit
Certifications & Testing
Related Product
FAQ
Q:Are you a factory?
A:Yes, we are indeed a factory. We specialize in manufacturing high-quality Air/Gas Compressors and are proud to be a primary source for these products.
Q:How long is your delivery time?
A:It varies depending on the specific situation. For our standard configuration compressors, the delivery time is around 30 days. For customized compressors, it usually takes about 30-45 days.
Q:What technical support do you offer?
A:We offer comprehensive technical support to our clients, including remote assistance for installation and commissioning processes. Additionally, we have a team of seasoned engineers ready to be deployed to international client locations for meticulous on-site debugging, installation, and post-installation services.
Q:What is your warranty period?
A:Our warranty policy is valid for a period of 18 months from the date of commissioning at the end customer’s site or 21 months from the date of receipt by the purchaser, whichever comes first. This comprehensive coverage is designed to ensure total customer satisfaction and the reliability of our products
Q:How do you package the compressors?
A:For smaller compressors, we utilize robust plywood boxes that conform to export specifications.
For the larger units, we strategically place them in freight containers, implementing secure fastening methods to safeguard against any potential damage during the shipping process.
Q:What are your payment terms?
A:Usually, the payment is made by T/T with a 30% down payment CHINAMFG confirmation of the Proforma Invoice (PI), and the balance is to be paid after inspection and before shipment. We accept both TT and L/C at sight.
Send message Get product Offer & Brochure!!!
↓↓↓
/* March 10, 2571 17:59:20 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | Local Teams |
|---|---|
| Warranty: | 18 Months |
| Principle: | Reciprocating Compressor |
| Application: | Back Pressure Type, Intermediate Back Pressure Type, High Back Pressure Type, Low Back Pressure Type |
| Performance: | Low Noise, Variable Frequency, Explosion-Proof |
| Mute: | Mute |
| Samples: |
US$ 40000/Set
1 Set(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|
.webp)
What Is the Typical Lifespan of a Gas Air Compressor?
The typical lifespan of a gas air compressor can vary depending on several factors, including the quality of the compressor, its usage patterns, maintenance practices, and environmental conditions. However, with proper care and maintenance, a gas air compressor can last for many years. Here’s a detailed explanation of the factors that can affect the lifespan of a gas air compressor:
1. Quality of the Compressor:
The quality and construction of the gas air compressor play a significant role in determining its lifespan. Compressors made with high-quality materials, precision engineering, and robust components are generally more durable and can withstand heavy usage over an extended period.
2. Usage Patterns:
The usage patterns of the gas air compressor can impact its lifespan. If the compressor is used consistently and for extended periods, it may experience more wear and tear compared to compressors used intermittently or for lighter tasks. Heavy-duty applications, such as continuous operation with high-demand tools, can put more strain on the compressor and potentially reduce its lifespan.
3. Maintenance Practices:
Regular maintenance is crucial for extending the lifespan of a gas air compressor. Following the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule, performing routine tasks like oil changes, filter cleaning/replacement, and inspection of components can help prevent issues and ensure optimal performance. Neglecting maintenance can lead to accelerated wear and potential breakdowns.
4. Environmental Conditions:
The operating environment can significantly impact the lifespan of a gas air compressor. Factors such as temperature extremes, humidity levels, presence of dust or debris, and exposure to corrosive substances can affect the compressor’s components and overall performance. Compressors used in harsh environments may require additional protection or specialized maintenance to mitigate these adverse conditions.
5. Proper Installation and Operation:
Proper installation and correct operation of the gas air compressor are essential for its longevity. Following the manufacturer’s guidelines for installation, ensuring proper ventilation, maintaining correct oil levels, and operating within the compressor’s specified capacity and pressure limits can help prevent excessive strain and premature wear.
Considering these factors, a well-maintained gas air compressor can typically last anywhere from 10 to 15 years or even longer. However, it’s important to note that this is a general estimate, and individual results may vary. Some compressors may experience shorter lifespans due to heavy usage, inadequate maintenance, or other factors, while others may last well beyond the expected lifespan with proper care and favorable conditions.
Ultimately, investing in a high-quality gas air compressor, adhering to recommended maintenance practices, and using it within its intended capabilities can help maximize its lifespan and ensure reliable performance for an extended period.
.webp)
How Do You Transport Gas Air Compressors to Different Job Sites?
Transporting gas air compressors to different job sites requires careful planning and consideration of various factors. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Equipment Size and Weight:
The size and weight of the gas air compressor are crucial factors to consider when planning transportation. Gas air compressors come in different sizes and configurations, ranging from portable units to larger, skid-mounted or trailer-mounted compressors. Assess the dimensions and weight of the compressor to determine the appropriate transportation method.
2. Transportation Modes:
Gas air compressors can be transported using different modes of transportation, depending on their size, weight, and distance to the job site:
- Truck or Trailer: Smaller gas air compressors can be loaded onto a truck bed or trailer for transportation. Ensure that the vehicle or trailer has the necessary capacity to accommodate the weight and dimensions of the compressor.
- Flatbed or Lowboy Trailer: Larger gas compressors or skid-mounted units may require transportation on a flatbed or lowboy trailer. These trailers are designed to carry heavy equipment and provide stability during transportation.
- Shipping Container: For long-distance transportation or international shipments, gas air compressors can be transported in shipping containers. The compressor must be properly secured and protected within the container to prevent any damage during transit.
3. Securing and Protection:
It is essential to secure the gas air compressor properly during transportation to prevent shifting or damage. Use appropriate tie-down straps, chains, or fasteners to secure the compressor to the transport vehicle or trailer. Protect the compressor from potential impacts, vibrations, and weather conditions by using suitable covers, padding, or weatherproof enclosures.
4. Permits and Regulations:
Depending on the size and weight of the gas air compressor, special permits or escorts may be required for transportation. Familiarize yourself with local, state, and federal regulations regarding oversize or overweight loads, and obtain the necessary permits to ensure compliance with transportation laws.
5. Route Planning:
Plan the transportation route carefully, considering factors such as road conditions, height and weight restrictions, bridges, tunnels, and any other potential obstacles. Identify alternative routes if needed, and communicate with transportation authorities or agencies to ensure a smooth and safe journey.
6. Equipment Inspection and Maintenance:
Prior to transportation, conduct a thorough inspection of the gas air compressor to ensure it is in proper working condition. Check for any leaks, damage, or loose components. Perform routine maintenance tasks, such as oil changes, filter replacements, and belt inspections, to minimize the risk of equipment failure during transportation.
In summary, transporting gas air compressors to different job sites requires considering factors such as equipment size and weight, choosing appropriate transportation modes, securing and protecting the compressor, obtaining necessary permits, planning the route, and conducting equipment inspection and maintenance. Careful planning and adherence to transportation regulations contribute to the safe and efficient transportation of gas air compressors.
.webp)
What Safety Precautions Should Be Taken When Operating Gas Air Compressors?
Operating gas air compressors safely is essential to prevent accidents, injuries, and equipment damage. It’s important to follow proper safety precautions to ensure a safe working environment. Here’s a detailed explanation of the safety precautions that should be taken when operating gas air compressors:
1. Read and Follow the Manufacturer’s Instructions:
Before operating a gas air compressor, carefully read and understand the manufacturer’s instructions, user manual, and safety guidelines. Follow the recommended procedures, maintenance schedules, and any specific instructions provided by the manufacturer.
2. Provide Adequate Ventilation:
Gas air compressors generate exhaust fumes and heat during operation. Ensure that the operating area is well-ventilated to prevent the accumulation of exhaust gases, which can be harmful or even fatal in high concentrations. If operating indoors, use ventilation systems or open windows and doors to allow fresh air circulation.
3. Wear Personal Protective Equipment (PPE):
Wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) when operating a gas air compressor. This may include safety glasses, hearing protection, gloves, and sturdy footwear. PPE helps protect against potential hazards such as flying debris, noise exposure, and hand injuries.
4. Perform Regular Maintenance:
Maintain the gas air compressor according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. Regularly inspect the compressor for any signs of wear, damage, or leaks. Keep the compressor clean and free from debris. Replace worn-out parts and components as needed to ensure safe and efficient operation.
5. Preventive Measures for Fuel Handling:
If the gas air compressor is powered by fuels such as gasoline, diesel, or propane, take appropriate precautions for fuel handling:
- Store fuel in approved containers and in well-ventilated areas away from ignition sources.
- Refuel the compressor in a well-ventilated outdoor area, following proper refueling procedures and avoiding spills.
- Handle fuel with caution, ensuring that there are no fuel leaks or spills near the compressor.
- Never smoke or use open flames near the compressor or fuel storage areas.
6. Use Proper Electrical Connections:
If the gas air compressor requires electrical power, follow these electrical safety precautions:
- Ensure that the electrical connections and wiring are properly grounded and in compliance with local electrical codes.
- Avoid using extension cords unless recommended by the manufacturer.
- Inspect electrical cords and plugs for damage before use.
- Do not overload electrical circuits or use improper voltage sources.
7. Secure the Compressor:
Ensure that the gas air compressor is securely positioned and stable during operation. Use appropriate mounting or anchoring methods, especially for portable compressors. This helps prevent tipping, vibrations, and movement that could lead to accidents or injuries.
8. Familiarize Yourself with Emergency Procedures:
Be familiar with emergency procedures and know how to shut off the compressor quickly in case of an emergency or malfunction. Have fire extinguishers readily available and know how to use them effectively. Develop an emergency action plan and communicate it to all personnel working with or around the compressor.
It’s crucial to prioritize safety when operating gas air compressors. By following these safety precautions and using common sense, you can minimize the risks associated with compressor operation and create a safer work environment for yourself and others.


editor by CX 2024-02-02
China manufacturer Nitrogen Gas Diaphragm Compressor Nitrogen Air Compressor for Tires (GZ-30/32~170) air compressor price
Product Description
Product Introduction
5Nm3/h 120bar High Pressure Nitrogen Gas Diaphragm Compressor GZ-5/30-120
Product Parameters
|
Product Name |
5Nm3/h 120bar High Pressure Nitrogen Gas Diaphragm Compressor GZ-5/30-120 | ||
|
Compress Medium |
High purity Nitrogen Gas |
||
|
Model No. |
GZ-5/30-120 | ||
|
Type |
diaphragm compressor |
||
|
Rated flow rate (F.A.D) |
5Nm3/h |
||
|
Power |
5.5KW |
||
|
Suction pressure(G) |
3.0Mpa(G) |
|
|
|
Rated outlet pressure |
12.0Mpa(G) |
||
|
Lubricating mode |
Oil Free , 100% high purity |
||
|
Transmission mode |
Belt Driven/ Direct driven |
||
|
Cooling method |
Industrial circulating water cooling tower |
||
|
Dimension |
1240*840*1060mm |
||
|
Weight |
600KG |
||
|
Motor Speed |
400 r/min |
||
|
Voltage |
380V, other voltage for special customize for each order |
||
|
After-sales Service |
Engineers available to service overseas |
||
|
OEM |
Welcomed (we have 5professional R&D engineers to do design & customizing service according to client’s different requirement) |
||
High purity oxygen compressor Oil Free Diaphragm Compressor
The diaphragm compressor booster is a special structure of the volume-type compressor with high compression ratio, good leak tightness, compressed gas without lubricating oil and other CHINAMFG impurities contaminated features, So it’s suitable for high purity compression, rare, valuable, inflammable, explosive, toxic, harmful, corrosive, and high pressure gas.
GZ Type Diaphragm Compressor Features
As a displacement compressor with special,diaphragm compressor is characterized by large compression ratio,good sealing performace,and that the compress air will not be polluted by lubricant or other CHINAMFG impurities.Therefore diaphragm compressor is applicable to compress high-purity,rare and precious,flammable and explosive,toxic and hazardous,corrosive and high_pressure gases.
Keepwin diaphragm compressors consist of 4 types that are Z type, V type, L type and D type.The exhaust pressure ranges from 1.3 to 49Mpa. The products are widely used in the industries of national defense,scientific research,petrochemical,nuclear power,parmaceutical,food-stuff and gas separation.
How does a diaphragm compressor work?
Diaphragm compressor. A diaphragm compressor is a variant of the classic reciprocating compressor with backup and piston rings and rod seal. The compression of gas occurs by means of a flexible membrane, instead of an intake element. The back and forth moving membrane is driven by a rod and a crankshaft mechanism.
Oil Free Diaphragm Compressor VS Reciprocating Piston Compressor
1. The diaphragm compressor is essentially different from the piston machine in structure.
2. Diaphragm machine separates oil and gas completely through diaphragm to ensure that the gas in cylinder is 100% pure and oil-free. The filler part of piston compressor needs oil injection lubrication. Once the filler wears too much, oil will inevitably leak out and make the gas impure. In addition, the cylinder of high pressure chamber is often lubricated with oil.
3. Diaphragm compressor only needs two-stage compression to achieve 150 bar pressure, while piston engine needs three-stage compression to achieve 150 bar pressure, which increases the maintenance workload and maintenance cost.
4. Diaphragm compressor vulnerable parts usually only diaphragm and valve, simple maintenance and low cost.
FAQ
Q1: What’s your delivery time?
A: Generally 5-10 days if the goods are in stock. Or it is 20-35 days if the goods are not in stock, it is according to quantity.
Q2: How long is your air compressor warranty?
A: Usually 1 year /12 Months for whole compressor machine, 2years/24months for air end (except maintenance spare parts.). And we can provide further warranty if necessary.
Q3: How long could your air compressor be used?
A: Generally, more than 10 years.
Q4: Can you do OEM for us?
A: Yes, of course. We have around 2 decades OEM experience.And also we can do ODM for you.
Q5: What’s payment term?
A: T/T, L/C, D/P, Western Union, Paypal, Credit Card, Trade Assurance and etc. Also we could accept USD, RMB, GBP, Euro and other currency.
Q6: How about your customer service?
A: 24 hours on-line service available. 48hours problem sovled promise.
Q7: How about your after-sales service?
A: 1. Provide customers with intallation and commissioning online instructions.
2. Well-trained engineers available to overseas after-sales service.
Q8. Are you factory?
A4: Absolutely! You have touched the primary sources of Air /Gas Compressor. We are factory.
How to contact with us?
| Lubrication Style: | Oil-free |
|---|---|
| Cooling System: | Water Cooling |
| Cylinder Arrangement: | Parallel Arrangement |
| Cylinder Position: | Angular |
| Structure Type: | Closed Type |
| Compress Level: | Single-Stage |
| Samples: |
US$ 19999/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|
.webp)
How are air compressors utilized in the aerospace industry?
Air compressors play a crucial role in various applications within the aerospace industry. They are utilized for a wide range of tasks that require compressed air or gas. Here are some key uses of air compressors in the aerospace industry:
1. Aircraft Systems:
Air compressors are used in aircraft systems to provide compressed air for various functions. They supply compressed air for pneumatic systems, such as landing gear operation, braking systems, wing flap control, and flight control surfaces. Compressed air is also utilized for starting aircraft engines and for cabin pressurization and air conditioning systems.
2. Ground Support Equipment:
Air compressors are employed in ground support equipment used in the aerospace industry. They provide compressed air for tasks such as inflating aircraft tires, operating pneumatic tools for maintenance and repair, and powering air-driven systems for fueling, lubrication, and hydraulic operations.
3. Component Testing:
Air compressors are utilized in component testing within the aerospace industry. They supply compressed air for testing and calibrating various aircraft components, such as valves, actuators, pressure sensors, pneumatic switches, and control systems. Compressed air is used to simulate operating conditions and evaluate the performance and reliability of these components.
4. Airborne Systems:
In certain aircraft, air compressors are employed for specific airborne systems. For example, in military aircraft, air compressors are used for air-to-air refueling systems, where compressed air is utilized to transfer fuel between aircraft in mid-air. Compressed air is also employed in aircraft de-icing systems, where it is used to inflate inflatable de-icing boots on the wing surfaces to remove ice accumulation during flight.
5. Environmental Control Systems:
Air compressors play a critical role in the environmental control systems of aircraft. They supply compressed air for air conditioning, ventilation, and pressurization systems, ensuring a comfortable and controlled environment inside the aircraft cabin. Compressed air is used to cool and circulate air, maintain desired cabin pressure, and control humidity levels.
6. Engine Testing:
In the aerospace industry, air compressors are utilized for engine testing purposes. They provide compressed air for engine test cells, where aircraft engines are tested for performance, efficiency, and durability. Compressed air is used to simulate different operating conditions and loads on the engine, allowing engineers to assess its performance and make necessary adjustments or improvements.
7. Oxygen Systems:
In aircraft, air compressors are involved in the production of medical-grade oxygen for onboard oxygen systems. Compressed air is passed through molecular sieve beds or other oxygen concentrator systems to separate oxygen from other components of air. The generated oxygen is then supplied to the onboard oxygen systems, ensuring a sufficient and continuous supply of breathable oxygen for passengers and crew at high altitudes.
It is important to note that air compressors used in the aerospace industry must meet stringent quality and safety standards. They need to be reliable, efficient, and capable of operating under demanding conditions to ensure the safety and performance of aircraft systems.
.webp)
How do you choose the right air compressor for woodworking?
Choosing the right air compressor for woodworking is essential to ensure efficient and effective operation of pneumatic tools and equipment. Here are some factors to consider when selecting an air compressor for woodworking:
1. Required Air Volume (CFM):
Determine the required air volume or cubic feet per minute (CFM) for your woodworking tools and equipment. Different tools have varying CFM requirements, so it is crucial to choose an air compressor that can deliver the required CFM to power your tools effectively. Make sure to consider the highest CFM requirement among the tools you’ll be using simultaneously.
2. Tank Size:
Consider the tank size of the air compressor. A larger tank allows for more stored air, which can be beneficial when using tools that require short bursts of high air volume. It helps maintain a consistent air supply and reduces the frequency of the compressor cycling on and off. However, if you have tools with continuous high CFM demands, a larger tank may not be as critical.
3. Maximum Pressure (PSI):
Check the maximum pressure (PSI) rating of the air compressor. Woodworking tools typically operate within a specific PSI range, so ensure that the compressor can provide the required pressure. It is advisable to choose an air compressor with a higher maximum PSI rating to accommodate any future tool upgrades or changes in your woodworking needs.
4. Noise Level:
Consider the noise level of the air compressor, especially if you’ll be using it in a residential or shared workspace. Some air compressors have noise-reducing features or are designed to operate quietly, making them more suitable for woodworking environments where noise control is important.
5. Portability:
Assess the portability requirements of your woodworking projects. If you need to move the air compressor frequently or work in different locations, a portable and lightweight compressor may be preferable. However, if the compressor will remain stationary in a workshop, a larger, stationary model might be more suitable.
6. Power Source:
Determine the power source available in your woodworking workspace. Air compressors can be powered by electricity or gasoline engines. If electricity is readily available, an electric compressor may be more convenient and cost-effective. Gasoline-powered compressors offer greater flexibility for remote or outdoor woodworking projects where electricity may not be accessible.
7. Quality and Reliability:
Choose an air compressor from a reputable manufacturer known for producing reliable and high-quality equipment. Read customer reviews and consider the warranty and after-sales support offered by the manufacturer to ensure long-term satisfaction and reliability.
8. Budget:
Consider your budget and balance it with the features and specifications required for your woodworking needs. While it’s important to invest in a reliable and suitable air compressor, there are options available at various price points to accommodate different budgets.
By considering these factors and evaluating your specific woodworking requirements, you can choose an air compressor that meets the demands of your tools, provides efficient performance, and enhances your woodworking experience.
.webp)
What maintenance is required for air compressors?
Maintaining air compressors is essential to ensure their optimal performance, longevity, and safe operation. Regular maintenance helps prevent breakdowns, improves efficiency, and reduces the risk of accidents. Here are some key maintenance tasks for air compressors:
1. Regular Inspection: Perform visual inspections of the air compressor to identify any signs of wear, damage, or leaks. Inspect the compressor, hoses, fittings, and connections for any abnormalities. Pay attention to oil leaks, loose bolts, and worn-out components.
2. Oil Changes: If your air compressor has an oil lubrication system, regular oil changes are crucial. Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for the frequency of oil changes and use the recommended oil type. Dirty or degraded oil can impact compressor performance and lead to premature wear.
3. Air Filter Cleaning or Replacement: Clean or replace the air filter regularly to ensure proper air intake and prevent contaminants from entering the compressor. Clogged or dirty filters can restrict airflow and reduce efficiency.
4. Drain Moisture: Air compressors produce moisture as a byproduct of the compression process. Accumulated moisture in the tank can lead to rust and corrosion. Drain the moisture regularly from the tank to prevent damage. Some compressors have automatic drains, while others require manual draining.
5. Belt Inspection and Adjustment: If your compressor has a belt-driven system, inspect the belts for signs of wear, cracks, or tension issues. Adjust or replace the belts as necessary to maintain proper tension and power transmission.
6. Tank Inspection: Inspect the compressor tank for any signs of corrosion, dents, or structural issues. A damaged tank can be hazardous and should be repaired or replaced promptly.
7. Valve Maintenance: Check the safety valves, pressure relief valves, and other valves regularly to ensure they are functioning correctly. Test the valves periodically to verify their proper operation.
8. Motor and Electrical Components: Inspect the motor and electrical components for any signs of damage or overheating. Check electrical connections for tightness and ensure proper grounding.
9. Keep the Area Clean: Maintain a clean and debris-free area around the compressor. Remove any dirt, dust, or obstructions that can hinder the compressor’s performance or cause overheating.
10. Follow Manufacturer’s Guidelines: Always refer to the manufacturer’s manual for specific maintenance instructions and recommended service intervals for your air compressor model. They provide valuable information on maintenance tasks, lubrication requirements, and safety precautions.
Regular maintenance is vital to keep your air compressor in optimal condition and extend its lifespan. It’s also important to note that maintenance requirements may vary depending on the type, size, and usage of the compressor. By following a comprehensive maintenance routine, you can ensure the reliable operation of your air compressor and maximize its efficiency and longevity.


editor by CX 2023-10-17
China Professional CHINAMFG High Pressure Compressor for Oxygen Nitrogen arb air compressor
Product Description
Nuzhuo High Pressure Compressor for Oxygen Nitrogen
|
Product Name |
Oil Free Gas Compressor |
|||
|
Power Range |
<55KW |
|||
|
Model No. |
GWX- 5/10/20/40/60/80/CUSTOMIZED |
|||
|
Cooling Method |
Air-cooled or Water-cooled |
|||
|
Speed Range |
300-600r/min |
|||
|
Compression Stages |
Level 3-4 |
|||
|
Exhaust Pressure Range |
≤25.0Mpa |
|||
|
Inspiratory Pressure Range |
0-0.6Mpa |
|||
Technical features
The equipment does not need to add lubricating oil, and the exhaust gas does not contain oil and oil vapor, so it can
be protected from pollution, eliminating the need for complex filtration and purification systems, saving equipment
costs and maintenance costs, and has significant features such as safety, reliability, and easy operation.
Technical features
Details Images
FAQ
Q1: Are you a trading company or manufacturer?
A:We are a manufacturer.
Q2: What is your term of payment?
A: 30%T/T in advance and balance before shipment.
Q3: How long is your delivery time?
A: Depending on what type of machine you are purchased, normally 5 to 10 working days.
Q4: What is your product quality assurance policy? A:We offer a warranty period of 1 year, free lifetime technology support.
Q5: Do you offer OEM/ODM service?
A: Yes.
Q6: Does your product used or new? RTS product or customized product?
A:Our machine is new unit, and following your specific require to design and make it.
| After-sales Service: | Support |
|---|---|
| Warranty: | 1year |
| Lubrication Style: | Oil-less |
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|
.shipping-cost-tm .tm-status-off{background: none;padding:0;color: #1470cc}
|
Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
about shipping cost and estimated delivery time. |
|---|
| Payment Method: |
|
|---|---|
|
Initial Payment Full Payment |
| Currency: | US$ |
|---|
| Return&refunds: | You can apply for a refund up to 30 days after receipt of the products. |
|---|
.webp)
What Is the Typical Lifespan of a Gas Air Compressor?
The typical lifespan of a gas air compressor can vary depending on several factors, including the quality of the compressor, its usage patterns, maintenance practices, and environmental conditions. However, with proper care and maintenance, a gas air compressor can last for many years. Here’s a detailed explanation of the factors that can affect the lifespan of a gas air compressor:
1. Quality of the Compressor:
The quality and construction of the gas air compressor play a significant role in determining its lifespan. Compressors made with high-quality materials, precision engineering, and robust components are generally more durable and can withstand heavy usage over an extended period.
2. Usage Patterns:
The usage patterns of the gas air compressor can impact its lifespan. If the compressor is used consistently and for extended periods, it may experience more wear and tear compared to compressors used intermittently or for lighter tasks. Heavy-duty applications, such as continuous operation with high-demand tools, can put more strain on the compressor and potentially reduce its lifespan.
3. Maintenance Practices:
Regular maintenance is crucial for extending the lifespan of a gas air compressor. Following the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule, performing routine tasks like oil changes, filter cleaning/replacement, and inspection of components can help prevent issues and ensure optimal performance. Neglecting maintenance can lead to accelerated wear and potential breakdowns.
4. Environmental Conditions:
The operating environment can significantly impact the lifespan of a gas air compressor. Factors such as temperature extremes, humidity levels, presence of dust or debris, and exposure to corrosive substances can affect the compressor’s components and overall performance. Compressors used in harsh environments may require additional protection or specialized maintenance to mitigate these adverse conditions.
5. Proper Installation and Operation:
Proper installation and correct operation of the gas air compressor are essential for its longevity. Following the manufacturer’s guidelines for installation, ensuring proper ventilation, maintaining correct oil levels, and operating within the compressor’s specified capacity and pressure limits can help prevent excessive strain and premature wear.
Considering these factors, a well-maintained gas air compressor can typically last anywhere from 10 to 15 years or even longer. However, it’s important to note that this is a general estimate, and individual results may vary. Some compressors may experience shorter lifespans due to heavy usage, inadequate maintenance, or other factors, while others may last well beyond the expected lifespan with proper care and favorable conditions.
Ultimately, investing in a high-quality gas air compressor, adhering to recommended maintenance practices, and using it within its intended capabilities can help maximize its lifespan and ensure reliable performance for an extended period.
.webp)
What Is the Role of Air Receivers in Gas Air Compressor Systems?
Air receivers play a crucial role in gas air compressor systems by serving as storage tanks for compressed air. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Storage and Stabilization:
The primary function of an air receiver is to store compressed air generated by the gas air compressor. As the compressor produces compressed air, the air receiver collects and stores it. This storage capacity helps meet fluctuating demand in compressed air usage, providing a buffer between the compressor and the system’s air consumption.
By storing compressed air, the air receiver helps stabilize the supply to the system, reducing pressure fluctuations and ensuring a consistent and reliable flow of compressed air. This is particularly important in applications where the demand for compressed air may vary or experience peaks and valleys.
2. Pressure Regulation:
Another role of the air receiver is to assist in pressure regulation within the gas air compressor system. As compressed air enters the receiver, the pressure inside increases. When the pressure reaches a predetermined upper limit, typically set by a pressure switch or regulator, the compressor stops supplying air, and the excess air is stored in the receiver.
Conversely, when the pressure in the system drops below a certain lower limit, the pressure switch or regulator signals the compressor to start, replenishing the compressed air in the receiver and maintaining the desired pressure level. This cycling of the compressor based on pressure levels helps regulate and control the overall system pressure.
3. Condensate Separation:
During the compression process, moisture or condensate can form in the compressed air due to the cooling effect. The air receiver acts as a reservoir that allows the condensate to settle at the bottom, away from the outlet. The receiver often includes a drain valve at the bottom to facilitate the removal of accumulated condensate, preventing it from reaching downstream equipment and causing potential damage or performance issues.
4. Energy Efficiency:
Air receivers contribute to energy efficiency in gas air compressor systems. They help optimize the operation of the compressor by reducing the occurrence of short-cycling, which refers to frequent on-off cycling of the compressor due to rapid pressure changes. Short-cycling can cause excessive wear on the compressor and reduce its overall efficiency.
The presence of an air receiver allows the compressor to operate in longer and more efficient cycles. The compressor runs until the receiver reaches the upper pressure limit, ensuring a more stable and energy-efficient operation.
5. Air Quality Improvement:
Depending on the design, air receivers can also aid in improving air quality in the compressed air system. They provide a space for the compressed air to cool down, allowing moisture and some contaminants to condense and separate from the air. This can be further enhanced with the use of additional filtration and drying equipment installed downstream of the receiver.
In summary, air receivers play a vital role in gas air compressor systems by providing storage capacity, stabilizing compressed air supply, regulating system pressure, separating condensate, improving energy efficiency, and contributing to air quality control. They are an integral component in ensuring the reliable and efficient operation of compressed air systems across various industries and applications.
.webp)
What Fuels Are Commonly Used in Gas Air Compressors?
Gas air compressors can be powered by various fuels depending on the specific model and design. The choice of fuel depends on factors such as availability, cost, convenience, and environmental considerations. Here’s a detailed explanation of the fuels commonly used in gas air compressors:
1. Gasoline:
Gasoline is a widely used fuel in gas air compressors, particularly in portable models. Gasoline-powered compressors are popular due to the widespread availability of gasoline and the convenience of refueling. Gasoline engines are generally easy to start, and gasoline is relatively affordable in many regions. However, gasoline-powered compressors may emit more exhaust emissions compared to some other fuel options.
2. Diesel:
Diesel fuel is another common choice for gas air compressors, especially in larger industrial models. Diesel engines are known for their efficiency and durability, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications. Diesel fuel is often more cost-effective than gasoline, and diesel-powered compressors typically offer better fuel efficiency and longer runtime. Diesel compressors are commonly used in construction sites, mining operations, and other industrial settings.
3. Natural Gas:
Natural gas is a clean-burning fuel option for gas air compressors. It is a popular choice in areas where natural gas infrastructure is readily available. Natural gas compressors are often used in natural gas processing plants, pipeline operations, and other applications where natural gas is abundant. Natural gas-powered compressors offer lower emissions compared to gasoline or diesel, making them environmentally friendly.
4. Propane:
Propane, also known as liquefied petroleum gas (LPG), is commonly used as a fuel in gas air compressors. Propane-powered compressors are popular in construction, agriculture, and other industries where propane is used for various applications. Propane is stored in portable tanks, making it convenient for use in portable compressors. Propane-powered compressors are known for their clean combustion, low emissions, and easy availability.
5. Biogas:
In specific applications, gas air compressors can be fueled by biogas, which is produced from the decomposition of organic matter such as agricultural waste, food waste, or wastewater. Biogas compressors are used in biogas production facilities, landfills, and other settings where biogas is generated and utilized as a renewable energy source. The use of biogas as a fuel in compressors contributes to sustainability and reduces dependence on fossil fuels.
It’s important to note that the availability and suitability of these fuel options may vary depending on the region, infrastructure, and specific application requirements. When selecting a gas air compressor, it’s crucial to consider the compatibility of the compressor with the available fuel sources and to follow the manufacturer’s guidelines regarding fuel selection, storage, and safety precautions.


editor by CX 2023-10-10
China supplier O2 Air Compressor Oxygen Argon Gas Cylinder Filling Station Nitrogen Booster Air Compressor air compressor parts
Product Description
O2 Air Compressor Oxygen Argon Gas Cylinder Filling Station Nitrogen Booster Air Compressor
Product Description
Product features
1.Touch display PLC control.
2.Remote control is optional.
3.Inlet and outlet pressure overload,temperature overheating,cooling water failure, circulation rolling alarm and stop.
4.Operation time display, maintenance cycle prompt.
5.With water tank and circulating pump without external pipeline, filling antifreeze at low temperature without obstruction.
| Compressed media | Nitrogen (must be dry and particle free) |
| Model | VWN-180/5-25-II |
| Rated flow (standard state) | 180Nm3/h |
| Intake air temperature | ≤40 |
| Intake pressure | 0.5Mpa |
| Exhaust pressure | 2.5Mpa |
| Cylinder diameter * quantity | (Φ90+φ65)*2 |
| Engine speed | 720r/min |
| Cooling mode | Air cooling |
| Lubrication method | Fully oil-free lubrication |
| Compression series | 2 |
| Structural type | Angle type, V type |
| Motor power | 11kw*2 |
| Transmission mode | Belt drive |
| Installation type | Basic type |
| Dual pressure controller | Intake 4-6 |
| Control mode | Completely oil-free lubrication, air cooling, reciprocating piston type |
| Size of inlet and outlet | RC1″ |
| Dimensions | 1500*1350*1100mm |
| Weight | 280kg |
Product Parameters
| Compressed media (General for oxygen and nitrogen) |
Model | Capacity (Nm3/h) |
Intake pressure (MPa) |
Exhaust pressure (MPa) |
Power (kW) |
Dimensions (mm) |
| Oxygen/Nitrogen | VW-0.33/5-25 | 20 | 0.5 | 2.5 | 4 | 1220*500*800 |
| Oxygen/Nitrogen | ZWN-3.6/4-8 | 3.6 | 0.4 | 0.8 | 0.75 | 750*500*650 |
| Oxygen/Nitrogen | VWN-10/5-25 | 10 | 0.5 | 2.5 | 4 | 1600*700*1500 |
| Oxygen/Nitrogen | VWN-60/5-16 | 60 | 0.5 | 1.6 | 5.5 | 1250*500*900 |
| Oxygen/Nitrogen | VWN-20/6-20 | 20 | 0.6 | 2.0 | 4 | 1250*600*900 |
| Oxygen/Nitrogen | VWN-20/5-25 | 20 | 0.5 | 2.5 | 4 | 1050*600*1000 |
| Oxygen/Nitrogen | VWN-40/7-25 | 40 | 0.7 | 2.5 | 4 | 1250*500*900 |
| Oxygen/Nitrogen | VWN-60/4-25 | 60 | 0.4 | 2.5 | 11 | 1250*700*900 |
| Oxygen/Nitrogen | WWN-80/4-25 | 80 | 0.4 | 2.5 | 11 | 1350*700*1200 |
| Oxygen/Nitrogen | VWN-80/7-25 | 80 | 0.7 | 2.5 | 7.5 | 1250*700*900 |
| Oxygen/Nitrogen | VWN-60/4-30 | 60 | 0.4 | 3.0 | 3 | 1250*500*900 |
| Oxygen/Nitrogen | VWN-50/4-30 | 50 | 0.4 | 3.0 | 7.5 | 1250*650*1000 |
| Oxygen/Nitrogen | VWN-80/5-30 | 80 | 0.5 | 3.0 | 11 | 1250*700*1000 |
| Oxygen/Nitrogen | VWN-30/5-35 | 30 | 0.5 | 3.5 | 5.5 | 1050*500*1000 |
| Oxygen/Nitrogen | VWN-50/5-35 | 50 | 0.5 | 3.5 | 7.5 | 1050*700*1000 |
| Oxygen/Nitrogen | VWN-40/5-40 | 40 | 0.5 | 4.0 | 7.5 | 1250*600*900 |
| Oxygen/Nitrogen | VWY-80/0.5-50 | 80 | 0.05 | 5.0 | 18.5 | 1250*700*900 |
| Oxygen/Nitrogen | VWND-55/5-8 | 55 | 0.5 | 0.8 | 4 | 1400*810*1300 |
| Oxygen/Nitrogen | VWN-60/5-10 | 60 | 0.5 | 1.0 | 4 | 1250*500*900 |
| Oxygen/Nitrogen | VWY-75/4-16 | 75 | 0.4 | 1.6 | 7.5 | 1050*500*1000 |
| Oxygen/Nitrogen | VWND-100/5-10 | 100 | 0.5 | 1.0 | 5.5 | 1400*930*1350 |
| Oxygen/Nitrogen | VWN-120/6-16 | 120 | 0.6 | 1.6 | 11 | 1250*700*1000 |
| Oxygen/Nitrogen | VWN-140/5-8 | 140 | 0.5 | 0.8 | 5.5 | 1250*600*900 |
| Oxygen/Nitrogen | WWND-150/4-10 | 150 | 0.4 | 1.0 | 11 | 1430*1030*1350 |
| Oxygen/Nitrogen | SWND-240/4-10 | 240 | 0.4 | 1.0 | 15 | 1500×1100×1620 |
| Oxygen/Nitrogen | VWY-120/5-10 | 120 | 0.5 | 1.0 | 7.5 | 1250*600*1000 |
| Oxygen/Nitrogen | SWY-150/4-16 | 150 | 0.4 | 1.6 | 15 | 1250*900*1480 |
| Oxygen/Nitrogen | WWN-100/4-25 | 100 | 0.4 | 2.5 | 15 | 1350*700*1200 |
| Oxygen/Nitrogen | WWN-120/6-30 | 120 | 0.6 | 3.0 | 15 | 1250*800*1200 |
| Oxygen/Nitrogen | WWN-120/6-45 | 120 | 0.6 | 4.5 | 18.5 | 1350*1100*1100 |
| Oxygen/Nitrogen | WWN-80/5-45 | 80 | 0.5 | 4.5 | 15 | 1350*700*1200 |
| Oxygen/Nitrogen | WWN-240/5-10 | 240 | 0.5 | 1.0 | 15 | 1350*800*1200 |
| Oxygen/Nitrogen | WWN-300/0.5-8-II | 300 | 0.05 | 0.8 | 22*2 | 2500*1200*800 |
| Oxygen/Nitrogen | WWNFB-900/4-8-II | 900 | 0.4 | 0.8 | 22*2 | 2600*1000*900 |
| Oxygen/Nitrogen | VWN-180/5-25-II | 180 | 0.5 | 2.5 | 11*2 | 1500*1350*1100 |
| Oxygen/Nitrogen | WWN-200/3-18-II | 200 | 0.3 | 1.8 | 11*2 | 1450*1350*1100 |
| Oxygen/Nitrogen | WWN-200/6-30-II | 200 | 0.6 | 3.0 | 11*2 | 1600*1600*1200 |
| Oxygen/Nitrogen | WWFB-430/4-9 | 430 | 0.4 | 0.9 | 22 | 1500*1000*800 |
Successful cases
FAQ
FAQ:
Q1. Are you trading company or manufacture ?
A: We are professional manufacture of screw air compressor of HangZhou,ZheJiang ,China. More than 18 years of experience in air compressor manufacturing.
Q2. How long is the delivery time ?
A: For standard voltage ,15 working days. Non-standard ,please contact our sales.
Q3. What’s payment term ?
A: T/T, L/C, D/P, Western Union, Paypal, Credit Card, and etc. Also we could accept USD, RMB, Euro and other currency.
Q4. How about your after-sales service ?
A: 1.Provide customers with installation and commissioning online instructions.
2. Well-trained engineers available to overseas service.
3.CHINAMFG agents and after service avaiable.arrange our engineers to help you training and installation.
Q5. How about your warranty?
A: One year for the whole machine and 2 years for screw air end, except consumable spare parts.
Q6. Do you have any certificate ?
A: Yes, per different customer’s market need ,we can offer CE ,ISO etc certificate.
Q7. What about the maintenance ?
A: First maintenance need to be done after 500Hours, and then every 2000-3000 hours to do the normal maintenance, and consider the actual environment.
Q8. How do you control quality ?
A: 1. The raw materials are strictly inspected
2. Some key parts are imported from overseas
3. Each compressor must pass at least 5 hours of continuous testing before leaving the factory.
Q9. Do you offer OEM service ?
A: Yes.Both OEM & ODM service can be accepted.
Q10.How long could your air compressor be used?
A: Generally, more than 10 years.
|
Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
To be negotiated |
|---|
| After-sales Service: | Online Support |
|---|---|
| Warranty: | 24 Months |
| Lubrication Style: | Oil-free |
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|
What Is the Typical Lifespan of a Gas Air Compressor?
The typical lifespan of a gas air compressor can vary depending on several factors, including the quality of the compressor, its usage patterns, maintenance practices, and environmental conditions. However, with proper care and maintenance, a gas air compressor can last for many years. Here’s a detailed explanation of the factors that can affect the lifespan of a gas air compressor:
1. Quality of the Compressor:
The quality and construction of the gas air compressor play a significant role in determining its lifespan. Compressors made with high-quality materials, precision engineering, and robust components are generally more durable and can withstand heavy usage over an extended period.
2. Usage Patterns:
The usage patterns of the gas air compressor can impact its lifespan. If the compressor is used consistently and for extended periods, it may experience more wear and tear compared to compressors used intermittently or for lighter tasks. Heavy-duty applications, such as continuous operation with high-demand tools, can put more strain on the compressor and potentially reduce its lifespan.
3. Maintenance Practices:
Regular maintenance is crucial for extending the lifespan of a gas air compressor. Following the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule, performing routine tasks like oil changes, filter cleaning/replacement, and inspection of components can help prevent issues and ensure optimal performance. Neglecting maintenance can lead to accelerated wear and potential breakdowns.
4. Environmental Conditions:
The operating environment can significantly impact the lifespan of a gas air compressor. Factors such as temperature extremes, humidity levels, presence of dust or debris, and exposure to corrosive substances can affect the compressor’s components and overall performance. Compressors used in harsh environments may require additional protection or specialized maintenance to mitigate these adverse conditions.
5. Proper Installation and Operation:
Proper installation and correct operation of the gas air compressor are essential for its longevity. Following the manufacturer’s guidelines for installation, ensuring proper ventilation, maintaining correct oil levels, and operating within the compressor’s specified capacity and pressure limits can help prevent excessive strain and premature wear.
Considering these factors, a well-maintained gas air compressor can typically last anywhere from 10 to 15 years or even longer. However, it’s important to note that this is a general estimate, and individual results may vary. Some compressors may experience shorter lifespans due to heavy usage, inadequate maintenance, or other factors, while others may last well beyond the expected lifespan with proper care and favorable conditions.
Ultimately, investing in a high-quality gas air compressor, adhering to recommended maintenance practices, and using it within its intended capabilities can help maximize its lifespan and ensure reliable performance for an extended period.
Can Gas Air Compressors Be Used in Agriculture?
Yes, gas air compressors can be used in various agricultural applications. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Pneumatic Tools and Equipment:
Gas air compressors can power a wide range of pneumatic tools and equipment used in agriculture. These tools include pneumatic drills, impact wrenches, nail guns, staplers, and pneumatic pumps. Gas air compressors provide the necessary compressed air to operate these tools, making various tasks more efficient and convenient on the farm.
2. Irrigation Systems:
Gas air compressors can be used to power irrigation systems in agriculture. They can supply compressed air to operate pneumatic valves, which control the flow of water in irrigation networks. Gas air compressors ensure reliable and efficient operation of irrigation systems, facilitating the distribution of water to crops in a controlled manner.
3. Grain Handling and Storage:
Air compressors play a vital role in grain handling and storage facilities. They are used to power aeration systems that provide airflow to grains stored in silos or bins. Aeration helps control the temperature and moisture levels, preventing spoilage and maintaining grain quality. Gas air compressors provide the airflow necessary for effective aeration in grain storage operations.
4. Cleaning and Maintenance:
In agriculture, gas air compressors are commonly used for cleaning and maintenance tasks. They can power air blowers or air guns to remove dust, debris, or chaff from machinery, equipment, or storage areas. Gas air compressors provide a high-pressure stream of compressed air, facilitating efficient cleaning and maintenance operations.
5. Livestock Operations:
Gas air compressors find applications in livestock operations as well. They can power pneumatic equipment used for animal care, such as pneumatic nail guns for building or repairing livestock enclosures, pneumatic pumps for water distribution, or pneumatic tools for general maintenance tasks.
6. Portable and Versatile:
Gas air compressors are often portable and can be easily transported around the farm, allowing flexibility in agricultural operations. Their versatility makes them suitable for various tasks, from powering tools and equipment in the field to providing compressed air for maintenance or cleaning in different farm locations.
7. Remote Locations:
In agricultural settings where access to electricity may be limited, gas air compressors offer a reliable alternative. They can be powered by gasoline or diesel engines, providing compressed air even in remote areas without electrical infrastructure.
8. Considerations:
When using gas air compressors in agriculture, it is essential to consider factors such as compressor size, capacity, and maintenance requirements. Selecting the right compressor based on the specific needs of the agricultural applications ensures optimal performance and efficiency.
In summary, gas air compressors have various applications in agriculture. They can power pneumatic tools and equipment, operate irrigation systems, facilitate grain handling and storage, assist in cleaning and maintenance tasks, support livestock operations, and offer portability and versatility. Gas air compressors contribute to increased efficiency, convenience, and productivity in agricultural operations.
Are There Different Types of Gas Air Compressors Available?
Yes, there are different types of gas air compressors available, each designed to suit specific applications and requirements. These different types vary in terms of design, power source, configuration, and intended use. Here’s a detailed explanation of the various types of gas air compressors:
1. Reciprocating Gas Air Compressors:
Reciprocating gas air compressors, also known as piston compressors, use a reciprocating motion of one or more pistons to compress the air. These compressors are commonly used for small to medium-scale applications and are available in both single-stage and two-stage configurations. Single-stage compressors compress the air in a single stroke, while two-stage compressors use an additional cylinder for further compression, resulting in higher pressures.
2. Rotary Screw Gas Air Compressors:
Rotary screw gas air compressors utilize two interlocking helical screws to compress the air. These compressors are known for their continuous and efficient operation, making them suitable for demanding industrial applications. They are often used in industries such as manufacturing, construction, and automotive where a constant supply of compressed air is required.
3. Rotary Vane Gas Air Compressors:
Rotary vane gas air compressors use a rotor with sliding vanes to compress the air. As the rotor rotates, the vanes slide in and out, creating compression chambers that compress the air. These compressors are compact, reliable, and often used for smaller-scale applications or in situations where space is limited.
4. Centrifugal Gas Air Compressors:
Centrifugal gas air compressors operate by accelerating the air using a high-speed impeller. The accelerated air is then redirected into a diffuser, which converts the velocity energy into pressure energy. These compressors are commonly used for large-scale applications requiring high volumes of compressed air, such as in power plants, refineries, or chemical processing industries.
5. Oil-Free Gas Air Compressors:
Oil-free gas air compressors are designed to provide clean, oil-free compressed air. They feature special sealing mechanisms and materials to prevent oil contamination in the compressed air. These compressors are commonly used in industries where oil-free air is essential, such as food and beverage processing, pharmaceuticals, electronics manufacturing, and painting applications.
6. Portable Gas Air Compressors:
Portable gas air compressors are specifically designed for mobility and ease of transportation. These compressors often feature wheels, handles, or trailers for convenient movement. They are commonly used in construction sites, remote job locations, outdoor events, or other situations where compressed air is needed at different locations.
7. High-Pressure Gas Air Compressors:
High-pressure gas air compressors are designed to generate compressed air at elevated pressures. These compressors are used in applications that require air pressure higher than the standard range, such as in diving operations, breathing air systems, or specialized industrial processes.
8. Biogas Air Compressors:
Biogas air compressors are specifically designed to compress biogas, which is generated from the decomposition of organic matter. These compressors are used in biogas production facilities, landfills, wastewater treatment plants, or agricultural operations where biogas is produced and utilized as an energy source.
These are just a few examples of the different types of gas air compressors available. Each type has its own advantages and is suitable for specific applications based on factors such as required airflow, pressure, mobility, oil-free operation, and environmental considerations. It’s important to choose the appropriate type of gas air compressor based on the specific needs of the application to ensure optimal performance and efficiency.


editor by CX 2023-10-07
China best Oil-Less Air Cooled Reciprocating Piston Type Nitrogen Oxygen CNG LPG Hydrogen Gas Compressors for Fuel Filling Stations air compressor for sale
Product Description
Piston compressor is a kind of piston reciprocating motion to make gas pressurization and gas delivery compressor mainly consists of working chamber, transmission parts, body and auxiliary parts. The working chamber is directly used to compress the gas, the piston is driven by the piston rod in the cylinder for reciprocating motion, the volume of the working chamber on both sides of the piston changes in turn, the volume decreases on 1 side of the gas due to the pressure increase through the valve discharge, the volume increases on 1 side due to the reduction of air pressure through the valve to absorb the gas.
We have various of gas compressor, such as Hydrogen compressor, Nitrogen compressor, Natrual gas compressor, Biogas compressor, Ammonia compressor, LPG compressor, CNG compressor, Mix gas compressor and so on.
Advantages of Gas Compressor:
1. High quality material, Stable & Reliable operation
2. Low Maintenance cost & Low noise
3. Easy to install on site and connect with the user’s pipeline system to operate
4. Alarm automatic shutdown to protection machine function
5. High pressure and flow
Lubrication includes : Oil lubrication and oil free lubrication;
Cooling method includes: Water cooling and air cooling.
Installation type includes: Stationary,Mobile and Skid Mounting.
Type includes: V-type, W-type,D-type,Z-type
Product description
Hydrogen compressor
Application
This series of compressors are mainly used for (methanol, natural gas, coal gas) cracking hydrogen production, water electrolysis hydrogen production, hydrogen filling bottle, benzene hydrogenation, tar hydrogenation, catalytic cracking and other hydrogen booster compressors.
Product features:
1. The product has the characteristics of low noise, small vibration, compact structure, stable operation, safety and reliability, and high automation level. It can also be configured with a digital remote display and control system according to customer requirements.
2. It has the function of alarm and shutdown of low compressor oil pressure, low water pressure, high temperature, low intake pressure and high exhaust pressure, which makes the compressor run more reliable.
Structure introduction: The unit consists of compressor host, motor, coupling, flywheel, piping system, cooling system, electrical equipment, and auxiliary equipment.
Technical parameters and specifications
| No | Model | Gas flow (Nm3/h) |
Inlet pressure (Mpa) |
Outlet pressure (Mpa) |
Gas | Power (kw) |
Dimensions (mm) |
| 1 | ZW-0.5/15 | 24 | Atmospheric pressure | 1.5 | Hydrogen | 7.5 | 1600*1300*1250 |
| 2 | ZW-0.16/30-50 | 240 | 3 | 5 | Hydrogen | 11 | 1850*1300*1200 |
| 3 | ZW-0.45/22-26 | 480 | 2.2 | 2.6 | Hydrogen | 11 | 1850*1300*1200 |
| 4 | ZW-0.36 /10-26 | 200 | 1 | 2.6 | Hydrogen | 18.5 | 2000*1350*1300 |
| 5 | ZW-1.2/30 | 60 | Atmospheric pressure | 3 | Hydrogen | 18.5 | 2000*1350*1300 |
| 6 | ZW-1.0/1.0-15 | 100 | 0.1 | 1.5 | Hydrogen | 18.5 | 2000*1350*1300 |
| 7 | ZW-0.28/8-50 | 120 | 0.8 | 5 | Hydrogen | 18.5 | 2100*1350*1150 |
| 8 | ZW-0.3/10-40 | 150 | 1 | 4 | Hydrogen | 22 | 1900*1200*1420 |
| 9 | ZW-0.65/8-22 | 300 | 0.8 | 2.2 | Hydrogen | 22 | 1900*1200*1420 |
| 10 | ZW-0.65/8-25 | 300 | 0.8 | 25 | Hydrogen | 22 | 1900*1200*1420 |
| 11 | ZW-0.4/(9-10)-35 | 180 | 0.9-1 | 3.5 | Hydrogen | 22 | 1900*1200*1420 |
| 12 | ZW-0.8/(9-10)-25 | 400 | 0.9-1 | 2.5 | Hydrogen | 30 | 1900*1200*1420 |
| 13 | DW-2.5/0.5-17 | 200 | 0.05 | 1.7 | Hydrogen | 30 | 2200*2100*1250 |
| 14 | ZW-0.4/(22-25)-60 | 350 | 2.2-2.5 | 6 | Hydrogen | 30 | 2000*1600*1200 |
| 15 | DW-1.35/21-26 | 1500 | 2.1 | 2.6 | Hydrogen | 30 | 2000*1600*1200 |
| 16 | ZW-0.5/(25-31)-43.5 | 720 | 2.5-3.1 | 4.35 | Hydrogen | 30 | 2200*2100*1250 |
| 17 | DW-3.4/0.5-17 | 260 | 0.05 | 1.7 | Hydrogen | 37 | 2200*2100*1250 |
| 18 | DW-1.0/7-25 | 400 | 0.7 | 2.5 | Hydrogen | 37 | 2200*2100*1250 |
| 19 | DW-5.0/8-10 | 2280 | 0.8 | 1 | Hydrogen | 37 | 2200*2100*1250 |
| 20 | DW-1.7/5-15 | 510 | 0.5 | 1.5 | Hydrogen | 37 | 2200*2100*1250 |
| 21 | DW-5.0/-7 | 260 | Atmospheric pressure | 0.7 | Hydrogen | 37 | 2200*2100*1250 |
| 22 | DW-3.8/1-7 | 360 | 0.1 | 0.7 | Hydrogen | 37 | 2200*2100*1250 |
| 23 | DW-6.5/8 | 330 | Atmospheric pressure | 0.8 | Hydrogen | 45 | 2500*2100*1400 |
| 24 | DW-5.0/8-10 | 2280 | 0.8 | 1 | Hydrogen | 45 | 2500*2100*1400 |
| 25 | DW-8.4/6 | 500 | Atmospheric pressure | 0.6 | Hydrogen | 55 | 2500*2100*1400 |
| 26 | DW-0.7/(20-23)-60 | 840 | 2-2.3 | 6 | Hydrogen | 55 | 2500*2100*1400 |
| 27 | DW-1.8/47-57 | 4380 | 4.7 | 5.7 | Hydrogen | 75 | 2500*2100*1400 |
| 28 | VW-5.8/0.7-15 | 510 | 0.07 | 1.5 | Hydrogen | 75 | 2500*2100*1400 |
| 29 | DW-10/7 | 510 | Atmospheric pressure | 0.7 | Hydrogen | 75 | 2500*2100*1400 |
| 30 | VW-4.9/2-20 | 750 | 0.2 | 2 | Hydrogen | 90 | 2800*2100*1400 |
| 31 | DW-1.8/15-40 | 1500 | 1.5 | 4 | Hydrogen | 90 | 2800*2100*1400 |
| 32 | DW-5/25-30 | 7000 | 2.5 | 3 | Hydrogen | 90 | 2800*2100*1400 |
| 33 | DW-0.9/20-80 | 1000 | 2 | 8 | Hydrogen | 90 | 2800*2100*1400 |
| 34 | DW-25/3.5-4.5 | 5700 | 0.35 | 0.45 | Hydrogen | 90 | 2800*2100*1400 |
| 35 | DW-1.5/(8-12)-50 | 800 | 0.8-1.2 | 5 | Hydrogen | 90 | 2800*2100*1400 |
| 36 | DW-15/7 | 780 | Atmospheric pressure | 0.7 | Hydrogen | 90 | 2800*2100*1400 |
| 37 | DW-5.5/2-20 | 840 | 0.2 | 2 | Hydrogen | 110 | 3400*2200*1300 |
| 38 | DW-11/0.5-13 | 840 | 0.05 | 1.3 | Hydrogen | 110 | 3400*2200*1300 |
| 39 | DW-14.5/0.04-20 | 780 | 0.004 | 2 | Hydrogen | 132 | 4300*2900*1700 |
| 40 | DW-2.5/10-40 | 1400 | 1 | 4 | Hydrogen | 132 | 4200*2900*1700 |
| 41 | DW-16/0.8-8 | 2460 | 0.08 | 0.8 | Hydrogen | 160 | 4800*3100*1800 |
| 42 | DW-1.3/20-150 | 1400 | 2 | 15 | Hydrogen | 185 | 5000*3100*1800 |
| 43 | DW-16/2-20 | 1500 | 0.2 | 2 | Hydrogen | 28 | 6500*3600*1800 |
Customized is accepted , Pls provide the following information to us ,then we will do the technical proposal and best price to you.
1.Flow rate: _______Nm3/h
2.Gas Media : ______ Hydrogen or Natural Gas or Oxygen or other gas
3.Inlet pressure: ___bar(g)
4.Inlet temperature:_____ºC
5.Outlet pressure:____bar(g)
6.Outlet temperature:____ºC
7.Installation location: _____indoor or outdoor
8.Location ambient temperature: ____ºC
9.Power supply: _V/ _Hz/ _3Ph
10.Cooling method for gas: air cooling or water cooing
Picture display
Applications
Company strength display
HangZhou CZPT Gas Equipment Co., Ltd. is a manufacturer engaged in the research and development, design and production of gas compressors. The company has its own production technology, processing equipment and assembly technology, and has many years of experience in the production of various flammable and explosive special gas compressors.
Huayan compressor products cover almost all gas media, up to 6th-stage compression and 3000kw power. Products can be customized according to customer requirements to better meet customer needs. The products are mainly used in gas compressors in the petroleum industry, chemical and natural gas compressors, industrial compressors, compressors for waste gas treatment and biogas utilization, and compressors for special gases.
After Sales Service
1.Quick response within 2 to 8 hours, with a reaction rate exceeding 98%;
2. 24-hour telephone service, please feel free to contact us;
3. The whole machine is guaranteed for 1 year (excluding pipelines and human factors);
4. Provide consulting service for the service life of the whole machine, and provide 24-hour technical support via email;
5. On-site installation and commissioning by our experienced technicians;
Exhibition Display
Certificate display
Packaging and Shipping
FAQ
1.How to get a prompt quotation of gas compressor ?
1)Flow Rate/Capacity : ___ Nm3/h
2)Suction/ Inlet Pressure : ____ Bar
3)Discharge/Outlet Pressure :____ Bar
4)Gas Medium :_____
5)Voltage and Frequency : ____ V/PH/HZ
2.How long is delivery time ?
Delivery time is around the 30-90 days .
3.What about the voltage of products? Can they be customized?
Yes, the voltage can be customized according to your inquire.
4.Can you accept OEM orders?
Yes, OEM orders is highly welcome.
5.Will you provide some spare parts of the machines?
Yes, we will .
| After-sales Service: | Proive After-Sales Service |
|---|---|
| Warranty: | 18monthes |
| Lubrication Style: | Lubricated |
| Cooling System: | Water Cooling |
| Cylinder Arrangement: | Balanced Opposed Arrangement |
| Cylinder Position: | Angular |
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|
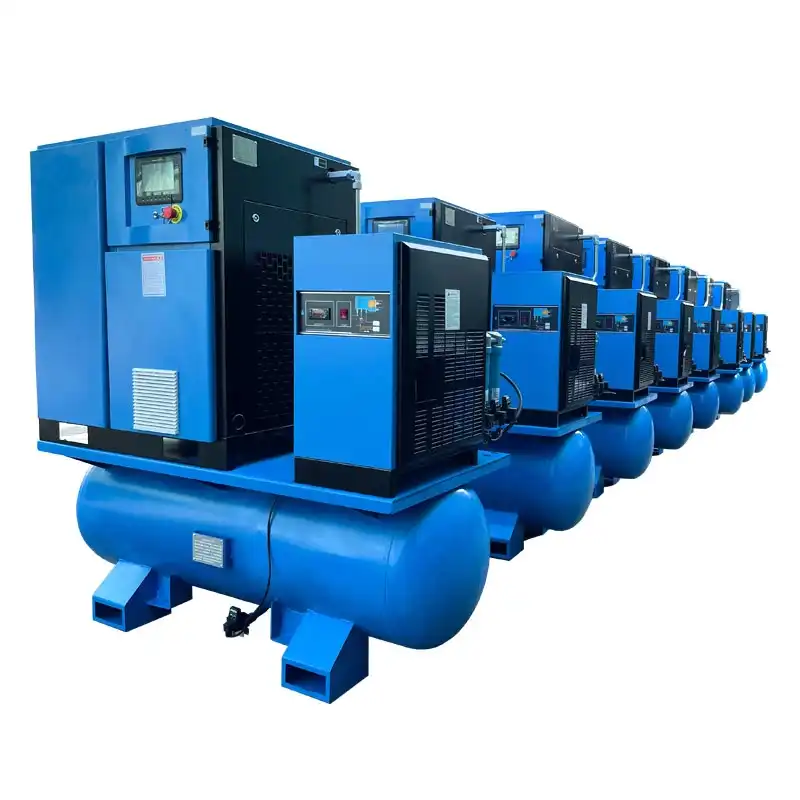

How to Choose the Right Air Compressor
An air compressor uses pressurized air to power a variety of tools. They are most commonly used to power nailers and impact wrenches. Other popular uses for air compressors include paint sprayers and impact wrenches. While all air compressors have the same basic construction, their specialty differs. Ultimately, their differences come down to the amount of air they can push. Read on for information on each type of air compressor. These tools are great for many different purposes, and choosing the right air compressor depends on your specific needs.
Electric motor
While purchasing an electric motor for air compressor, compatibility is a key factor. Not all motors work with the same type of air compressor, so it’s important to check the manufacturer’s instructions before purchasing. By doing this, you can avoid wasting money on an incompatible motor. Another important consideration is speed. A motor’s speed is its rate of rotation, measured in revolutions per minute. It is critical that you purchase a motor with sufficient speed to meet the needs of your air compressor.
Typically, an electric motor for air compressor is 1.5 hp. It is ideal for use with medical equipment and metal-cutting machines. It also performs well under continuous operation and offers a high efficiency and energy-saving performance. Moreover, it features an attractive price, making it a good choice for a wide range of applications. If you are looking for a motor for an air compressor, look no further than a ZYS series.
A motor’s protection class indicates how the motor will operate. Protection classes are specified by the IEC 60034-5. These are stated with two digits and represent the protection against solid objects and water. For example, an IP23 rating means that the motor will be protected from solid objects, while IP54 means that it will protect from dust and water sprayed from all directions. It is vital to choose a motor with the correct protection class for your air compressor.
When choosing an electric motor, you should consider whether it’s compatible with the brand of air compressor. Some may be compatible, while others may require advanced electronics skills to repair. However, most air compressors are covered by warranty, so it’s important to check with the manufacturer if the warranty is still in effect before you spend a dime on a replacement. The motor should be replaced if it has failed to perform as designed.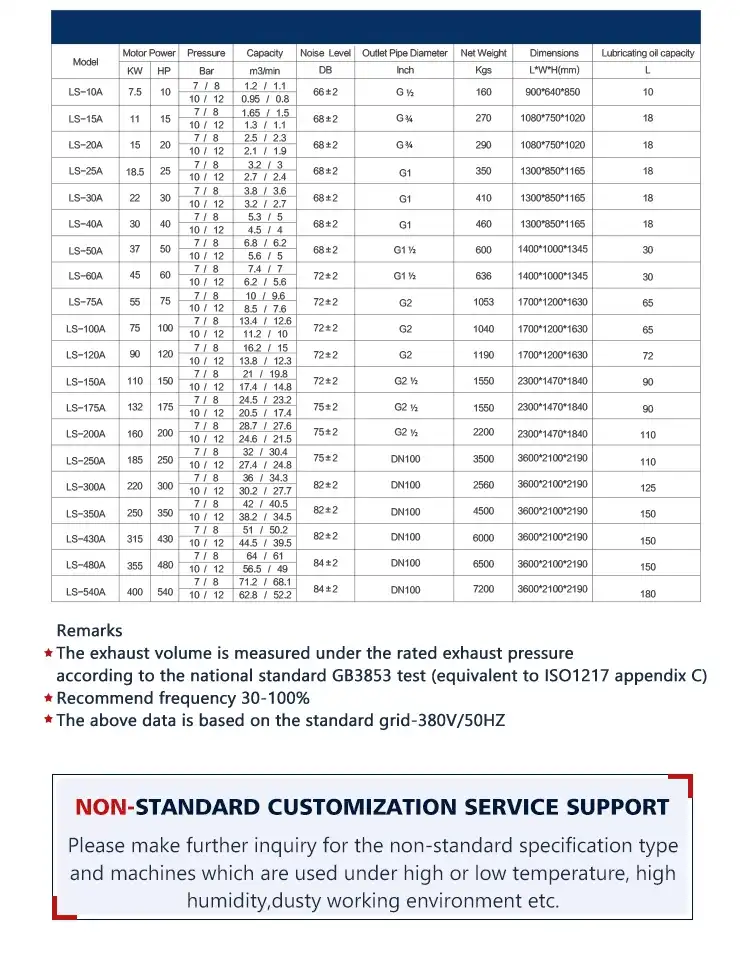
Oil bath
Air compressors require proper lubrication to function efficiently. The piston must draw air with minimal friction. Depending on their design, air compressors can either be oil-lubricated or oil-free. The former uses oil to reduce piston friction, while the latter splashes it on the cylinder bearings and walls. Such air compressors are commonly known as oil-flooded air compressors. In order to keep their oil baths clean, they are recommended for use in locations with high dust levels.
Start/stop control
An air compressor can be controlled by a start/stop control. This type of control sends a signal to the main motor that activates the compressor when the demand for air falls below a preset limit. This control strategy is effective for smaller air compressors and can be useful for reducing energy costs. Start/stop control is most effective in applications where air pressure does not change frequently and where the compressor is not required to run continuously.
To troubleshoot this problem, you need to check the power supply of your compressor. To check the supply side, use a voltage monitor to determine if power is flowing to the compressor. Ensure that the power supply to the compressor is steady and stable at all times. If it fluctuates, the compressor may not start or stop as expected. If you cannot find the problem with the air compressor power supply, it may be time to replace it.
In addition to the start/stop control, you may want to purchase additional air receivers for your air compressor. These can increase the capacity of air stored and reduce the number of times it starts and stops. Another way to decrease the number of starts per hour is to add more air receivers. Then, you can adjust the control to match your requirements. You can also install a pressure gauge that monitors the compressor’s performance.
Start/stop control for air compressors can be complex, but the basic components are relatively easy to understand. One way to test them is to turn the compressor on or off. It is usually located on the exterior of the motor. If you’re unsure of the location of these components, check the capacitors and make sure that the air compressor is not running while you’re not using it. If it does, try to remove the capacitor.
Variable displacement control is another way to adjust the amount of air flowing into the compressor. By controlling the amount of air, the control can delay the use of additional compressors until more required air is available. In addition to this, the device can also monitor the energy used in the compressor. This control method can result in substantial energy savings. You can even save on the amount of electricity by using variable displacement control. It is essential for efficient compressed air systems.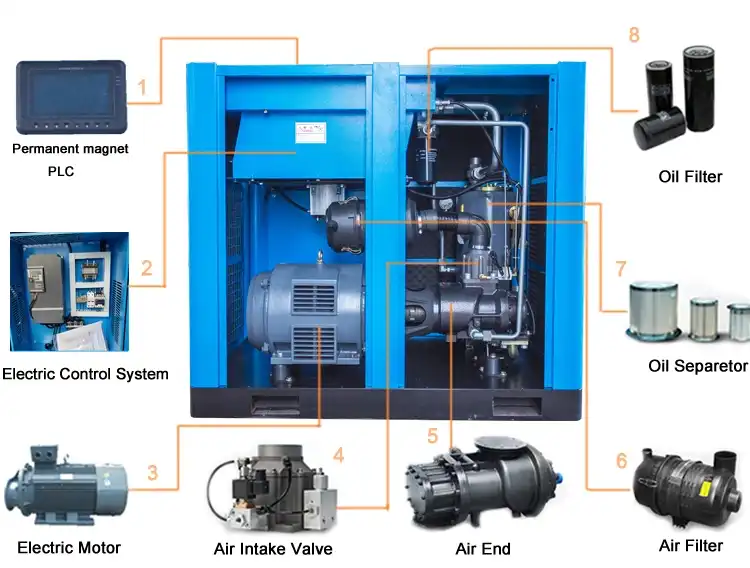
Variable speed drive
A VFD, or variable frequency drive, is a type of electric motor that adjusts its speed to match the demand for air. It is an efficient way to reduce energy costs and improve system reliability. In fact, studies have shown that a 20% reduction in motor speed can save up to 50% of energy. In addition, a VFD can monitor additional variables such as compressor oil pressure and motor temperature. By eliminating manual checks, a VFD will improve the performance of the application and reduce operating costs.
In addition to reducing energy costs, variable-speed drives also increase productivity. A variable-speed air compressor reduces the risk of system leaks by 30 percent. It also reduces the risk of system leaks by reducing pressure in the system. Because of these advantages, many governments are promoting this technology in their industries. Many even offer incentives to help companies upgrade to variable-speed drives. Therefore, the variable-speed drive can benefit many air compressor installations.
One major benefit of a variable-speed drive is its ability to optimize energy use. Variable frequency drives are able to ramp up and down to match the demand for air. The goal is to optimize the pressure and flow in the system so that the best “dead band” occurs between forty percent and eighty percent of full load. A variable-speed compressor will also increase energy efficiency because of its programmability.
A variable-speed air compressor can also be used to control the amount of air that is compressed by the system. This feature adjusts the frequency of power supplied to the motor based on the demand. If the demand for air is low, the frequency of the motor will reduce to save energy. On the other hand, if there is an excess demand for air, the variable-speed compressor will increase its speed. In addition, this type of air compressor is more efficient than its fixed-speed counterpart.
A VFD has many benefits for compressed air systems. First, it helps stabilize the pressure in the pipe network, thereby reducing the power losses due to upstream pressure. It also helps reduce the power consumption caused by fluctuations in upward pressure. Its benefits are also far-reaching. And as long as the air pressure and air supply is properly sized, a VFD will help optimize the efficiency of compressed air systems.


editor by CX 2023-05-16